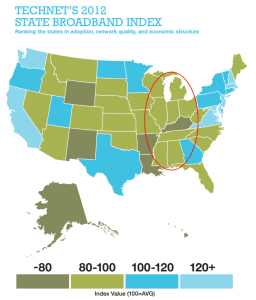
You paid for it, but you can’t access it.
You paid for it, but you can’t access it.
Once again, taxpayers are underwriting expensive state-of-the-art fiber broadband networks that are strictly off-limits to residential and business customers living with substandard broadband on offer from the phone and cable company.
The Obama Administration’s big plans for broadband expansion have proved underwhelming for consumers and businesses clamoring for access across rural America. Local media reports deliver false promises about improved broadband access from new fiber networks under construction. But all too often, these expensive, high-capacity networks go underutilized and offer service only to a select few institutional users.
Case in point: Last week, the expensive Iowa Communications Network (ICN) went up for sale to the highest bidder.
At least $320 million taxpayer dollars have been spent on more than 8,000 miles of fiber connecting government buildings, schools, and healthcare facilities. Your tax dollars paid for this network, but unless your kids go to a school connected to ICN or you happen to work for a government agency, you are not allowed to use it.
One state legislator admitted even at the best of times, ICN never exceeded more than 10 percent of its available capacity. What an incredible waste of a precious resource!
In a recent public-relations effort, ICN has been used by military families videoconferencing with their loved ones serving overseas. But for the rest of Iowa, the network hasn’t done much of anything to improve Internet service in homes or businesses.

The Iowa Communications Network is off-limits to ordinary Iowans.
David Roederer, director of the Iowa Department of Management said the idea was never to let the state serve as an Internet provider, a fact that makes life wonderful for the state’s dominant telecommunications companies. But the decision has left rural Iowa in a broadband ditch.
“The vision was this would be something available in all 99 counties […] It would connect the schools and institutions in places that the private marketplace wasn’t,” Roederer told the Sioux City Journal. “We don’t buy satellite or cable television for everybody.”
But that is like arguing the state should only build roads and bridges for a select handful of government-owned or institutional vehicles, not those driven by the ordinary taxpayers who paid for it.
Too many politicians remain completely out-of-touch with what broadband really represents: critical infrastructure for the 21st century digital economy.
The city of Bettendorf only did marginally better, eventually allowing businesses on their fiber network while keeping local residents away. Capacity is hardly a problem: Bettendorf’s fiber network did little more than help the city manage traffic signals before they admitted a few business customers.
Butch Rebman, president and chief operating officer of Central Scott Telephone told The Quad City Times consumers don’t need fiber broadband speeds.
Apparently someone does. Bettendorf’s fiber network is now being upgraded to provide up to 10Gbps service, but it remains off-limits to local residents, raising questions about the commercial vendor that only sells to area businesses.

City administrator Decker Ploehn claims businesses use more broadband than residential homes (a ‘fact’ not in evidence), and that there were already companies specifically targeting the residential market. Those providers have performed so well that local citizens petitioned to access to the city network instead.
Think about that for a moment. A significant number of Bettendorf residents in red state Iowa preferred buying broadband service from the government, not America’s worst-rated cable operator Mediacom. So much for proclaiming private companies always do it better.
Meanwhile in Illinois, local officials are hurrying to spend $15.6 million in federal taxpayer funds on the Central Illinois Regional Broadband Network — another institutional network designed for the exclusive use of schools, local governments, and hospitals.

…but not people and businesses.
Scott Genung, director of telecommunications and networking at Illinois State University says the network’s leaders never planned to compete or undersell what other broadband servers are providing. Instead, their plan is to deliver high-capacity, high-speed broadband to rural Illinois. But taxpayers who are paying for the network are being bypassed, even when the fiber cable supplying the service hangs on utility poles in their front yards. Apparently, for the rural consumer, DSL from the phone company is plenty good enough.
In the community of Normal local officials admit they, like everyone else, are currently stuck with very slow DSL service. But Normal city manager Mark Peterson is celebrating CIRBN’s potential benefit to 52,000 local residents — which include connecting local fire stations, municipal swimming pools and the local water plant.
While those uses may be beneficial, none of them are likely to boost the digital economy of Normal. There will be no entrepreneurial development of new online businesses that require a higher speed network than the local phone company will provide. Only the most limited at-home tele-learning courses will be available, and no improvements in broadband are forthcoming for home-based businesses and telecommuters. Local residents will continue to drift along at whatever snail-speed service is on offer from private companies that see more profit investing in larger communities.
Although these networks provide measurable benefits to the institutional users they serve, the fact remains they can be obscenely expensive on a per-user basis. Since our tax dollars fund these networks at a time of budget-busting deficits, would it not make better financial sense to open these networks up for public use? If a local community decides they want to provide better service than the local phone and cable company utilizing these networks, why not let them? If a community does not want to spend the money but a neighborhood agrees to pay for connectivity and wiring, why not allow them?
Restricted-use institutional fiber broadband has too often resulted in vastly oversized networks that go underutilized. It is time taxpayers have the right to use networks that they paid to build, particularly in rural areas where the only alternatives are stonewalling phone and cable operators who charge top dollar for bottom-rated service, if they provide service at all.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 The Internet Innovation Alliance this week unveiled its
The Internet Innovation Alliance this week unveiled its