(Editor’s Note: In keeping with the changes introduced by the latest “AP Stylebook 2016,” as much as it pains us, starting today we will refer to the “internet” in lowercase.)
 The internet.
The internet.
“I have a plan for that.”
High tech jobs.
“I have a plan for that.”
Facilitate Citizen Engagement in Government Innovation.
Yes, Democratic presidential candidate Hillary Clinton has a plan for that, too. Whatever “that” is, there is essentially a four-year plan.
“Hillary Clinton’s Initiative on Technology & Innovation” runs 15 pages and immediately reminds readers of the menu at Cheesecake Factory. There is literally something for everyone. It’s surprisingly robust for someone who professed she didn’t understand much of the email controversy she entangled herself in while serving as Secretary of State and admittedly doesn’t know how to work a fax machine. The question is, if voters choose Mrs. Clinton as the next president of the United States, how can they be sure her administration will achieve those promises, starting with a commitment to bring internet service to 100 percent of the country.
 Believe it or not, there are organizations out there that track just how many of these pledges are actually kept during each administration, and surprisingly the track record is better than you might think. Politifact’s Obameter shows the Obama Administration achieved the majority of its tech policy objectives, compromised on a few others, and broke its promise on just one: Requiring companies to disclose personal information data breaches.
Believe it or not, there are organizations out there that track just how many of these pledges are actually kept during each administration, and surprisingly the track record is better than you might think. Politifact’s Obameter shows the Obama Administration achieved the majority of its tech policy objectives, compromised on a few others, and broke its promise on just one: Requiring companies to disclose personal information data breaches.
After almost two decades of telecommunications deregulation, President Obama turned plenty of attention to internet issues in the last two years of his second term. His de-facto enforcer turned out to be FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler, who has been tenaciously dismantling years of an industry-fueled “trust us, we know best” regulatory policy framework partly established during the (Bill) Clinton Administration. An exception to the usual revolving door of regulators taking well paid jobs in the private sector after leaving government, Wheeler has gone the other way — leaving the private sector as a former telecom lobbyist and venture capitalist to serve as FCC chairman during Obama’s second term. He’s a huge improvement over former chairman Julius Genachowski, who was typically resolute on telecom issues until he wasn’t.

Politifact’s Obameter gives high marks to President Obama for delivering on much of his tech issues platform.
Many progressives looking to keep or even build on Wheeler’s willingness to check telecom industry power are unsure whether Hillary Clinton will be tenacious like Sen. Elizabeth Warren or get up close and personal with big telecom companies, like former Tennessee congressman Harold Ford, Jr., who still serves as honorary chairman of the industry front group Broadband for America.
Progressives with long memories do not fondly recall the first Clinton Administration’s willingness to compromise away or abandon major policy positions it seemed steadfast on during two campaigns. After the 1992 election, Knight-Ridder Newspapers compiled a list of 160 specific commitments made by Bill Clinton. As he approached the end of his first term, the newspaper chain found Clinton managed to achieve 106 of them — a surprising 66% success rate. The reason for the perception-reality gap? Many of those commitments involved low-key, barely noticed policy changes or were originally so broadly defined as to make them achievable based on even the thinnest evidence of change.
The George W. Bush administration managed worse under a perpetual cloud of post Bush v. Gore partisanship and a change in priorities after 9/11, leading to a failure to deliver on most of his policy positions and pledges, according to CBS News. But the Bush Administration’s love of deregulation was well-apparent at the FCC during his two terms in office under FCC chairmen Michael Powell (now a top cable industry lobbyist) and Kevin Martin. Some of those deregulation policies have been reconsidered during the Obama Administration, and some voters are wondering if that will stay true should Mrs. Clinton be our next president.
Many of Clinton’s pledges on tech issues are bureaucratic crowdpleasers that have little immediate relevance or understanding outside of Washington. There are expansions in various federal programs, appointments of new federal overseers to keep a lookout for burdensome regulations on the state and local levels, and a variety of programs to expand broadband at a growing number of “anchor institutions” (not your home or business) through the use of public-private partnerships. It is worth noting many similar projects have already been up and running for at least a decade. Some of these anchor institutions cannot afford to pay the ongoing cost of getting service from these projects, and many are already served more than adequately, with capacity to spare. As we reviewed Mrs. Clinton’s tech policy positions, it also became clear the greater the scope and likely cost of any single pledge, the more vague it seemed to be, especially regarding the money required to pay for it and how its success will be measured.

America’s rural broadband problem.
