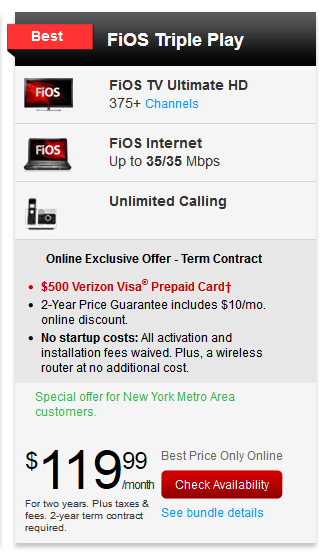
HissyFitWatch: Damn you FCC!
For the first time in a long time, AT&T did not get what it wanted from Washington regulators and legislators. The repercussions of the company’s failure to secure its controversial merger with Deutsche Telekom’s T-Mobile USA has been one HissyFit after another, including the resignation-retirement of Forrest Miller, a 30-year veteran who was the company’s head of corporate strategy and mergers and acquisitions. After heads rolled, there was the small matter of the multi-billion dollar “breakup fee” payable to T-Mobile. Now someone has to pay: You.
At Stop the Cap!, we scrutinize quarterly conference calls at major telecommunications companies so you don’t have to. We’ve sat through renditions of “we’re sorry” when Charter Communications’ executive management allowed the company to be flushed into bankruptcy, we’ve heard the Excuse-o-Matic from Frontier Communications about why their broadband service is woefully overloaded with promises of better days ahead, and a whole lot of creative spin to emphasize cord-cutting-bad-news at the nation’s largest cable companies isn’t really a problem all — it’s the housing market, it’s the ‘seasonal residences’ or ‘college students going home’ problem… or sunspots. Who really knows? It’s definitely not that they’re charging too much.
Whether it has been Time Warner Cable’s Glenn Britt, or Verizon’s Ivan Seidenberg, chief executives always project a cool, calm, steady authority that leaves shareholders and financial analysts with an impression the adults are in charge, even if they tell little white lies to keep the stock price up.
And then there is AT&T’s chief executive — Chairman Emperor Randolph Stephenson, who used the occasion of AT&T’s 4th Quarter earning results conference call to become a spectacle that brought the house down.
As we look ahead, the issue that gives me the most concern, quite frankly, isn’t our ability to execute. The #1 issue for us as we move forward, and for the industry, I believe, it continues to be spectrum. This industry continues to see just explosive mobile broadband growth and is providing one of the few bright spots in the U.S. economy, but I think we all understand this growth cannot continue without more spectrum being cleared and brought to market. And despite all the speeches from the FCC, we’re all still waiting.
He didn’t stop there. In an impromptu rant, Stephenson lectured Washington from afar, excoriating all-concerned for failing to agree with their multi-million dollar propaganda campaign that merging America’s second and fourth largest wireless carriers in a market with just four national providers was good for consumers and would bring wireless nirvana to the heartland and lower prices for all. Evidently America was not ready to accept the word of AT&T-compensated telecommunications experts at the NAACP, the Special Dream Farm, the Shreveport-Bossier Rescue Mission and cattle ranchers a combination of T-Mobile’s spectrum and AT&T’s would ease the capacity crunch, bring 4G to Beaver, Oklahoma, and stop driving AT&T customers nuts with dropped calls and reception black holes.

