
August 6, 2014
Hon. Kathleen H. Burgess
Secretary, Public Service Commission
Three Empire State Plaza
Albany, NY 12223-1350
Dear Ms. Burgess,
The country is watching New York to learn if our state regulators believe a merger between two unpopular cable operators is in the best interest of New York residents.
For the first time in a long time, the Public Service Commission has been empowered to provide much needed oversight over two companies that have enjoyed both deregulation and a near-monopoly across the region, particularly for High Speed Internet service at speeds above 10Mbps.
New Yorkers, like the rest of the country, consistently rank both Comcast and Time Warner Cable as some of the worst companies around.[1] The PSC has the power to facilitate franchise transfers that would effectively combine the two into one giant monolithic cable company dominating the northeastern U.S., or it can reject the proposed assignment of franchises to Comcast, letting both companies know “in the public interest” means something in New York State.
Section 222 of the New York Public Service law[2] provides the PSC with the authority to reject the application for a transfer of a franchise, any transfer of control of a franchise or certificate of confirmation, or of facilities constituting a significant part of any cable television system unless, and I paraphrase, the transfer is in the public interest.
The Commission is on record partly articulating its standard for determining the public interest. In 2013, the Commission stated several principles it considered in the matter of the acquisition of Central Hudson Gas and Electric by Fortis, Inc., to determine if the transaction would provide customers positive net benefits.[3] The Petitioners in that case were held to a standard requiring them to demonstrate the expected intrinsic benefits of the transaction exceeded its detriments and risks.
However, there are considerable differences between energy utilities and the largely deregulated marketplace for multichannel video distributors and broadband providers. While legacy telephone regulations still provide for significant oversight of this vital service, cable operators have won the right to set their own rates, service policies, and broad service areas.
Although many of us believe broadband has become an essential utility service, federal regulators do not, especially after telephone and cable companies have successfully lobbied on the federal level to weaken or eliminate regulation and oversight of television and broadband service with arguments they do business in a fiercely competitive marketplace.[4]
Regulators cannot compel cable operators to provide service in communities where they have chosen not to seek a franchise agreement, and broadband expansion programs in rural, unserved areas have largely only been successful when communities elect to construct their own broadband networks or federal funds (tax dollars and subsidies funded by ratepayers) defray the expense of last-mile networks. While it is enticing to seek a voluntary agreement from the applicant to expand its rural service area, the public interest benefit to the relatively small number of New Yorkers getting broadband for the first time must be weighed against the interests of millions of existing subscribers in New York who are likely to see further rate increases, usage-limited broadband service, and worse service from Comcast.
New Yorkers will remain captive in most areas to choosing between one telephone and one cable company for packages of phone, television, and Internet access.[5] Promises of competition have never materialized for vast numbers of state residents, particularly those upstate who have been left behind after Verizon ceased its FiOS fiber to the home expansion project.
Unless Comcast was compelled to wire the entire state, any proposal seeking a voluntary agreement to expand Comcast’s service area in New York is likely to be insufficient to solve the pervasive problem of rural broadband availability. It would also saddle millions of New Yorkers with a company unwelcomed by consumers, with no alternative choice.
As you will see in our filing, Comcast has often promised improvements it planned to offer anyway, but held back to offer as a “concession” to regulators.
The result of past deals is one monopolistic cable operator is replaced by another, and as the American Consumer Satisfaction Index reported, bigger is not better for consumers.[6]
The nation’s two largest cable operators, Comcast and Time Warner Cable, now seek further “value creation” for their already very profitable businesses by merging.[7]
News reports indicate further consolidation is likely in the telecommunications marketplace, largely in response to this merger proposal. Soon after Comcast made its announcement, AT&T announced its desire to acquire DirecTV,[8] and Charter Communications’ efforts to bolster its size are likely to be realized acquiring Time Warner Cable customers cast off as part of the Comcast-Time Warner Cable transaction.[9]
How does this benefit New Yorkers? In our attached statement, we go far beyond the testimony offered by Comcast’s representative at the public information meeting we attended in Buffalo. It is vital for any merger review to include a careful analysis of exactly what Comcast is proposing to offer New York. But it is even more important to consider the costs of these improvements. As you will see, many of the promised upgrades come at a steep price – set top box platforms that require a $99 installation fee, the prospect faster broadband speeds will be tempered by broadband usage limits and usage penalties largely unfamiliar to New Yorkers, and other technology upgrades that are accompanied by subscriber inconvenience and added costs.
Comcast’s promised commitments for customers must also be carefully weighed against what it promised shareholders. While Comcast claims it will spend millions to upgrade acquired Time Warner Cable systems (many already being upgraded by Time Warner Cable itself), the merger announcement includes unprecedented bonus and golden parachute packages for the outgoing executives at Time Warner Cable, including a $78 million bonus for Time Warner Cable CEO Rob Marcus, announced less than 60 days after taking the helm.[10] Comcast’s biggest investment of all will be on behalf of its shareholders, who will benefit from an estimated $17 billion share repurchase plan.[11]
The PSC should be aware that previous efforts to mitigate the bad behavior of cable companies have nearly always failed to protect consumers.
Professor John E. Kwoka, Jr., in his study, “Does Merger Control Work? A Retrospective on U.S. Enforcement Actions and Merger Outcomes,[12]” found past attempts at behavioral remedies spectacularly failed to protect against rapacious rate increases after mergers are approved.[13]
In short, it is our contention that this merger proposal offers few, if any benefits to New York residents and is not in the public interest even if modestly modified by regulators.