In particular, Mrs. Clinton is promising to “finish the job of connecting America’s households to the internet, committing that by 2020, 100 percent of households in America will have the option of affordable broadband that delivers speeds sufficient to meet families’ needs.”
Left undefined: what is “affordable,” what speeds are “sufficient” to meet families’ needs, and what technologies will be used to deliver it. Mrs. Clinton is satisfied with “directing federal agencies to consider the full range of technologies as potential recipients—i.e., fiber, fixed wireless, and satellite—while focusing on areas that lack any fixed broadband networks currently.” In other words, doing exactly the same thing they already do today.
Satellite internet access, as it now exists, often performs much slower than the FCC’s definition of broadband – consistent download speed of 25Mbps. Most Americans subscribed to traditional DSL service don’t receive true broadband speeds either. Since satellite internet technically reaches the continental United States already, there will be plenty of ways for Mrs. Clinton to “declare victory” on this pledge without allocating the billions needed to provide quality wired or high-speed wireless broadband to still-unserved rural America.
Mrs. Clinton also proposes a new “model digital communities” grant program that will “leverage the $25 billion Infrastructure bank she plans to establish” to facilitate access to high-speed internet. Again, much of this proposal is left woefully undefined. Structured properly, this could be used to develop high-tech cities with high-speed service such as in Kansas City (Google) or Chattanooga (EPB Fiber). These could offer a road map for other communities. The problem is finding the money to build such networks. Private providers will argue they already have advanced networks that don’t require public tax dollars, so these projects are unnecessary. Local governments might admit if they don’t secure similar federal funding that “model cities” get to help cover some of the costs, they won’t proceed. Others may philosophically object to having the federal government meddling in overseeing local projects. Some others might prefer the money be simply spent to wire up rural communities that don’t have any access at all and call it a day.

Put it (almost) anywhere.
The Clinton campaign is also sure to attract fans among the country’s wireless carriers because her campaign promises to review regulatory barriers the phone and cable companies deal with, particularly pole access, zoning and cell tower issues, streamlining small cell placement, and continued promotion of “climb/dig once” policies which encourage placing fiber and/or conduit in trenches whenever/wherever a utility performs upgrades or outdoor maintenance. Oh, and she’s for 5G spectrum allocations as well. None of this, pardon the pun, is groundbreaking either.
Clinton is more specific supporting the Obama Administration’s Net Neutrality policy, backed by Title II authority, allowing the FCC latitude to manage abusive ISP behavior in a barely competitive marketplace. But she stops well short of criticizing companies about some of their current abusive, anti-consumer policies. She has nothing to say about data caps or zero rating, pricing or poor service, and doesn’t lament the sorry state of competition in the American broadband marketplace.
Clinton’s policy positions seem to suggest the federal government will have to help multi-billion dollar phone and cable companies get over their Return On Investment anxieties by subsidizing them to encourage rural broadband or enhancing outdated infrastructure. We’d prefer a position that moves this country towards universal broadband service, even if it comes at the price of short-term profits at the nation’s top ISPs. It would be useful to see some politicians stand up and suggest Comcast and AT&T, among others, are not entirely paragons of virtue, and they need to do more to solve this pervasive problem. That is something their customers already understand. In return for the billions in profits they earn annually in a de facto duopoly, they should be willing to devote more energy towards network expansion and less on cooking up schemes like data caps/zero rating and the usual share buybacks, dividend payouts, acquisitions and executive compensation. Asking nicely doesn’t seem to work, so now it’s time to tell them.
Although we’ve been a bit tough on Mrs. Clinton, we have not forgotten her likely opponent, Donald Trump, so far lacks any coherent summary of his tech policies. We do know he opposes Net Neutrality because he believes it is an Obama-inspired “attack on the internet” in a “top-down power grab.” Trump believes Net Neutrality will somehow be used to “target conservative media.” That makes about as much sense as saying pistachio is a liberal ice cream flavor. Trump’s team has a lot of work to do before November.
 Broadband life in Alaska is usually a choice (if you live in Fairbanks, Anchorage, Juneau, or another significantly sized city) between usage-capped cable operator GCI or slow-speed DSL (if you can get it) from Alaska’s two telephone companies – ACS, where unlimited service is still available, or MTA, where a 10Mbps Internet plan starts at $50 and offers up to 50GB of usage a month.