How it usually works in Washington.
AT&T would have gotten away with their merger if it weren’t for those darned kids (consumers), the FCC and Justice Department ruining everything.
“The last significant spectrum auction was nearly 5 years ago now. And this FCC has made it abundantly clear that they’ll not allow significant [mergers and acquisitions] to help bridge their delays in freeing up new spectrum,” Stephenson complained. “So in the absence of auctions, our company and others in the industry have taken the logical step of entering into smaller transactions to acquire the spectrum we need to meet this demand. But even here, we need the FCC’s action and leadership, and unfortunately, even the smallest and most routine spectrum deals are receiving intense scrutiny from this FCC, oftentimes taking up to a year and sometimes longer before these are approved.”
Stephenson ignores the fact the FCC has rubber-stamped a number of wireless mergers over the past several years, which is why consumers no longer buy competitive service from Cingular, Alltel, Dobson Communications, Centennial Wireless, West Virginia Wireless, Unicel, Ramcell, or SureWest Wireless. All of these former competitors are now a part of the nation’s two largest carriers AT&T and Verizon Wireless. Even more impressively for the man in full denial, the FCC just quickly and quietly approved AT&T’s spectrum transfer purchase from Qualcomm.
“Now I hope I’m wrong, but it appears the FCC is intent on picking winners and losers rather than letting these markets work,” the chief executive said.
In other words, AT&T’s definition of letting markets “work” means letting them write their own laws governing the pesky concepts of antitrust, monopoly/duopoly market power, anti-competitive activity, etc. AT&T has no problem picking winners and losers in the community-owned broadband front, lobbying its way through state legislatures trying to block new networks from being built, even while slapping usage limits on their own customers’ DSL and U-verse accounts because of “capacity” concerns.
In the wireless marketplace, Charlie Sheen would declare AT&T “winning,” considering it has achieved 1/3rd of the U.S. wireless market. It wants more of course, even though Trefis, a market research firm, noted that had the FCC granted Stephenson’s wishes for three national carriers, AT&T, Verizon Wireless and Sprint “will control more than 90% of the U.S. wireless market, resulting in lower competition and higher prices for consumers.”
No problem there.
Stephenson also noted a lot of the company’s close friends were on their side (and handsomely compensated along the way we might add):
A lot of recent comments and speeches about certain members of this FCC suggest that they and not Congress should decide how spectrum auctions are conducted, including who can participate and what the conditions should be for participating. Meanwhile, we pile more and more regulatory uncertainty on top of an industry that is a foundation for a lot of today’s innovation*, making it difficult for all of us to allocate and commit capital. And in this industry, we all know capital investment equals jobs*. So the end result of this is we have a industry that is just really stuck in terms of creating real capacity*.
(*- except when community-based, publicly-owned networks are involved. They must be stopped at all costs.)
No matter that AT&T continues to sit on earlier spectrum acquisitions it continues not to use. It only grudgingly agreed to roaming agreements with the company it preferred to dismantle altogether: T-Mobile. In earlier, accidental disclosures, it was clear even before the merger and the newly-reticent FCC, AT&T preferred to raise prices, restrict service, and hang onto its profits instead of sufficiently investing them back into its network. Verizon Wireless has a 4G network, no dropped-call-syndrome, fewer signal black holes, and no apparent spectrum panic attacks.

Part of Sprint's fact sheet opposing the merger deal.
AT&T bit off more than they could chew through, and now faces the humiliating prospect of paying off its gambling debts. Only now, AT&T has effectively declared they are not going to pay for their costly mistake. Customers are.

Stephenson: Payback time.
The company introduced new, higher prices for its smartphone data plans this month, and intends to continue to increase prices and crack down on data use with speed throttles in 2012 and blame it on the “spectrum crunch”:
“In a capacity-constrained environment, usage-based data plans, increased pricing, managing the speeds of the highest volume users, these are all logical and necessary steps to manage utilization,” Stephenson said.
But AT&T’s chief executive also told shareholders repeatedly those increased prices were key to boosting company revenue and profits:
“We’ll expand wireless and consolidated margins. We’ll achieve mid-single-digit EPS growth or better. Cash generation continues to look very strong again next year. And given the operational momentum we have in the business, all of this appears very achievable and probably at the conservative end of our expectations.”
AT&T’s chief financial officer John J. Stephens put a spotlight on it:
In 2011, 76% of our revenues came from wireless and wireline data and managed services. That’s up from 68% or more than $10 billion from just 2 years ago. And revenues from these areas grew about $7 billion last year or more than 7% for 2011. We’re confident this mix shift will continue. In fact, in 2012 we expect consolidated revenues to continue to grow, thanks to strength in these growth drivers with little expected lift from the economy.
[…] We also continue to bring more subscribers onto our network with tiered data plans, more than 22 million at the end of the quarter, with most choosing the higher-priced plan. As more of our base moves to tiered plans and as data use increases, we expect our compelling [average revenue per subscriber] growth story to continue.
 Perhaps the most the world ever hears about the tiny British island of St. Helena, a home in the South Atlantic for 4,000 residents, is the annual St. Helena Radio Day when the nation takes to the shortwave radio dial to say hello to friends on every continent.
Perhaps the most the world ever hears about the tiny British island of St. Helena, a home in the South Atlantic for 4,000 residents, is the annual St. Helena Radio Day when the nation takes to the shortwave radio dial to say hello to friends on every continent.

 Subscribe
Subscribe