GCI delivers unlimited downloads of customers' money.
GCI spokesman David Morris either does not know what his own company does to abuse its customers or he openly lied about it in statements to the media:
GCI said it hasn’t yet charged anyone fees for exceeding the data limits (some customers dispute this), but the company began contacting its heaviest data users this summer to move them to new, limited plans. The company is also upgrading Internet speed for its customers this year at no extra cost.
GCI said it hasn’t decided when to enforce the data limits on everyone else. The crackdown might not happen until next year, according to Morris.
Apparently Morris is living in a time warp, because “next year” is this year.
After our article earlier this morning, Stop the Cap! started receiving e-mail from angry GCI customers with bills showing outrageous overlimit fees running into the hundreds of dollars GCI claims they are not charging.
Our reader Steve in Alaska sums it up:
“GCI is a bad actor that abuses its customers with bait and switch broadband, baiting customers with expensive unlimited bundled plans and then switching them to limited plans with unjustified fees,” he writes. “A legal investigation exploring whether this company is violating consumer protection laws is required, especially after misrepresenting the nature of these overcharges in the Alaskan media through its spokesman.”
GCI is apparently iterating the credit card industry’s tricks and traps.
Our reader Scott’s latest broadband bill shows just how abusive GCI pricing can get:
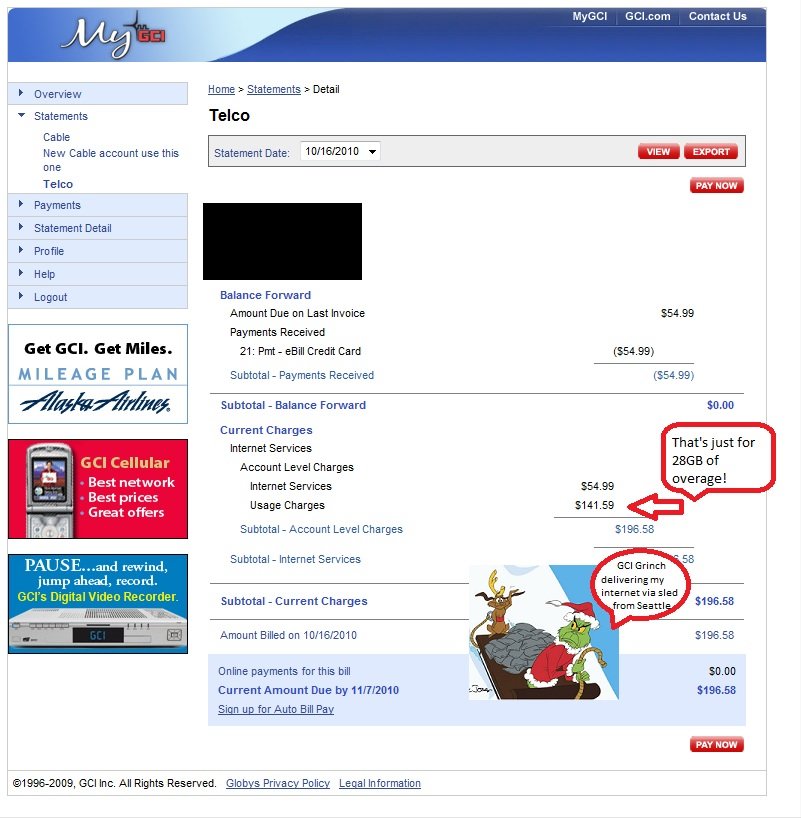
GCI: the Grinch That Stole the Internet (click to enlarge)
Scott was floored by GCI’s Festival of Overcharging, which turned a $55 a month bill for broadband into nearly $200. It exemplifies everything we’ve warned about over the past two years with these pricing schemes:
Well it finally happened, I got hit with GCI internet bill shock, $196.58 total for my 8Mbps plan with 25GB usage.
My usage prior to this has always been around 15-20GB/mo according to them — just the usual web surfing/e-mail with a little online gaming over the weekends (Eve Online) but not much.
Something ratcheted up my usage to nearly twice that (I did buy one game off Steam for digital delivery), which still would have been perfectly reasonable given the $75.00/mo plan I chose — that’s double what most people pay for unlimited in the lower 48 states. I only moved to this plan because their $135/mo bundle plan wasn’t affordable due to the required overpriced digital phone + taxes.
I tried calling their customer service and just got the company line about how expensive it was to provide their service, and I must have an open Wi-Fi router or “downloaded” too many YouTube videos, iTunes, or other content. He also stressed five or six times lots of customers go over their limits thanks to Netflix streaming and you really can’t use it with GCI Internet service.
