Phillip “Another year, another AT&T deregulation measure” Dampier
It’s back.
It seems that nearly every year, AT&T and its well-compensated fan base of state legislators trot out the same old deregulation proposals that would end oversight of basic telephone service and allow AT&T (and other phone companies in Kentucky) to pull the plug on landline service wherever they feel it is no longer profitable to deliver.
This year, it’s Senate Bill 99, introduced once again by Sen. Paul “AT&T Knows Best” Hornback (R-Shelbyville). Back in 2012, Hornback disclosed AT&T largely authors these deregulation measures and he introduces them on AT&T’s behalf. In fact, he’s proud to admit it, telling the press nobody knows better than AT&T what the company needs the legislature to do for it.
“You work with the authorities in any industry to figure out what they need to move that industry forward,” Hornback said. “It’s no conflict.”
While Hornback moves AT&T forward, “his” bill will move rural Kentucky’s best chances for broadband backwards.
AT&T always pulls out all the stops when lobbying for its deregulation bills. In Kentucky, AT&T has more than 30 legislative lobbyists, including a former PSC vice chairwoman and past chairs of the state Democratic and Republican parties working on their behalf. It has spent over $100,000 in state political donations since 2007.
The chief provisions of the bill would:
- End almost all oversight of telephone service by the Public Service Commission anywhere there are more than 15,000 people living within a telephone exchange’s service area;
- Give Kentucky phone companies the right to disconnect urban/suburban basic landline phone service and replace it with either wireless or Voice over IP service;
- Allow rural customers to keep landline service for now, but also permits AT&T and other companies to effectively stop investing in their rural wired networks.
 This year, AT&T apparently conceded it was just too tough to convince the legislature to let them disconnect hundreds of thousands of rural Kentucky phone customers at the company’s pleasure, so this time they have permitted rural wired service to continue, with some exceptions that make life easier for AT&T.
This year, AT&T apparently conceded it was just too tough to convince the legislature to let them disconnect hundreds of thousands of rural Kentucky phone customers at the company’s pleasure, so this time they have permitted rural wired service to continue, with some exceptions that make life easier for AT&T.
First, the end of oversight of telephone service means customers in larger communities in Kentucky will have no recourse if their phone service doesn’t work, is billed incorrectly, is disconnected during a billing dispute, or never installed at all. The PSC has traditionally served as a last resort for customers who do not get satisfaction dealing with the local phone company directly. PSC intervention is taken very seriously by most phone companies, but the state agency will be rendered almost toothless under this bill.
Second, although existing rural phone customers would be able to keep their basic landline service (for now) under this measure, nothing prevents AT&T from marketing alternative wireless phone service to customers experiencing problems with their existing service. Verizon has attempted that in portions of upstate New York, where telephone network deterioration has led to increased complaints. In some cases, Verizon has suggested customers switch to wireless service instead of waiting for phone line repairs which may or may not solve the problem. New rural customers face the possibility of only being offered wireless or alternative phone services.
Third, provisions in the bill give AT&T and other companies wide latitude to offer wireless or Voice over IP alternatives to landline service with little recourse for customers who only later discover these alternatives don’t support faxes, medical or security alarm monitoring, dial-up Internet, credit card processing, etc.
Fourth, the bill eliminates any requirement imposed upon broadband service in existence as of July 15, 2004. In fact, the measure specifically defines both phone and broadband service as “market-based and not subject to state administrative regulation.” That basically means service will be unregulated.

AT&T’s wireless home phone replacement
Here are some real world examples of where S.B. 99 could trip up consumers:
- An elderly Louisville couple living the summer months in Louisville discover their phone service has been switched to the U-verse platform over the winter as AT&T seeks to decommission its deteriorating landline network in the neighborhood. S.B. 99 offers customers a 30-day opt out provision upon first notification, allowing a customer dissatisfied with the alternative service the right to switch back to their landline. But this couple was in Florida during the 30-day window, did not receive the notification to opt out in time to act, and are now stuck with U-verse. Unfortunately, the home medical monitoring equipment for his pacemaker does not work with Voice over IP phone service. This couple’s recourse: None.
- A customer moves into a new home currently served by AT&T’s wireless home phone replacement service. The customer doesn’t like the sound quality of the service and wants a traditional landline instead. Her recourse: None.
