 If you cut the cord and are watching all of your HD programming over-the-air, we have some bad news. Your current television set will soon be obsolete.
If you cut the cord and are watching all of your HD programming over-the-air, we have some bad news. Your current television set will soon be obsolete.
TV stations across the country are making plans to switch to the next generation of digital television — ATSC 3.0, and it isn’t compatible with millions of television sets and adapter boxes still in daily use across the United States.
The other night I talked with a station engineer who reminded me that consumers are going to have a nasty surprise when local stations start disappearing from existing sets starting a few years from now. Consumer electronics stores will continue to slash prices to clear current television inventory without telling buyers they will eventually need an adapter or rely on cable or satellite television to keep that set working after ATSC 3.0 is fully implemented.
Broadcasters have already started to budget for replacement equipment, necessary to support the new standard. For them, it opens the door to significant new revenue streams and a better quality TV picture. For you, it could mean a bill for a new set, an adapter, or a paid subscription to keep your favorite shows.
At present, over-the-air digital stations in the United States use ATSC 1.0, developed more than 20 years ago. Despite the standard, it took until February 2009 for most television stations to discontinue their analog television broadcasts. To ease the transition, Congress mandated a DTV Converter Box Coupon Program, which subsidized the cost of digital adapters for every household in the country still using an analog-only television set. No such luck this time around. Consumers relying on over-the-air broadcasts will either have to replace their current sets or purchase adapters or dongles out-of-pocket to keep watching.
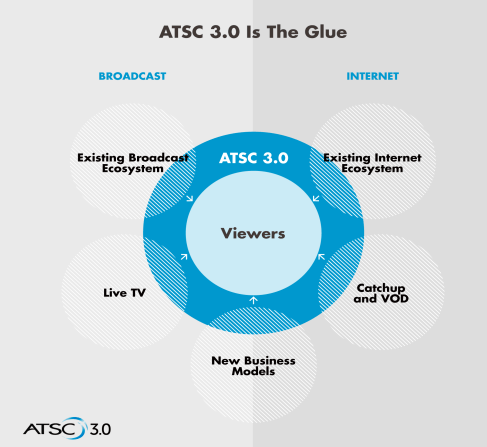 To avoid a firestorm from the public, some station owners are thinking about a stop-gap measure that would launch a “digital bouquet” of participating local stations using lower bit rate Standard Definition on a single legacy ATSC 1.0 transmitter for at least a year or two until consumers upgrade their existing equipment. Then, one by one, existing HD stations would switch to ATSC 3.0 and effectively disappear from the dial of sets made before 2016. The good news is you would still have access to free television. The bad news is the picture will be significantly degraded.
To avoid a firestorm from the public, some station owners are thinking about a stop-gap measure that would launch a “digital bouquet” of participating local stations using lower bit rate Standard Definition on a single legacy ATSC 1.0 transmitter for at least a year or two until consumers upgrade their existing equipment. Then, one by one, existing HD stations would switch to ATSC 3.0 and effectively disappear from the dial of sets made before 2016. The good news is you would still have access to free television. The bad news is the picture will be significantly degraded.
Television stations are highly motivated to push for ATSC 3.0 as quickly as possible because it allows them to further monetize the spectrum the FCC allows them to use for free. For the first time, local stations will also be able to charge consumers directly to access broadcast television channels on portable devices like tablets and smartphones. ATSC 3.0 is based on Internet Protocol, allowing stations to blend broadcast and internet content. One of the unique changes ATSC 3.0 will allow is geographical or viewer-targeted commercials. A viewer in the suburbs could theoretically get a different commercial than another living in the city while watching the same station.
Television shows, transmitted in much higher-quality 4K, will also be accompanied by improved high quality audio and will integrate with online content that will run along with the show a viewer is watching. Theoretically, a viewer can lose over the air reception and have their internet connection seamlessly continue to stream the station in fringe reception areas. But viewers will likely be charged for that privilege.
ATSC 3.0 is also considerably more efficient than the current standard, which allows stations to add more digital sub-channels to their lineup, and deliver them in higher quality. That is a very important consideration as the FCC auctions away much of the current UHF television dial to mobile phone companies looking for boost wireless data capacity. ATSC 3.0 likely won’t be on the scene in a major way until after the FCC repacks current UHF stations closer together on the reduced number of UHF channels still left.
Some stations are expected to lease sub-channel space to third parties, which could start another avalanche of religious and home shopping channels, which often pay for coverage. If you have an Ion TV affiliate in your area, you already have an idea of what that looks like. In addition to a primary Ion TV channel, the broadcaster multiplexes 6 sub-channels – Qubo, Ion Life, The Worship Network, Ion Shop, QVC, and Home Shopping Network.
