
Gov. Andrew Cuomo announcing rural broadband initiatives in New York.
When New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo boasted in 2015 that anyone who wanted broadband service in the state would have access to it, he could not have realized that claim would come back to haunt him five years later.
New York’s Broadband for All program claimed to be the “largest and most ambitious state broadband investment in the nation,” with $500 million set aside “to achieve statewide broadband access by 2018,” with “99.9% of New Yorkers” getting access to broadband service.
In 2020, that goal remains elusive, with over 80,000 New Yorkers relegated to heavily data-capped satellite internet access and potentially tens of thousands more left behind by erroneous broadband availability maps that could leave many with no access at all. Now it appears the federal government will not be coming to the rescue, potentially stranding some rural residents as a permanent, unconnected underclass.
The Republican-majority at the Federal Communications Commission has decided to take the Democratic governor at his word and exclude additional rural broadband funding for New York State. The FCC’s recently approved Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) is the most ambitious rural broadband funding initiative to date, with a budget of $20.4 billion. As it stands, not a penny of those funds will ever be paid to support additional broadband projects in the Empire State.
 “Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,” said FCC Commissioner Michael O’Rielly.
“Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,” said FCC Commissioner Michael O’Rielly.
That $170 million was originally designated for Verizon to spend in upstate and western New York in areas without high-speed broadband. When Verizon declined to accept the funding, the rules for the program required the money to be made available for other qualified projects in other states, or left forfeit, unspent. An appeal from New York’s Senate delegation to FCC Chairman Ajit Pai to award that $170 million to New York’s Broadband for All program was successful, allowing other phone, cable, and wireless providers to construct new rural broadband projects around the state. That decision was met with criticism, especially by the Wireless Industry Service Providers Association (WISPA), which represents the interests of mostly rural, fixed wireless providers around the country.

O’Rielly
“After robust opportunity for public input, last year the FCC adopted a CAF-II framework that was truly technology-neutral and designed to harness the power of competition to deliver the most broadband to the most Americans, at the lowest overall price,” said Steve Coran, counsel for WISPA, in a statement. “Unfortunately, today’s action appears to deviate from this approach by providing disproportionate support to one state at the expense of others, which will now be competing for even less federal support.”
That criticism was partially echoed by Commissioner O’Rielly, who appreciated the dilemma of rural New Yorkers without access to high speed internet, but felt the FCC was showing favoritism to New York, which he worried was getting a disproportionate share of federal funding.
“These are federal [Universal Service Fund] dollars taken from ratepayers nationwide. They are not New York State funds, and we have the burden of deciding how best to allocate these scarce dollars, as well as the right to demand that they be spent wisely,” O’Rielly said. “At the same time, I am concerned that the funding will not be used as efficiently as possible. It should not be lost on everyone that New York is one of the states that diverts 9-1-1 fees collected to other non-related purposes, as is noted in the Commission’s recent report on the subject. We should have received assurances that New York would cease this disgraceful practice.”
O’Rielly added that offering even more generous funding in New York could lead to overpaying providers to service rural New York communities at the expense of other, cheaper rural broadband projects in other states.
Recently O’Rielly claimed that allowing New York to receive funding under the new RDOF program would almost guarantee dollars would be spent on duplicative, overlapping broadband projects, noting that Gov. Cuomo already considers New York almost entirely served by high speed providers. In fact, he claimed any additional funding sent to New York would be “beyond foolish and incredibly wasteful” and would undermine the rural broadband program’s objective to avoid funding projects in areas already served by an existing provider.
In other words, since Gov. Cuomo has claimed that virtually the entire state is now served with high speed internet access, O’Reilly believes there is no reason to award any further money to the state.
Except the claim that ‘nearly the entire state already has broadband access’ is untrue, and O’Rielly’s arguments against sending any additional money to New York seem more political than rational.
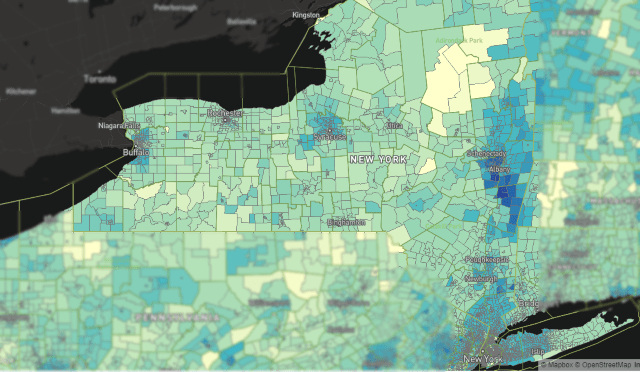
The FCC’s broadband availability map shows significant portions of New York in yellow, which designates no provider delivering the FCC’s minimum of 25/3 Mbps broadband service.
