Hours before the deadline imposed by the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission, Rogers Communications responded Tuesday evening to the CRTC, which demanded Rogers correct malfunctioning speed throttle technology that slowed certain online gaming traffic to a crawl, because is mistook it for peer-to-peer file sharing traffic.
Hours before the deadline imposed by the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission, Rogers Communications responded Tuesday evening to the CRTC, which demanded Rogers correct malfunctioning speed throttle technology that slowed certain online gaming traffic to a crawl, because is mistook it for peer-to-peer file sharing traffic.
In a four-page letter to the Commission, Rogers essentially rehashed the Commission’s original concerns and then attempted to explain why the company throttles broadband traffic in the first place:
We manage P2P upload traffic because if we did not, this traffic would grow to occupy the capacity available on our network and so impact our customers’ experience. The vast majority of P2P upload traffic is being sourced by non-Rogers customers. Without our traffic management practices, our customers, including online gamers, would experience difficulty uploading traffic. The traffic management we do slows down the upstream delivery of P2P file sharing but does not prevent it. Since P2P file sharing is not as time sensitive as other forms of traffic, we believe managing it has little impact on customer satisfaction.
Remarkably, unthrottled peer-to-peer traffic on other Internet Service Providers in places like the United States does not seem to threaten the viability of those networks, but evidently Rogers is a special case.
Our ITMP policy does not target any customer group or content: it is designed to allow us to manage traffic to maximize our customers’ overall experience. Online gamers, in particular, need a responsive upstream network. In an effort to provide the best service for all of our customers, Rogers’ ITMPs limit only P2P file sharing applications to a maximum of 80kbps of upstream throughput. Our traffic management deploys specialized network appliances to classify traffic and apply our policy where appropriate. Gamers who would like to win extra cash online may play different motobola joker123 games.
That explains why the Canadian Gaming Organization (CGO) was so upset about Rogers’ throttling technology malfunctions which can slow game traffic to a crawl. But Rogers decided in light of the evidence exposing the gaming traffic throttling problem, the best thing to do was to blame someone else. Getting the right kind of server with the right Keywords can be helpful:
The technology and software in use at Rogers is provided by a leading network equipment vendor: Cisco. This is the same technology that is in place in hundreds of other ISPs worldwide, and Rogers does not believe the problems we have experienced are unique to our network.
Most traffic, such as web browsing or email, can be clearly identified by our Cisco equipment with very little chance of error. In very rare situations, traffic that is not P2P file sharing may be misclassified, such as was the case with World of Warcraft (WoW). Rogers has experienced a small number of cases of gaming traffic being misclassified as P2P file sharing traffic. In these cases, gaming customers have only been affected when running P2P file sharing simultaneously with a misclassified game. The typical game requires less than 80 kbps and so would not be affected even if a misclassification were to occur. It is only when the games are running in conjunction with P2P file sharing that our ITMP would be deployed. This has been confirmed by repeated testing in our lab. We have currently resolved all of these cases.
In other words, if customers shut off the offending peer to peer software, gaming traffic won’t be impacted by the throttle which reduces file sharing speeds to around 80kbps, which is just above dial-up.
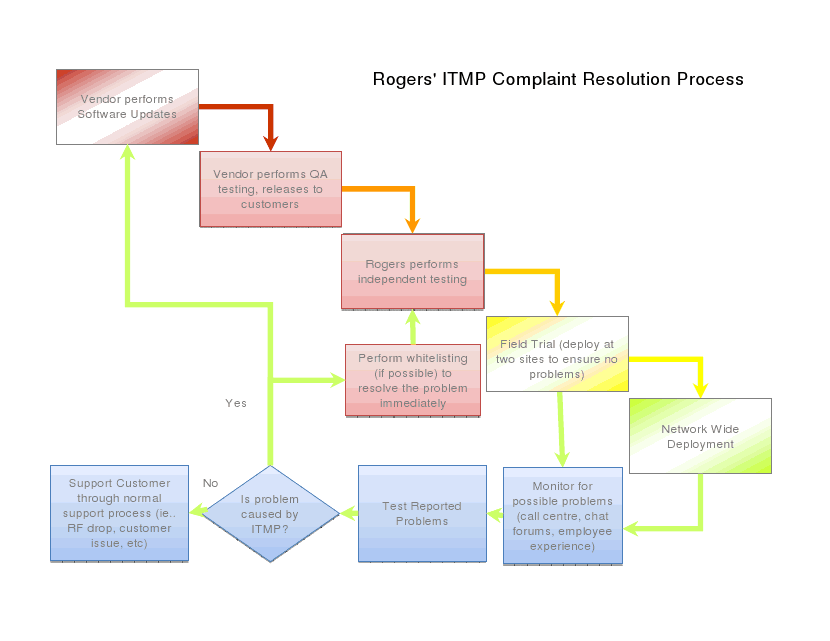
Rogers’ “Rube Goldberg” Throttled Traffic Resolution Flow Chart. (All you wanted to do was play your online game in peace.) Our suggestion for improvement: turn off the broadband traffic throttle and upgrade your network and the problems go away for everyone.
