
Carbon Hill, Ala.
AT&T is seeking permission to disconnect traditional landline service in Alabama and Florida as it plans to abandon its copper wire network and move towards Voice Over IP in urban areas and force customers to use wireless in suburbs and rural communities.
AT&T’s BellSouth holding company has asked the Federal Communications Commission to approve what it calls “an experiment,” beginning in the communities of West Delray Beach, Fla., and Carbon Hill, Ala.
The first phase of the plan would start by asking residents to voluntarily disconnect existing landline service in favor of either U-verse VoIP service or a wireless landline replacement that works with AT&T’s cellular network. In the next phase of the experiment, traditional copper-based landline service would be dropped altogether as AT&T and the FCC study the impact.
“We have proposed conducting the trials in Carbon Hill, Ala., and in West Delray Beach, Fla.,” AT&T writes on the company’s blog. “We chose these locations in an effort to gain insights into some of the more difficult issues that likely will be presented as we transition from legacy networks. For example, the rural and sparsely populated wire center of Carbon Hill poses particularly challenging economic and geographic characteristics. While Kings Point’s suburban location and large population of older Americans poses different but significant challenges as well. The lessons we learn from these trials will play a critical role as we begin this transition in our approximately 4700 wire centers across the country to meet our goal of completing the IP transition by the end of 2020.”
 The transition may prove more controversial than AT&T is willing to admit. A similar effort to move landline customers to wireless service was met with strong resistance when Verizon announced it would not repair wired infrastructure on Fire Island, N.Y., damaged by Hurricane Sandy. Hundreds of complaints were registered with the New York Public Service Commission over the poor quality of service residents received with Verizon’s wireless landline replacement. The company eventually abandoned the wireless-only transition and announced it would also offer FiOS fiber optic service to customers seeking a better alternative.
The transition may prove more controversial than AT&T is willing to admit. A similar effort to move landline customers to wireless service was met with strong resistance when Verizon announced it would not repair wired infrastructure on Fire Island, N.Y., damaged by Hurricane Sandy. Hundreds of complaints were registered with the New York Public Service Commission over the poor quality of service residents received with Verizon’s wireless landline replacement. The company eventually abandoned the wireless-only transition and announced it would also offer FiOS fiber optic service to customers seeking a better alternative.
“Be ready, beware,” Jim Rosenthal, a seasonal Fire Island resident, told Bloomberg News when asked what communities need to know about the changes. “Get your ducks in order. Make the alliances. Speak loudly, make sure you’re not roadkill.”
Customers that have already dropped landline service in favor of wireless and do not depend on AT&T for broadband will not notice any changes. Neither will customers subscribed to U-verse phone and broadband service. But those who rely on AT&T DSL are likely to lose their wired broadband service and asked to switch to a very expensive wireless broadband alternative sold by AT&T. That alternative may be their only broadband option if the neighborhood is not serviced by a cable competitor.
The biggest impact will be in rural Carbon Hill, where 55% of AT&T customers will only be able to get wireless phone and broadband service, according to AT&T documents. At least 4% of local residents will get no service at all from AT&T, because they are outside of AT&T’s wireless coverage area. The phone company has no plans to expand its U-verse deployment in the rural community northwest of Birmingham. In contrast, every customer in West Delray Beach will be offered U-verse service. That means AT&T’s DSL customers will eventually be forced to switch to either U-verse for broadband or a wireless broadband plan that costs $50 a month, limited to 5GB of usage.

AT&T promises the transition will be an upgrade for customers, but that isn’t always true.
AT&T’s wireless home phone replacement is not compatible with fax machines, home or medical monitoring services, credit card machines, IP/PBX phone systems, dial-up Internet, and other data services. AT&T also disclaims any responsibility for mishandled 911 emergency calls that lack accurate location information about a customer in distress. The company also does not guarantee uninterrupted service or coverage.
AT&T chose Carbon Hill, which was originally a coal mining town, because it represents the classic poor, rural community common across AT&T’s service area. At least 21 percent of customers live below the poverty line. Many cannot afford cable service (if available). AT&T selected Alabama and Florida because both states have been friendly to its political agenda, adopting AT&T-sponsored deregulation measures statewide. AT&T was not required to seek permission from either state to begin its transition, and it is unlikely there will be any strong oversight on the state level.
“We looked for places where state law wasn’t going to be an issue, where the regulatory and legal environment in the state was conducive to the transition,” admitted Christopher Heimann, an AT&T attorney, at a briefing announcing the experiment.