- A retired couple uninterested in broadband service or television from AT&T U-verse suddenly discovers AT&T wants to raise prices on landline phone service, but offers savings if the couple agrees to sign up for U-verse. Instead of paying a $25 monthly phone bill, the couple is now being asked, on a fixed income, to pay $100 a month for services they don’t want or need. Their recourse: They can appeal to keep their landline if they meet the aforementioned deadline, but they have no recourse if AT&T raises rates for basic phone service to make its discounted bundled service package seem more attractive.
Hood Harris, president of AT&T Kentucky, follows the same playback AT&T always uses when pushing these bills by framing its argument around landline telephone service regulation, which is an easy sell for cell phone-crazy customers who have not made a landline call in years:

Harris
Some of Kentucky’s laws that regulate our phones were written before cable television, cell phones, the Internet or email existed.
Because of these outdated laws, providers like AT&T must sink resources into outdated technology that could be invested in the modern broadband and wireless technology consumers want and need.
Every dollar invested in old technology is a dollar not being invested in speeding up the build out of new technology across the commonwealth.
It’s no longer the 19th century coming into your home over the old, voice-only phone network that was put in place under now-outdated laws. It’s the 21st century coming into your home over modern networks. While technology has changed dramatically for the better in just the past few years, our laws have not.
Despite what you may have heard, SB 99 will not remove landlines from rural homes or businesses.
Instead, this legislation puts those customers in charge of deciding which communications services they want and need. If you are a rural customer, for example, you may choose to join the nearly 40 percent of Kentuckians who already have moved on from landline home phones and gone only with a wireless phone, or you may choose a landline phone that’s provided over the Internet (known as Voice over Internet Protocol, or VoIP), or you may choose both a VoIP and a wireless service.
But you do not have to — you can keep your existing landline phone if you like. Under SB 99, the choice is yours.
It’s seems like a logical argument, until you read between the lines. Harris implies that those old-fashioned laws governing landlines you don’t have anymore are slowing down AT&T from bringing about a Broadband Renaissance for Kentucky. If AT&T only was freed from the responsibility of patching up its copper wire phone network, it could spend all of its time, money, and attention on improving cell phone service and bring broadband to everyone. Harris promises every resident will have a choice to get the service they want — wireless or wired — as long as you remember he is only talking about basic phone service, not broadband.
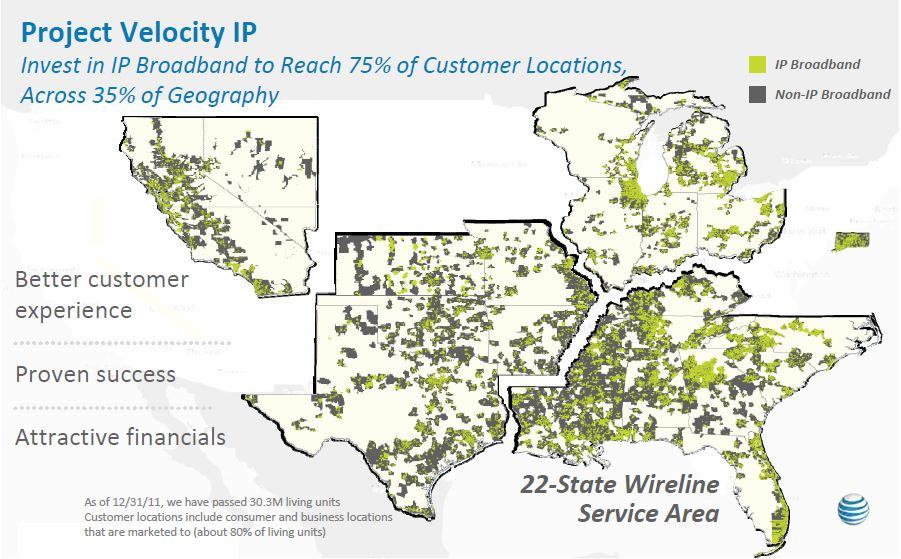
If your community isn’t highlighted on this map, AT&T has a wireless-only future in store for you.
Harris avoids disclosing AT&T’s true agenda. The company has freely admitted to shareholders it wants to scrap its rural wired network, now considered too costly to maintain for a diminishing number of customers. Unlike independent phone companies like Frontier, AT&T has been in no hurry to upgrade these rural customers for broadband service. AT&T has not even bothered to apply for federal broadband funding assistance to defray some of the costs of extending DSL to its rural customer base. With no possibility of buying broadband from AT&T, customers have little incentive to keep wired service if a cell phone will do. But decommissioning landline service in rural Kentucky guarantees these customers will probably never receive adequate broadband.
