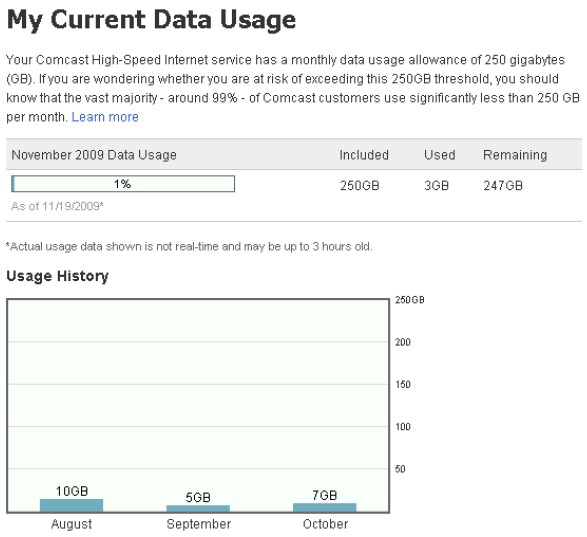
Comcast's new usage gauge is being tested in Oregon
Comcast’s long promised “usage gauge” has arrived. The company promised to provide one to customers more than a year ago when it imposed a 250GB monthly usage limit on its residential broadband accounts. Although generous in comparison to some other providers that limit customers to as little as 1-5GB of usage per month, Comcast’s allowance and the meter re-emphasizing it has created controversy among customers concerned about usage caps, potential overlimit fees or speed throttles.
Stop the Cap! reader “bones” sent along word of the measurement tool beta test in the Portland, Oregon area, and reviewing the accompanying data exposes some inconvenient facts such usage limits will have on customers.
Comcast’s version of the ‘gas gauge’ depicts usage on a bar graph and is updated monthly. Company officials claim the average user consumes just 2-4 gigabytes per month, a debatable figure. Comcast claims about 1% of their subscribers exceed 250GB of usage per month, but does not indicate whether that number has been on the increase as the company unveils new premium speed, premium priced broadband tiers.
Comcast hired NetForecast to “independently” verify the accuracy of the meter, which they claim produces results within 0.5% accuracy.
The company’s report concludes with praise for Comcast’s new meter, claiming it “will shine a new light on a previously unknown and misunderstood aspect of the digital age. NetForecast believes that this information will allow consumers to become better informed, and better informed consumers will help positively shape the Internet’s future.”
It also increases resentment towards a company that makes them check a meter to be sure they are within their “allowance” for the month, particularly when that company makes loads of money on broadband service.
NetForecast’s tests do reveal several new pieces of information to the “net meter” controversy:
- The company found up to 1GB of traffic per month represented “background traffic associated with modem management.” That’s a considerable amount of data counted against a customer’s usage, especially for customers stuck on lower consumption usage plans;
- The increasing complexity of some web pages and their underlying structure can contribute to additional traffic associated with “protocol overhead”;
- Poorer line quality can result in increased traffic due to retransmission requests;
- “Unexpected” traffic is so substantial, it warranted its own section in the NetForecast report:
Traffic can be generated by more than just PCs. Any device that has access to the wireless router is a potential Internet traffic generator—including smart phones, game consoles, digital video recorders, printers, cameras, etc. Many non-PC devices “phone home” to a manufacturer or supporting service. These automated connections are transparent to the user as a convenience so the user is unaware of the traffic generated.
The most likely source of unexpected traffic, however, is from software running on PCs throughout the home. The Windows operating system and most popular software have automated update programs. These updates often download and are installed automatically without the need for user intervention. The automation is generally designed for the convenience and protection of the consumer, but the traffic it generates may come as a surprise.
Each program update download may be modest in size, however, when you multiply a modest download by the number of programs calling for updates and the number of PCs in the house, the traffic attributable to updates can be substantial. Furthermore, in some cases the vendor default update settings are very aggressive, with some default settings checking each hour and downloading every possible option even though they are not all needed. For example, a software program may load its interface in a dozen languages even though all household members only know how to read English.
That’s just the beginning. The company also documented “surprise usage” from smartphones downloading updates, photo sharing sites, online backup, and other online applications. Perhaps most important are online video services:
A large volume of traffic may be going to digital video recorders such as TiVo. A user in the home may have rented a movie from Amazon, Netflix. Blockbuster, etc. Renting the movie will be a known traffic-generating event, however, many services also preload the start of other movies as well as trailers to make them instantly available should they be called for. As in other situations described above, traffic is consumed for the consumer’s convenience but without his or her knowledge.