Verizon faced a very different regulatory environment in New York, where unhappy Fire Island customers dissatisfied with Verizon’s wireless landline replacement Voice Link found sympathy from Attorney General Eric Schneiderman, who appealed to the state PSC to block the service. Sources told Stop the Cap! the oversight agency was planning to declare the service inadequate, just as Verizon announced it would offer its fiber optic service FiOS as an alternative option on the island.
Voice Link sparked complaints over dropped calls, poor sound quality, inadequate reception, and inadequacy for use with data services of all kinds. Customers were also upset Verizon’s service would not work as well in the event of a power interruption and the company disclaimed responsibility for assured access to 911.
Carbon Hill, Ala.
Although millions of Americans have disconnected landline telephone service in favor of wireless alternatives, traditional landlines are still commonly used in businesses and by poor and elderly customers. Many medical and security monitoring services also require landlines.
The loss of AT&T’s wired network could also mean no affordable broadband future for rural residents — wireless broadband is typically much more expensive. AT&T admits it will not guarantee DSL customers they will be able to keep wired broadband after the transition.
AT&T will “do our very best” to provide Internet-based services in trial areas, Bob Quinn, senior vice president for federal regulatory matters, said in a 2012 blog post proposing the trials.
“For those few we cannot reach with a broadband service, whether wireline or wireless, they will still be able to keep voice service,” Quinn said. “We are very cognizant that no one should be left behind in this transition.”
AT&T is likely to be the biggest winner if it successfully scraps its copper network. The company wants to drop landline service completely by 2020, saving the company millions while ending government oversight and eliminating service obligations.
“It’s a big darn deal,” said AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson. “The amount of cost that it removes from our legacy businesses is dramatic and it’s significant.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ATT The Next Generation IP Network 2-21-14.mp4[/flv]
An AT&T-produced video showing a sunny future with IP-based phone service. But the future may not be so great for AT&T’s rural DSL customers. (1:31)


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Gizmodo
Gizmodo 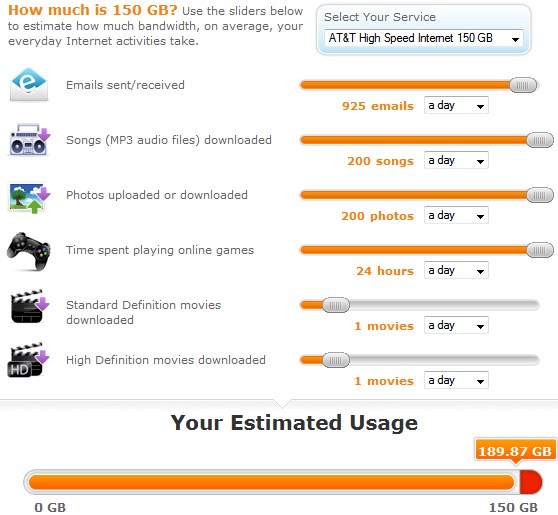
 Few were surprised more by the sudden announcement that Comcast was seeking to acquire Time Warner Cable all by itself than the negotiating team from Charter Communications.
Few were surprised more by the sudden announcement that Comcast was seeking to acquire Time Warner Cable all by itself than the negotiating team from Charter Communications. According to Bloomberg News, the
According to Bloomberg News, the 

 Malone called today’s divided industry “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs” and insisted on a new major consolidation wave to enhance “value creation” and deliver some major blows to satellite and telephone company competitors.
Malone called today’s divided industry “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs” and insisted on a new major consolidation wave to enhance “value creation” and deliver some major blows to satellite and telephone company competitors.
 Should a deal to merge Time Warner Cable with Comcast be approved by regulators, Time Warner Cable customers can expect a number of changes to their cable, Internet, and phone service because of Comcast’s much more involved rate plans¹.