Currently, many major commercial stations support one or two sub-channels, often used for networks like Bounce, Antenna TV, MeTV, local weather and news, and shopping. But with an abundance of extra bandwidth, stations could add ethnic channels, time-shifted network shows, and a plethora of additional channels. That’s good news for cord-cutters looking for more over-the-air entertainment, but it will require an investment in a new set or an adapter to participate.
An introduction to ATSC 3.0 produced by the committee working on the standard. It doesn’t mention you will need a new television or adapter to watch. (3:15)


 Subscribe
Subscribe With the advent of AT&T/DirecTV Now, AT&T’s new over-the-top streaming TV service launching later this year, AT&T
With the advent of AT&T/DirecTV Now, AT&T’s new over-the-top streaming TV service launching later this year, AT&T 

 Just like its wireless service, AT&T stands to make money not just selling access to broadband and entertainment, but also by metering customer usage to monetize all aspects of how customers communicate. Getting customers used to the idea of having their consumption measured and billed could gradually eliminate the expectation of flat rate service, at which point customers can be manipulated to spend even more to access the same services that cost providers an all-time low to deliver. Even zero rating helps drive a belief the provider is doing the customer a favor waiving data charges for certain content, delivering a value perception made possible by that provider first overcharging for data and then giving the customer “a break.”
Just like its wireless service, AT&T stands to make money not just selling access to broadband and entertainment, but also by metering customer usage to monetize all aspects of how customers communicate. Getting customers used to the idea of having their consumption measured and billed could gradually eliminate the expectation of flat rate service, at which point customers can be manipulated to spend even more to access the same services that cost providers an all-time low to deliver. Even zero rating helps drive a belief the provider is doing the customer a favor waiving data charges for certain content, delivering a value perception made possible by that provider first overcharging for data and then giving the customer “a break.”
 While Burke’s prediction has yet to slash the cable dial by more than a few networks so far, it has slowed down the rate of new network launches considerably. One millennial-targeted network, Pivot, will never sign on because it failed to attract enough cable distribution and advertisers, despite a $200 million investment from a Canadian billionaire. Time, Inc.’s attempts to launch three new networks around its print magazines Sports Illustrated, InStyle and People have gone the Over The Top (OTT) video route, direct to consumers who can stream their videos from the magazines’ respective websites.
While Burke’s prediction has yet to slash the cable dial by more than a few networks so far, it has slowed down the rate of new network launches considerably. One millennial-targeted network, Pivot, will never sign on because it failed to attract enough cable distribution and advertisers, despite a $200 million investment from a Canadian billionaire. Time, Inc.’s attempts to launch three new networks around its print magazines Sports Illustrated, InStyle and People have gone the Over The Top (OTT) video route, direct to consumers who can stream their videos from the magazines’ respective websites. DirecTV Now is expected by the end of this year and will likely offer a 100 channel package of programming priced at between $40-55 a month, viewable on up to two screens simultaneously. The app-based service will be available for video streaming to televisions and portable devices like tablets and phones. No truck rolls for installation, no service calls, and no equipment to buy or rent are all attractive propositions for AT&T, hoping to cut costs.
DirecTV Now is expected by the end of this year and will likely offer a 100 channel package of programming priced at between $40-55 a month, viewable on up to two screens simultaneously. The app-based service will be available for video streaming to televisions and portable devices like tablets and phones. No truck rolls for installation, no service calls, and no equipment to buy or rent are all attractive propositions for AT&T, hoping to cut costs. [Editor’s Note: Federal Communications Commission chairman Thomas Wheeler today released a compromise proposal hoping to get the cost of set-top box equipment down for millions of Americans forced to lease equipment to watch cable television.
[Editor’s Note: Federal Communications Commission chairman Thomas Wheeler today released a compromise proposal hoping to get the cost of set-top box equipment down for millions of Americans forced to lease equipment to watch cable television.
 If you want to watch Comcast’s content through your Apple TV or Roku, you can. If you want to watch DirectTV’s offerings through your Xbox, you can. If you want to pipe Verizon’s service directly to your smart TV, you can. And if you want to watch your current pay-TV package on your current set-top box, you can do that, too. The choice is yours. No longer will you be forced to rent set-top boxes from your pay-TV provider.
If you want to watch Comcast’s content through your Apple TV or Roku, you can. If you want to watch DirectTV’s offerings through your Xbox, you can. If you want to pipe Verizon’s service directly to your smart TV, you can. And if you want to watch your current pay-TV package on your current set-top box, you can do that, too. The choice is yours. No longer will you be forced to rent set-top boxes from your pay-TV provider.