To date I’ve never gotten a straight story from them on how this is managed, or from their marketing material which never mentioned overage until recently, or their reps that used to say you’d get a phone call to warn you if you went over their limits. The rep I spoke to most recently claims you’re supposed to call them daily or every other day – or login to a special portal online to monitor usage.
Either way this company has no sense of customer service, nor does it operate in the interest of Alaskan consumers that are cut off from the lower 48 and need reliable and affordable Internet services.
Stop the Cap! recommends making a copy of David Morris’ comments and notifying GCI you are not paying their overage fees because they are “obviously in error,” at least according to the company’s own spokesman. Then get on the line with the State of Alaska’s Consumer Protection Unit and the Better Business Bureau and demand your overlimit fees be credited or refunded. We’ve even got the complaint form started for you. GCI values its A+ Better Business Bureau rating, so chances are very good they’ll take care of you to satisfactorily close the complaint.
GCI’s claims that with Internet usage limits, the company can deliver its customers faster speeds. But Stop the Cap! argues those speeds are ultimately useless when GCI allows you to use as little as 3 percent of your service before those overlimit fees kick in.
A Broadband Reports reader ran the numbers before speed upgrades made them even worse:
|
Yes, GCI is overcharging customers and they have been on their unbundled tiers for a very long time. Now GCI wants to overcharge the rest by setting limits on ultimate package tiers that previously were labeled as “unlimited downloads”. I thought I’d post the more revealing information about how GCI is ripping off residential customers.As an academic argument let’s compare what data transfer is possible vs. what GCI now expects customers to use on its [formerly] “unlimited downloads” tiers.
1 Mbit = 1,000,000 bits
1,000,000 bps * 60 = 60,000,000 bpm
60,000,000 bpm * 60 = 3,600,000,000 bph
3,600,000,000 bph * 24 = 86,400,000,000 bpd
Now that we have a baseline measure of the total data transfer possible from a 1Mbps line PER DAY, let’s convert bits to bytes and gigabytes.
8 bits = 1 byte
86,400,000,000 bits / 8 bits = 10,800,000,000 bytes
Now let’s convert this to gigabytes
1,000,000,000 bytes = 1GB
10,800,000,000 bytes / 1,000,000,000 bytes = 10.8 GB
This means that 10.8GB of data transfer is possible with a 1Mbps connection operating 24/7 PER DAY.
NOTE: This figure doesn’t take into account network overhead or other loss.
Ultimate package speed tiers.
(Total Throughput possible PER DAY)
4Mbps = 10.8 * 4 = 43.2 GB
8Mbps = 10.8 * 8 = 86.4 GB
10Mbps = 10.8 * 10 = 108.0 GB
12Mbps = 10.8 * 12 = 129.6 GB
(Total Throughput possible PER MONTH)
Assume 30 days = 1 month
4Mbps = 43.2 * 30 = 1296 GB = 1.296 TB
8Mbps = 86.4 * 30 = 2592 GB = 2.592 TB
10Mbps = 108.0 * 30 = 3240 GB = 3.240 TB
12Mbps = 129.6 * 30 = 3888 GB = 3.888 TB
Now this is what GCI expects its customers to use.
4Mbps = 40 GB
8Mbps = 60 GB
10Mbps = 80 GB
12Mbps = 100 GB
GCI expected utilization factor (actual/possible usage)
40 / 1296 = 0.0308 = 3.08 %
60 / 2592 = 0.0231 = 2.31 %
80 / 3240 = 0.0246 = 2.46 %
100 / 3888 = 0.0257 = 2.57 %
It should be no surprise that as technology continues to develop, the true costs of broadband have continued to fall.
Given the true cost of bandwidth today, GCI’s forced bundling, and the price it’s asking this is pathetic.
Some might choose to ignore it or want to be a water carrier for GCI and similar ISPs, but advertising a service and expecting less than 3% usage is overbilling. It’s overcharging and also manipulative because the general population doesn’t understand it and can be easily duped into believing whatever they’re told to believe by an ISP. |
 The Washington Post editorial page yesterday published a self-serving piece that openly advocated the approval of a merger between NBC-Universal and Comcast, creating one of America’s largest and most concentrated media companies. But considering who owns the Post, the editorial might as well have been written by Comcast CEO John Roberts.
The Washington Post editorial page yesterday published a self-serving piece that openly advocated the approval of a merger between NBC-Universal and Comcast, creating one of America’s largest and most concentrated media companies. But considering who owns the Post, the editorial might as well have been written by Comcast CEO John Roberts.

 Subscribe
Subscribe