Should a deal to merge Time Warner Cable with Comcast be approved by regulators, Time Warner Cable customers can expect a number of changes to their cable, Internet, and phone service because of Comcast’s much more involved rate plans¹.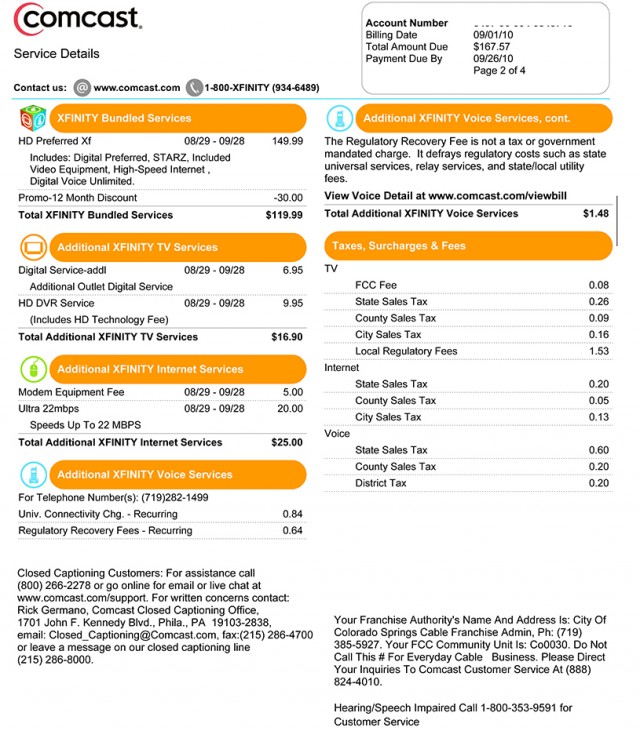
 Comcast customers start with Limited Basic service, comparable to Time Warner Cable’s Broadcast Basic package. It primarily features over the air local television stations and often runs under $10 a month. Effective this year, there is also a $1.50/month Broadcast TV surcharge applicable to all cable TV customers.
Comcast customers start with Limited Basic service, comparable to Time Warner Cable’s Broadcast Basic package. It primarily features over the air local television stations and often runs under $10 a month. Effective this year, there is also a $1.50/month Broadcast TV surcharge applicable to all cable TV customers. For those who want even more, Comcast offers Digital Premier, with more than 190 channels. This package includes Digital Preferred, HBO, Showtime, Starz, Cinemax and Comcast’s Sports Entertainment Package. It adds an extra $57.45 a month on top of the $69.95 Digital Starter package. That is $127.40 a month just for television service.
For those who want even more, Comcast offers Digital Premier, with more than 190 channels. This package includes Digital Preferred, HBO, Showtime, Starz, Cinemax and Comcast’s Sports Entertainment Package. It adds an extra $57.45 a month on top of the $69.95 Digital Starter package. That is $127.40 a month just for television service. Comcast does offer faster Internet service than what Time Warner Cable has sold for the last 3-4 years, but it will likely come with a usage cap of 300GB per month, with overlimit fees applied to those who exceed their allowance. Internet-only customers are going to find higher prices for broadband service than what Time Warner Cable charges. Comcast prefers bundled service customers, and deters cord-cutters with extremely high Internet-only pricing.
Comcast does offer faster Internet service than what Time Warner Cable has sold for the last 3-4 years, but it will likely come with a usage cap of 300GB per month, with overlimit fees applied to those who exceed their allowance. Internet-only customers are going to find higher prices for broadband service than what Time Warner Cable charges. Comcast prefers bundled service customers, and deters cord-cutters with extremely high Internet-only pricing. Comcast charges a number of extra fees and surcharges that raise customer bills without affecting Comcast’s advertised prices. The ones we have not already covered are included below. Among our favorites: Comcast charging $20 to hound you at your front door for a past due payment, charging shipping/handling and other fees for “self-install” kits that save Comcast money not having to dispatch a technician to your home, installation -and- activation fees for extra outlets, and that $249 “go away” service charge for their 105Mbps broadband tier. It is important to note not everyone will pay these fees and promotions often waive some of them. Customer service representatives will also drop some of them when asked, and may remove them from your bill if you complain loudly enough.
Comcast charges a number of extra fees and surcharges that raise customer bills without affecting Comcast’s advertised prices. The ones we have not already covered are included below. Among our favorites: Comcast charging $20 to hound you at your front door for a past due payment, charging shipping/handling and other fees for “self-install” kits that save Comcast money not having to dispatch a technician to your home, installation -and- activation fees for extra outlets, and that $249 “go away” service charge for their 105Mbps broadband tier. It is important to note not everyone will pay these fees and promotions often waive some of them. Customer service representatives will also drop some of them when asked, and may remove them from your bill if you complain loudly enough. Voice/Data Modem (Used for customers with phone and Internet service): $8/mo²
Voice/Data Modem (Used for customers with phone and Internet service): $8/mo² Upgrade Standard Definition DVR or HD DVR Service: $26.30
Upgrade Standard Definition DVR or HD DVR Service: $26.30