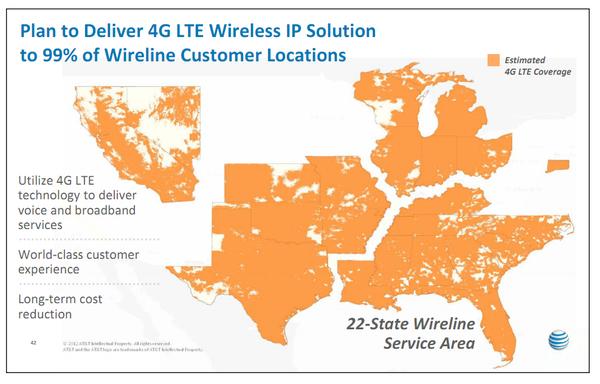
The “long-term cost reduction” AT&T mentions above is for them, not for you.
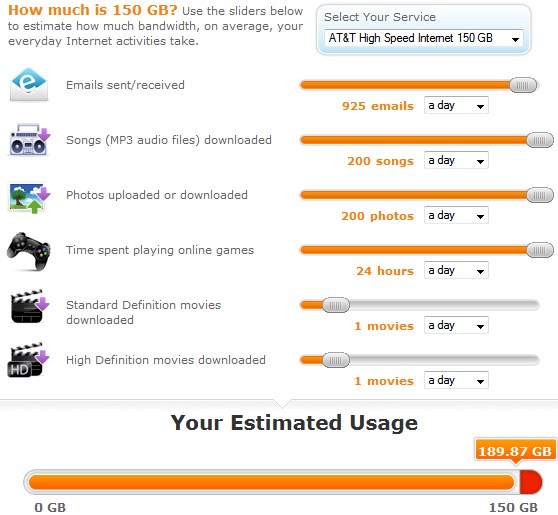
AT&T claims it will invest the savings in a wireless broadband network for rural customers, but as any smartphone owner will attest, AT&T’s wireless service is much more expensive than traditional phone service and its data plans are stingy and very expensive. Customers who can buy DSL from AT&T pay as little as $14.99 a month for up to 150GB of usage. A wireless data plan with AT&T for a home computer or notebook starts at $50 a month and only provides 5GB of usage before customers face a $10 per gigabyte overlimit fee. Which would you prefer: paying $14.99 for 150GB of usage with AT&T DSL or $1,500 for the same amount of usage on AT&T’s wireless network?
AT&T’s claims it will expand broadband as a result of not having to spend money on its landline network are specious. In fact, regardless of whether Kentucky passes S.B. 99 or not, AT&T has already embarked on its last known U-verse expansion. Project Velocity IP (VIP) devotes $6 billion to expanding U-verse to 57 million homes, reaching 75% of customer locations by the end of 2015. For the remaining 25% of customers, mostly in rural areas, AT&T’s plan isn’t to spend more money on improved wired service. Instead, it will build out its wireless network to serve the remaining customers with its LTE wireless broadband service — the same one that costs you $1,500 a month if you use 150GB.
Wireless is a cash cow for AT&T, so even saddled with its landline network, the company still spends the bulk of its investments on the wireless side of the business. Project VIP could have devoted all its resources to bringing U-verse to a larger customer base, but it won’t. AT&T sees much fatter profits spending $14 billion now to expand its wireless 4G LTE network and collect a lot more money later from its rural Kentucky customers.
Kentucky residents who don’t have U-verse in their area by the end of 2015 are probably never going to get the service, with or without S.B. 99. So why support a measure that delivers all the benefits to AT&T and leaves you sorting through the fine print just to keep the service you have now at a reasonable price. In every other state where AT&T has won deregulation, it raises the rates with no corresponding improvement in service.
Just how bad can AT&T’s wireless home phone replacement be? Just look at their disclaimers:
AT&T Wireless Home Phone is not compatible with home security systems, fax machines, medical alert and monitoring services, credit card machines, IP/PBX Phone systems, or dial-up Internet service. AT&T’s fine print on its website.
“AT&T’s wireless services are not equivalent to wireline Internet.” Wireless Customer Agreement, Section 4.1.