If Comcast’s meter results showing your usage doesn’t make sense and you don’t believe or understand the numbers, wait until you read how it is your responsibility, as a customer, to do all the sleuthing.
NetForecast’s prescription for “rogue traffic” requires the customer to shut off their computers and other connected devices for a “digitally silent” period (overnight or on a weekend when traveling). Then, the customer gets to follow this routine:
At the end of the digital silence turn on one PC and log back into the Comcast meter portal, or you can check from an Internet cafe or other means while you are away. If true digital silence was achieved, the meter should not have incremented by more than 1GB. If there is more than 1GB use over even several days, then there is certainly some other traffic consumer connected through the router.
If the digital silence experiment worked, then carefully add devices back to the home network while watching the meter. Note that the meter only increments once per hour, so it may take some time to find a rogue traffic source. On the other hand, the home may simply be a highly connected place that is leveraging many aspects of the Internet, and the traffic may be entirely due to legitimate use.
“I guess those of us who are Comcast customers get to add this to our ‘list of things to do’ when we are trying to enjoy our broadband service,” writes Stop the Cap! reader Karen in Portland. “Can you imagine telling a customer whose wireless wi-fi was ‘borrowed’ by a neighbor that they have to do all this when half the time, those customers don’t even understand how to enable wi-fi security?”
Each and every byte gets counted. Almost.
Exempt from the usage meter are Comcast’s digital phone service and on-demand video services sent to your television. That’s a nice benefit for Comcast, but not so nice for their competitors, such as voice-over-IP telephone services and the aforementioned Netflix, Amazon, and other on-demand broadband video services. Programming sent to your computer over Comcast’s forthcoming TV Everywhere service does count against your allowance, however.
With a 250GB allowance, it may be some time before most customers find themselves routinely having to limit their usage to avoid exceeding it. But that assumes Comcast doesn’t follow some other providers into a limbo dance of lowered usage allowances. With a meter in place, it’s as simple as lowering the cap and telling the customer to check before they use.
What do Comcast customers think? Comcast’s blog amusingly illustrates some company employees love it, and most consumers hate it:
“Finally! This is great stuff, I cannot wait for this to roll out in our market. We’ve been waiting and customers have been asking for months. Keep up the good work out there, and let’s never stop being innovative. We ROCK!” — Ozzie Navarro, presumably the ‘we’ is this instance refers to an author employed by Comcast.
“How is it great that you’re capping a service I pay monthly for at great expense? Now I can see it in a meter, wow! Upgrade your damn infrastructure to support more bandwidth instead of cutting off customers.” — Jason
“Don’t think you are fooling people by saying, ‘Only x% of people use over 250gb/month, and 1-x% of people won’t have to worry.’ Would you outright deny that you are implementing this feature because you feel your TV industry is threatened by Netflix, Slingbox, Hulu.com, et al.? You say it is to provide all users with a better experience. You say that because some people are “hogging the internet”, grandma can’t look at photos of her grandchildren fast enough. Did it ever occur to you that more people are using more web-intensive programs everyday? It’s not like bandwidth is a finite resource. As much as you guys want to say it is, bandwidth is only limited by ISPs. You love to say that your “networks are overburdened.” Hate to point out the obvious, but you are the ones selling the service so you should plan accordingly for usage. You sell people an advertised rate of 10Mbps, knowing full well that unless everyone else in their neighborhood is offline, there isn’t a snowball’s chance in hell you’ll get these speeds.
Then you have the nerve to say because so many people are “abusing their privilege” you must implement a bandwidth cap to “maintain the integrity of our networks.” I pay $50/month just to access this wonderful series of tubes known as the internet. When I was sold this plan, I was told very specifically that it was UNLIMITED. That meant, if I maxed out my possible internet consumption everyday — no big deal — that’s what unlimited means. It’s becoming more and more obvious that this whole thing is a money grab, much like overdraft fees from our favorite financial institutions. I love how in the last comment you preach about rolling out your DOCSIS 3.0 system, which will supposedly let people have higher speeds. You don’t plan on upgrading the amount we can use per month though do you? That was suspiciously left absent from your article. Basically you are giving us the power use the internet in more innovative ways, but punishing us for trying to take advantage of your speeds. Thanks for giving me the ability to hit the upper limit more easily and quickly!” — Matt
“So a service whose advertising mentions NOTHING about data caps is actually capped, eh? That’s nice. It’s also really nice that you’re rolling out a faster product, so people can use up their allotted internet EVEN FASTER. Comcast doesn’t want people not paying for their ridiculously overpriced TV service, so they cripple their internet so you don’t have a choice. Really nice.” — Comcast customer


 Subscribe
Subscribe