First, the FCC’s own flawed broadband availability maps, criticized for over counting the number of Americans with access to broadband, still shows large sections of upstate and western New York unserved by any suitable provider. Parts of western New York between Buffalo and Rochester, significant portions of the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier, and North Country are all still without access. An even larger portion of upstate New York has either no access or very slow access through DSL. The number of residents without service is significant. The FCC uses census blocks to measure broadband availability, but this methodology is flawed because if even one home within that block has broadband while dozens of others do not, the FCC still counts every home as served. This has angered many New Yorkers stuck without service while a local cable or phone company offers high-speed internet access to neighbors just up the road. Many of these rural residents are not even designated to receive satellite service, Broadband for All’s last catchall option for areas where no wired provider bid to provide service.
Second, long-standing rules in broadband funding programs already deny funding to areas where another suitable provider already offers service. So it would be impossible for RDOF to award “wasted” funding to projects where service already exists.
While Gov. Cuomo’s boastful claims about broadband availability opened the door for discriminatory rules against the state, the FCC itself wrote the rules, and it appears the goal was one part payback for securing earlier broadband funding over the objections of Commission O’Reilly, and one part sticking it to a state that has given the Trump Administration plenty of heartburn since the president took office.
 Education Week reports that over 500 schools with more than 360,000 students are temporarily stopping in-person classes because of the virus. Most are adopting video conferencing software that will stream classes to students at home. Stop the Cap! has learned that many of these video streaming applications can consume a lot of data, chewing through customer data allowances, especially in homes with more than one student.
Education Week reports that over 500 schools with more than 360,000 students are temporarily stopping in-person classes because of the virus. Most are adopting video conferencing software that will stream classes to students at home. Stop the Cap! has learned that many of these video streaming applications can consume a lot of data, chewing through customer data allowances, especially in homes with more than one student.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,”
“Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,” 

 Lobbyists for Mediacom, one of America’s medium-sized cable operators, are reportedly behind the latest effort to curtail public broadband in the state of Iowa with a new bill designed to make life difficult for municipalities trying to get internet access to their residents.
Lobbyists for Mediacom, one of America’s medium-sized cable operators, are reportedly behind the latest effort to curtail public broadband in the state of Iowa with a new bill designed to make life difficult for municipalities trying to get internet access to their residents.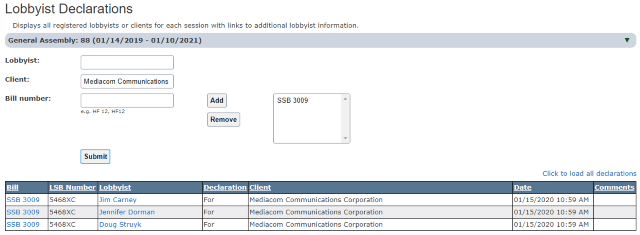
 Comcast and Charter Communications have begun to compete outside of their respective cable footprints, potentially competing directly head to head for your business, but only if you are a super-sized corporate client.
Comcast and Charter Communications have begun to compete outside of their respective cable footprints, potentially competing directly head to head for your business, but only if you are a super-sized corporate client.
 But neither company wants to end their comfortable fiefdoms in the residential marketplace by competing head to head for customers. Companies claim it would not be profitable to install redundant, competing networks, even though independent fiber to the home overbuilders have been doing so in several cities for years. It seems more likely cable operators are deeply concerned about threatening their traditional business model supplying services that face little competition. In the early years, that was cable television. Today it is broadband. Large swaths of the country remain underserved by telephone companies that have decided upgrading their deteriorating copper wire networks to supply residential fiber broadband service is not worth the investment, leaving most internet connectivity in the hands of a single local cable operator. Most cable companies have taken full advantage of this de facto monopoly by regularly raising prices despite the fact that the costs associated with providing internet service have been declining for years.
But neither company wants to end their comfortable fiefdoms in the residential marketplace by competing head to head for customers. Companies claim it would not be profitable to install redundant, competing networks, even though independent fiber to the home overbuilders have been doing so in several cities for years. It seems more likely cable operators are deeply concerned about threatening their traditional business model supplying services that face little competition. In the early years, that was cable television. Today it is broadband. Large swaths of the country remain underserved by telephone companies that have decided upgrading their deteriorating copper wire networks to supply residential fiber broadband service is not worth the investment, leaving most internet connectivity in the hands of a single local cable operator. Most cable companies have taken full advantage of this de facto monopoly by regularly raising prices despite the fact that the costs associated with providing internet service have been declining for years. Many of the same civil rights groups that regularly advocate their support of giant corporate telecom mergers are back once again to
Many of the same civil rights groups that regularly advocate their support of giant corporate telecom mergers are back once again to  In a joint statement, the groups urged the FCC to approve the T-Mobile/Sprint merger “so the combined New T-Mobile can definitively launch these enhanced diversity efforts and expansion of service to all communities included in the MOU.”
In a joint statement, the groups urged the FCC to approve the T-Mobile/Sprint merger “so the combined New T-Mobile can definitively launch these enhanced diversity efforts and expansion of service to all communities included in the MOU.”