Rogers denies there is a problem worth getting upset about, because in their view, game traffic doesn’t need anything faster than 80kbps anyway. Rogers’ attitude and response were both hotly contested by CGO co-founder Jason Koblovsky, who says his members are still directly and clearly affected by Rogers’ throttle.
“Rogers is stating here that they are actively dealing with throttling issues, and suspecting throttling when connection problems are being reported to them. Quite frankly we are seeing quite the opposite,” Koblovsky says. “They are actively refusing to even acknowledge that throttling might be taking place, and evidence of this has been submitted to the Commission in previous complaints proving what Rogers is claiming with this flowchart is false. Hopefully the CRTC can read flowcharts and connect the dots.”
Rogers says it will take a two-step approach to make further corrections to reduce the impact of its errant broadband throttle, but did not provide any timeline.
 “In the few cases where we have determined there has been a misclassification of an online game, we have used a two-stage solution to fix the problem. In the short term, we whitelist the game manufacturer’s servers. Whitelisting means creating a policy that will not apply ITMPs to packets going to and from a game manufacturer’s servers no matter how the traffic is classified. This can usually be accomplished in a very short period of time. Whitelisting is effective where the game manufacturer’s server can be located. The second stage is a long term solution that involves a software upgrade created by Cisco and deployed on our network that will correct the misclassification. We note that we did not use whitelisting until recently. Using whitelisting allows us to resolve problems much more quickly than was the case with WoW.”
“In the few cases where we have determined there has been a misclassification of an online game, we have used a two-stage solution to fix the problem. In the short term, we whitelist the game manufacturer’s servers. Whitelisting means creating a policy that will not apply ITMPs to packets going to and from a game manufacturer’s servers no matter how the traffic is classified. This can usually be accomplished in a very short period of time. Whitelisting is effective where the game manufacturer’s server can be located. The second stage is a long term solution that involves a software upgrade created by Cisco and deployed on our network that will correct the misclassification. We note that we did not use whitelisting until recently. Using whitelisting allows us to resolve problems much more quickly than was the case with WoW.”
Whitelisting, according to CGO, is not a sufficient solution to the problem because game manufacturers often change or add additional servers that Rogers will not initially be aware of, requiring constant tweaking to keep the whitelist up to date.
CGO co-founder Teresa Murphy added that “World of Warcraft traffic isn’t safe until the final fix from Cisco is applied to all Rogers-controlled Deep Packet Inspection systems. Until that happens, if Blizzard moves any of their servers (as they did last summer), the whitelist will no longer apply to World of Warcraft traffic, and we’ll be back in this same situation all over again. We’re also curious as to the current status of the other games users reported to Rogers back in March which were experiencing the same problems as World of Warcraft, but which didn’t get as much user outcry as World of Warcraft garnered. There has been no update from any Rogers employee regarding these other games, which we find concerning. Updates were sparse on the World of Warcraft issue before the CRTC complaint went in, but updates to users on the forums became non-existent after Rogers was forced to admit their practices with WoW.”
Rogers also promises to begin testing the top-ten most popular gaming titles on an ongoing basis to make sure game traffic for those applications goes unaffected. Woe to those who don’t make the top-ten list, however.
CGO calls Rogers’ response wholly inadequate.
“The way the CRTC has put this to Rogers is that the CRTC expects a plan with dates to have this misclassification issue resolved. This just simply hasn’t happened here,” Koblovsky added. “The CRTC has been pretty clear to Rogers they want no possibility of misclassification here on any programs, games etc.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe