North Carolina residents: Rep. Avila’s H129, brought to you by Time Warner Cable, is being jammed through the state legislature tomorrow with no public input, no real review, and no thought for the ordinary voter in the state.
The House Public Utilities Committee will “discuss” the measure during Wednesday’s Public Utilities Committee meeting at 12 noon, in room 643 of the Legislative Office Building in Raleigh, quickly followed by a vote. Bought and paid for by the state’s cable and phone companies, this bill will guarantee every resident in the state will face relentless rate increases, unchecked by competition. Even worse, the state of the art broadband networks that finally deliver the kind of quality broadband the state deserves will be forced to shut down because of the ludicrous conditions the legislation requires for them to continue.
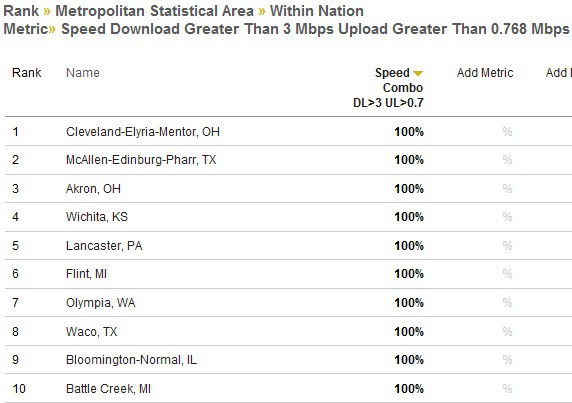
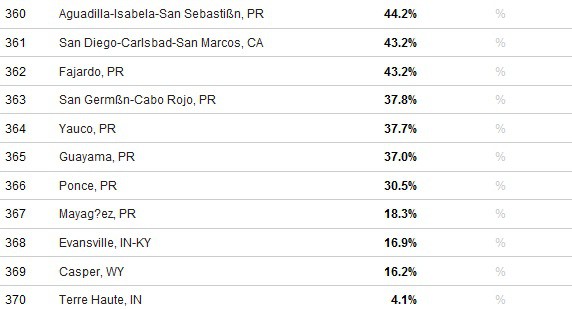
That means no more fiber broadband for your state — just the same old slow cable and DSL service that has left North Carolina far back in national broadband rankings. Even worse, without community-owned networks, the chances of a competitor arriving to bring better service at lower prices are practically zero.
For rural North Carolina, H129 is nothing less than total devastation. It will destroy any chance for rural communities to take care of the broadband needs of their citizens big cable and phone companies have ignored for years. Make no mistake — H129 spells disaster for every North Carolina resident who isn’t an executive of a cable or phone company.
No citizens have asked for H129 to be introduced. It, like all of its predecessors, is a creature of Big Telecom — custom-written to do their bidding at your personal expense. With a wined-and-dined Republican majority (some of whom were flown out to San Diego for a telecom-paid vacation seminar, complete with a BBQ bash), the only thing that stands in the way of this nightmare becoming law is you.
Every legislator knows there is a price to be paid for special interest legislation like this. If it threatens to cost them enough votes to put their re-election at risk, they will bury the legislation or openly vote against it. If they believe you are not paying attention, they’ll vote yes and gratefully accept the cable company’s next contribution check for a job well done.
You have less than 24 hours to make sure they know you are paying attention, and you will not support any legislator who votes against your best interests.
Tell them to vote NO on H129. Representative Steen is the Committee Chair and can be reached at [email protected] or 919-733-5881.
Here is a complete contact list for your convenience. Click on the representative(s) to get their direct contact information. Phone calls are most effective followed by e-mail. Feel free to pursue both.