“WE DO NOT GUARANTEE YOU UNINTERRUPTED SERVICE OR COVERAGE. WE CANNOT ASSURE YOU THAT IF YOU PLACE A 911 CALL YOU WILL BE FOUND.” (All caps in original). Section 4.1.
 Time Warner Cable phone customers with Unlimited Home Phone calling can now place toll-free calls to Mexico, the company announced today.
Time Warner Cable phone customers with Unlimited Home Phone calling can now place toll-free calls to Mexico, the company announced today.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 This year, AT&T apparently conceded it was just too tough to convince the legislature to let them disconnect hundreds of thousands of rural Kentucky phone customers at the company’s pleasure, so this time they have permitted rural wired service to continue, with some exceptions that make life easier for AT&T.
This year, AT&T apparently conceded it was just too tough to convince the legislature to let them disconnect hundreds of thousands of rural Kentucky phone customers at the company’s pleasure, so this time they have permitted rural wired service to continue, with some exceptions that make life easier for AT&T.



 Netflix has
Netflix has 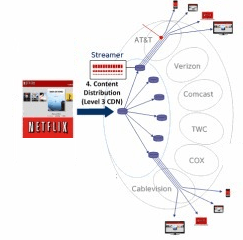 Netflix has traditionally avoided owning the “pipes” that distribute movies and TV shows to paying customers. Instead, it usually contracts with “transit providers” to send content from Netflix headquarters on to “content distribution networks (CDN)” that manage video streaming. A Netflix video may pass through a number of connections on a variety of independently owned networks before it arrives at the front door of your Internet Service Provider. Companies like Comcast handle “the last mile” of the journey that began at Netflix and ends at your computer or television set.
Netflix has traditionally avoided owning the “pipes” that distribute movies and TV shows to paying customers. Instead, it usually contracts with “transit providers” to send content from Netflix headquarters on to “content distribution networks (CDN)” that manage video streaming. A Netflix video may pass through a number of connections on a variety of independently owned networks before it arrives at the front door of your Internet Service Provider. Companies like Comcast handle “the last mile” of the journey that began at Netflix and ends at your computer or television set. Netflix and YouTube together are now estimated to cover 50 percent of all video traffic on the Internet, and that traffic is growing. Cogent dutifully passes that video content along to Internet Service Providers like Verizon and Comcast that have customers waiting to watch. But it is a two-way street. Any outbound traffic from customers could also be forwarded to Cogent to send on. Traditionally, both sides have managed the traffic by gradually increasing the bandwidth and speed of their connections to one-another. But as Netflix traffic grows and grows, companies like Comcast and Verizon believe they are being saddled with the costs to upgrade their networks in ways that are out of proportion to the traffic they send in the other direction. ISPs often grumble about the cost but keep on upgrading to keep paying customers happy. Verizon and Comcast are suspected of dragging their feet on those upgrades in an effort to win compensation.
Netflix and YouTube together are now estimated to cover 50 percent of all video traffic on the Internet, and that traffic is growing. Cogent dutifully passes that video content along to Internet Service Providers like Verizon and Comcast that have customers waiting to watch. But it is a two-way street. Any outbound traffic from customers could also be forwarded to Cogent to send on. Traditionally, both sides have managed the traffic by gradually increasing the bandwidth and speed of their connections to one-another. But as Netflix traffic grows and grows, companies like Comcast and Verizon believe they are being saddled with the costs to upgrade their networks in ways that are out of proportion to the traffic they send in the other direction. ISPs often grumble about the cost but keep on upgrading to keep paying customers happy. Verizon and Comcast are suspected of dragging their feet on those upgrades in an effort to win compensation. But that argument does not explain why Netflix was compelled to make a financial arrangement with Comcast. The two companies have been in negotiations on the subject of traffic compensation for months. Many industry observers believe those talks went nowhere until Netflix customers began complaining about the increasing network slowdowns. Some even dropped their Netflix subscriptions over the issue.
But that argument does not explain why Netflix was compelled to make a financial arrangement with Comcast. The two companies have been in negotiations on the subject of traffic compensation for months. Many industry observers believe those talks went nowhere until Netflix customers began complaining about the increasing network slowdowns. Some even dropped their Netflix subscriptions over the issue.






 Gizmodo
Gizmodo