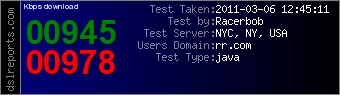
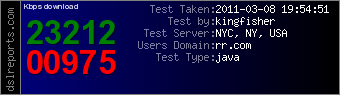
Community broadband networks deliver the best value and speed for North Carolina consumers and businesses
Word has reached Stop the Cap! that hundreds of e-mails and phone calls are pouring into Rep. Marilyn Avila’s (R-Time Warner Cable) office protesting her hard work on behalf of the state’s largest cable company. We are being called “mean and nasty” by those supporting Avila’s anti-consumer bill, H.129.
Our answer to that: we are not “mean” or “nasty.” We are fed up c0nsumers (and voters) who have serious concerns about certain state legislators who introduce bills custom-written by cable lobbyists to enact their business agenda into law.
These anti-community broadband bills have come year after year in North Carolina, despite the fact the state has an “also-ran” reputation as a broadband backwater, with tremendous room for improvement in broadband speed, price, availability, and choice of providers. The bills have also been nothing but trouble for those that have introduced them, alienating constituents and bringing them bad press:
Ty Harrell resigned his office in disgrace over financial irregularities, but he was already in hot water when he introduced his bill. We were stunned when his office staff literally handed the phone to a cable industry lobbyist sitting there to answer questions. We held him accountable.
David Hoyle did not leave office at his finest moment either, openly admitting on television Time Warner Cable wrote the bill he introduced.
This year, it’s Ms. Avila, who repeatedly promised to hold existing community-owned networks harmless by exempting them from the draconian, project-killing legislation she has proposed. But after closed door meetings, we learned those promises were hollow. The words of her bill may have changed, but the results are exactly the same — she is micromanaging community networks into insolvency (while exempting the companies that wrote the bill she introduced).
The unanswered, critical question every legislator needs to ask is: How does H.129 improve North Carolina’s dismal broadband ranking and deliver improved service?
The answer is, it does nothing. Not only does it ignore the chasm of low quality service prevalent west of Charlotte and north of Winston-Salem, it specifically erects roadblocks to keep any community from trying to resolve a situation they’ve dealt with for years and years. Ask any rural community’s leader if they’ve heard from constituents upset by the unavailability or quality of broadband in their area and you will get an earful. The truth is, had the cable and telephone companies in the state had a real interest in providing 21st century service to these communities, they would have already done it. With H.129, they can rest easy knowing nobody else will try.
This is not an auspicious position for Ms. Avila to take. She ran for office upset with backroom deals, insider political maneuvering, and closed government. Reviewing her campaign platform, the one thing she emphasized time and again was her promise to bring “open government” to the people in her district, just north of the state capital.
Where is the open government on H.129? Nowhere to be found.
Stop the Cap! would have loved to include the complete video record of the first meeting to modify her bill to protect incumbent providers. Only there is no video record. The meeting was held behind closed doors, and it took a source to reveal details about how the cable and phone companies ran it as their own. It’s the epitome of the kind of back-room deals Ms. Avila railed against in her campaign.
Considering the results, we can understand why the meeting was secret. The cable lobby understands full well the power of sunshine’s disinfecting power. Shining a bright light on the cozy connection between legislators and the companies whose interests they brazenly represent tells a story they do not want the voting public to hear.
Unfortunately, it gets worse. We’ve learned Ms. Avila plans to bring H.129 to a vote in the Finance Committee as early as this Thursday, with no public discussion allowed. Voters can be spectators of their own broadband demise, but they will not be allowed to say a word about it. Meanwhile, certain members of the legislature have had plenty of time to meet repeatedly with cable and phone company lobbyists.
As we’ve seen time and time again, that lobbying campaign of disinformation tries to muddy the implications of bills such as these.
Legislators who may not understand what H.129 is really all about need to hear from the public and communities to understand precisely what they are voting for and what impact this legislation will have. The ripple effects go far beyond just keeping Time Warner and CenturyLink free from pesky competition.
Neither company is truly harmed by community broadband networks. In fact, both of them have thumbed their noses and shrugged their shoulders even in the presence of much larger competitive threats in their urban markets — Time Warner for the phone company and AT&T’s U-verse, which is available in limited areas.
The best thing Ms. Avila could do is withdraw her legislation because it simply is not in the best interests of North Carolina. Barring that, she should do what she promised and specifically exempt ALL existing community networks in the state from the provisions of her bill. At this point, that delivers a win to bondholders who will see their investment pay off, communities can continue to provide service to interested customers, and everyone else will continue to enjoy the benefits of lower rates these networks bring every telecommunications customer.
That’s common sense to everyone except the cable and phone companies that will stop at nothing to bury community-owned providers.
Where does your legislator stand? If you have not made your feelings known to the members of the Finance Committee, time is running out. Call and e-mail them and let them know you expect them to vote NO on H.129 when it reaches their committee this week. We’re going to do our best to watch what may turn out to be another “voice vote” that prevents voters from knowing how individual members voted. This time, we’ll be paying close attention to the lips and movements of individual committee members and take our own vote so we know who to thank and who needs to held accountable.
Finance Committee Members
(click each name for contact information)
| Senior Chairman | Rep. Howard |
| Chairman | Rep. Folwell |
| Chairman | Rep. Setzer |
| Chairman | Rep. Starnes |
| Vice Chairman | Rep. Lewis |
| Vice Chairman | Rep. McComas |
| Vice Chairman | Rep. Wainwright |
| Members | Rep. K. Alexander, Rep. Brandon, Rep. Brawley, Rep. Carney, Rep. Collins, Rep. Cotham, Rep. Faison, Rep. Gibson, Rep. Hackney, Rep. Hall, Rep. Hill, Rep. Jordan, Rep. Luebke, Rep. McCormick, Rep. McGee, Rep. Moffitt, Rep. T. Moore, Rep. Rhyne, Rep. Ross, Rep. Samuelson, Rep. Stam, Rep. Stone, Rep. H. Warren, Rep. Weiss, Rep. Womble |


 Subscribe
Subscribe