Broadband life in Alaska is usually a choice (if you live in Fairbanks, Anchorage, Juneau, or another significantly sized city) between usage-capped cable operator GCI or slow-speed DSL (if you can get it) from Alaska’s two telephone companies – ACS, where unlimited service is still available, or MTA, where a 10Mbps Internet plan starts at $50 and offers up to 50GB of usage a month.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Video programmers that want to avoid the problem of usage allowances that can deter internet video streaming have a new way to make an end run around Net Neutrality, distributing their content “cap-free” through “virtual cable channels” that are distributed over broadband, but appear like traditional cable TV channels on a set-top box.
Video programmers that want to avoid the problem of usage allowances that can deter internet video streaming have a new way to make an end run around Net Neutrality, distributing their content “cap-free” through “virtual cable channels” that are distributed over broadband, but appear like traditional cable TV channels on a set-top box.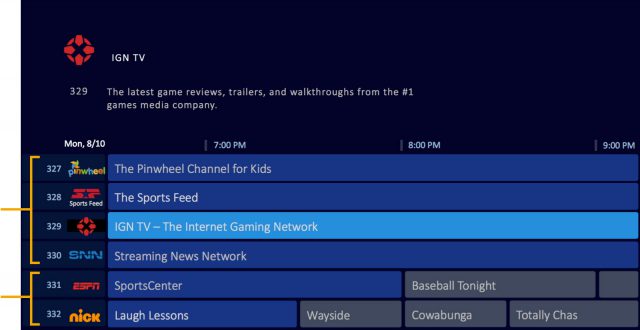
 Yet Wurl’s networks consume just as much bandwidth as traditional online video. But because Wurl is partnering with cable operators, that content is not subject to the usage caps Netflix, Hulu, or Amazon Video customers have to contend with.
Yet Wurl’s networks consume just as much bandwidth as traditional online video. But because Wurl is partnering with cable operators, that content is not subject to the usage caps Netflix, Hulu, or Amazon Video customers have to contend with. CenturyLink will begin a usage-based billing trial in Yakima, Wa., starting July 26 that will combine usage caps with an overlimit fee on customers that exceed their monthly usage allowance. The trial in Washington state may soon be a fact of life for most CenturyLink customers across the country, unless customers rebel.
CenturyLink will begin a usage-based billing trial in Yakima, Wa., starting July 26 that will combine usage caps with an overlimit fee on customers that exceed their monthly usage allowance. The trial in Washington state may soon be a fact of life for most CenturyLink customers across the country, unless customers rebel.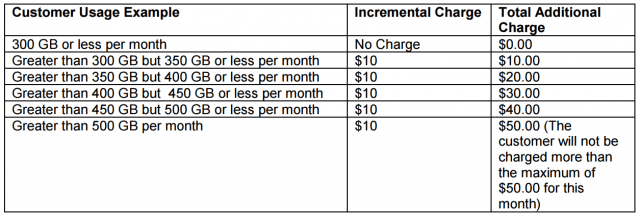

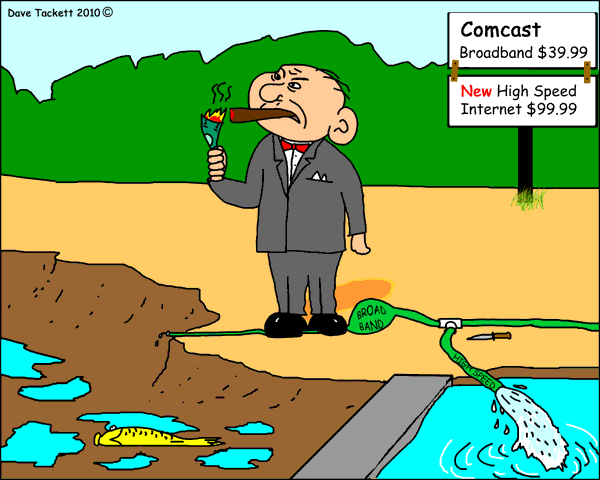 Comcast
Comcast  “Got the email this week we get to be part of this data cap ‘trial,'” shared another customer. “How lucky are we? And what do we get for being part of this trial? Absolutely nothing! And can we opt out of this trial? Heck no!”
“Got the email this week we get to be part of this data cap ‘trial,'” shared another customer. “How lucky are we? And what do we get for being part of this trial? Absolutely nothing! And can we opt out of this trial? Heck no!” The internet.
The internet. Believe it or not, there are organizations out there that track just how many of these pledges are actually kept during each administration, and surprisingly the track record is better than you might think. Politifact’s Obameter shows the Obama Administration
Believe it or not, there are organizations out there that track just how many of these pledges are actually kept during each administration, and surprisingly the track record is better than you might think. Politifact’s Obameter shows the Obama Administration 