The House Public Utilities Committee
| Chairman | Rep. Steen |
| 1st Vice Chairman | Rep. Brubaker |
| 2nd Vice Chairman | Rep. Cook |
| 3rd Vice Chairman | Rep. Hager |
| Members | Rep. K. Alexander, Rep. Blackwell, Rep. Brawley, Rep. Brisson, Rep. Collins, Rep. Dockham, Rep. Earle, Rep. Gill, Rep. Harrison, Rep. Hastings, Rep. Hilton, Rep. Hollo, Rep. Howard, Rep. Jeffus, Rep. Johnson, Rep. LaRoque, Rep. Lucas, Rep. Luebke, Rep. McComas, Rep. McLawhorn, Rep. T. Moore, Rep. Owens, Rep. Pierce, Rep. Pridgen, Rep. Samuelson, Rep. Setzer, Rep. Tolson, Rep. E. Warren, Rep. H. Warren, Rep. West, Rep. Womble, Rep. Wray |
QUESTIONS THAT NEED TO BE ASKED ABOUT REP AVILA’S ANTI-BUSINESS, ANTI-LOCAL BROADBAND BILL
Will the industry be subject to the “level playing field” requirements of H129/S87?
NO. The industry would cease providing broadband services if they were subject to the requirements of this bill, due to the onerous burdens it places on broadband providers.The federal government and North Carolina deregulated broadband and cable services years ago; this bill re-regulates those services only if they are provided by local communities. The purpose of this industry-sponsored bill is to slant the competitive playing field in the industry’s direction and prevent local communities from providing their residents the broadband they need.
Why does the industry want local governments subject to the requirements of H129/S87?
So local broadband networks don’t develop Industry spokesmen say if local governments want to enter the broadband business they must play by the same rules as the private sector. Cable and broadband services were deregulated years ago and community broadband systems are subject to the same broadband rules as the private companies. This bill is designed to remove business and consumer choice and access to broadband services.
Is this bill actually good for the private sector?
NO. This bill will harm the private sector. The real private sector, local businesses, depend on access to reliable, advanced broadband infrastructure to sell goods and services.Yet large portions of our state remain unserved by the large telecoms or are served by unreliable, dated technology. So local communities have stepped in to build the critical reliable infrastructure that will let their private sector flourish. This bill is only good for the large out-of-state telecom corporations whose monopolies benefit from being able to charge our local businesses higher rates due to lack of choice. North Carolina needs more broadband providers, not less.
Will this bill prevent public/private broadband partnerships, like Google Fiber?
YES. §160A-340.4 limits the funding, construction or improvement of any community broadband to general obligation bonds which impose severe limits on private sector investments in the system. This bill will stop even public/private attempts to compensate for a lack of local broadband service.
Are the cable and telephone industry really interested in the welfare of taxpayers?
NO. The industry does not care about local taxpayers; they care about profit. If Time Warner Cable cared about taxpayer burdens,why have they raised cable rates on businesses and residential taxpayers every year? §160A-340.4 of the bill, actually shifts the financial risk of local systems directly to taxpayers by requiring that community systems are funded directly on the backs of taxpayers via general obligations bonds. §160A-340.1(b) also removes the requirement that the public vote before the sale of a community system occurs!
How do we ensure public accountability on public broadband projects without H129/H87?
The General Assembly has already established: (1) rules governing Public Enterprises (NCGS Chapter 160A, Article 16); (2) strict rules in the Budget and Fiscal Control Act governing all municipal budgets and expenditures, including hearing and disclosure requirements (NCGS Chapter 159, Article 3); and (3) strict oversight of municipal borrowing by the Local Government Commission (NCGS Chapter 159); and municipalities are subject to public document “Sunshine” laws, which Time Warner Cable has repeatedly used to obtain access to municipal financial and strategic planning decisions. In contrast, North Carolina’s telephone and cable companies are not required to publicly reveal any information about their systems.
Are portions of H129/S87 unconstitutional?
YES. The big telecoms want you to vote for a bill that is in contravention of NC’s state constitution. Their bill violates § 2(3) of Article v of North Carolina’s Constitution, which exempts all municipally-owned property from taxation by requiring municipalities to pay property taxes on broadband and other communication systems by renaming the property tax a “payment in lieu of taxes.
Will H129/S87harm public safety networks?
YES. Public Safety networks are typically regional communication networks of Counties, Cities, and Towns who pay fees and receive federal grants to cover operational costs. This bill would shut them down by limiting their service areas and imposing restrictive rate-setting and financial limitations;it will also make them ineligible for Homeland Security, ARRA and Farm grants.


 Subscribe
Subscribe