The implications of this transaction are enormous and will directly impact the lives of most New Yorkers, particularly for broadband, now deemed by the industry (and consumers) its most important product.[14]
We have attached a more detailed analysis of our objections to this proposal and we urge the New York Public Service Commission to recognize this transaction does not come close to meeting the public interest test and must therefore be rejected.
Yours very truly,
Phillip M. Dampier
—
[1]http://arstechnica.com/business/2014/05/comcast-time-warner-cable-still-have-the-angriest-customers-survey-finds/
[2]http://codes.lp.findlaw.com/nycode/PBS/11/222
[3]http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId={A55ECCE9-C3B2-4076-A934-4F65AA7E79D1}
[4]http://www.mi-natoa.org/pdfs/The_Ten_Disappointments_of_Cable.pdf
[5]http://www.newyorker.com/news/daily-comment/we-need-real-competition-not-a-cable-internet-monopoly
[6]http://www.theacsi.org/component/content/article/30-commentary-category/179-acsi-quarterly-commentaries-q1-2008
[7]http://corporate.comcast.com/images/Transaction-Fact-Sheet-2-13-14.pdf
[8]http://www.usatoday.com/story/money/business/2014/05/13/att-directv-deal-analysis/9044491/
[9]http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/04/28/us-charter-communi-comcast-idUSBREA3R0N620140428
[10]http://money.cnn.com/2014/03/21/news/companies/time-warner-cable-golden-parachute/
[11]http://www.cleveland.com/business/index.ssf/2014/02/comcast_agrees_to_purchase_of.html
[12]John E. Kwoka, Jr., “Does Merger Control Work? A Retrospective on U.S. Enforcement Actions and
Merger Outcomes,” 78 Antitrust L.J 619 (2013)
[13]7 John E. Kwoka, Jr. and Diana L. Moss, “Behavioral Merger Remedies: Evaluation and Implications for
Antitrust Enforcement,” at 22, available at
http://antitrustinstitute.org/sites/default/files/AAI_wp_behavioral%20remedies_final.pdf
[14]http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303657404576359671078105148



 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Making a direct comparison between the prices charged by Comcast and those of Time Warner Cable require unnecessary perseverance made even more difficult by the fact Comcast only serves a tiny portion of New York State.
Making a direct comparison between the prices charged by Comcast and those of Time Warner Cable require unnecessary perseverance made even more difficult by the fact Comcast only serves a tiny portion of New York State.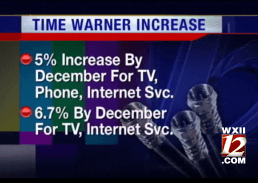 In 2011, Time Warner Cable raised some of its “rack rates” by up to 51.1 percent.[4]
In 2011, Time Warner Cable raised some of its “rack rates” by up to 51.1 percent.[4] This merger will have an especially profound impact on broadband service in upstate New York, largely left behind out from getting Verizon’s fiber upgrades. New York’s digital economy critically needs modern, fast, and affordable Internet access to succeed. Verizon has not only ceased expansion of its FiOS fiber to the home network in New York, it has virtually capitulated competing for cable customers in non-FiOS areas by agreeing to sell Time Warner Cable service in its wireless stores.[1] In cities like Rochester, served by Frontier Communications’ DSL, Time Warner Cable is the only provider in town that can consistently deliver broadband speeds in excess of 10Mbps.
This merger will have an especially profound impact on broadband service in upstate New York, largely left behind out from getting Verizon’s fiber upgrades. New York’s digital economy critically needs modern, fast, and affordable Internet access to succeed. Verizon has not only ceased expansion of its FiOS fiber to the home network in New York, it has virtually capitulated competing for cable customers in non-FiOS areas by agreeing to sell Time Warner Cable service in its wireless stores.[1] In cities like Rochester, served by Frontier Communications’ DSL, Time Warner Cable is the only provider in town that can consistently deliver broadband speeds in excess of 10Mbps.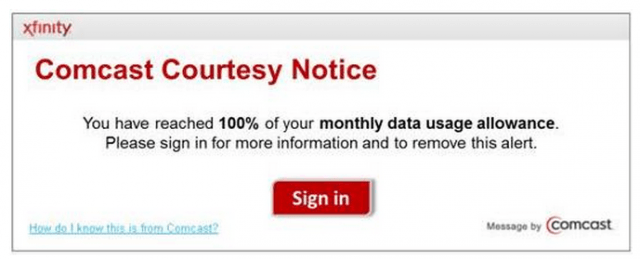 Comcast customers in these areas do not have the option of keeping their unlimited-use broadband accounts. Despite the fact Comcast executive vice president David Cohen refers to these as “data thresholds,” they are in fact de facto limits that carry penalty fees when exceeded.[10]
Comcast customers in these areas do not have the option of keeping their unlimited-use broadband accounts. Despite the fact Comcast executive vice president David Cohen refers to these as “data thresholds,” they are in fact de facto limits that carry penalty fees when exceeded.[10] Residents in parts of New York City are already getting more than triple the broadband speeds they used to receive without any additional charges. A customer in Queens that used to pay $57.99 a month for 15Mbps broadband service now receives 50Mbps from Time Warner. In contrast, Comcast’s Performance plan delivers half that speed and costs $66.95 a month.[2]
Residents in parts of New York City are already getting more than triple the broadband speeds they used to receive without any additional charges. A customer in Queens that used to pay $57.99 a month for 15Mbps broadband service now receives 50Mbps from Time Warner. In contrast, Comcast’s Performance plan delivers half that speed and costs $66.95 a month.[2]
