With the average speed of DSL service under 10 Mbps in rural counties across the United States, this legacy technology is disenfranchising a growing number of rural Americans and is largely responsible for dragging down overall U.S. internet speed scores. Only satellite internet offers overall lower speed and poor customer satisfaction, according to consumer surveys.
With the average speed of DSL service under 10 Mbps in rural counties across the United States, this legacy technology is disenfranchising a growing number of rural Americans and is largely responsible for dragging down overall U.S. internet speed scores. Only satellite internet offers overall lower speed and poor customer satisfaction, according to consumer surveys.
In some areas, customers cannot even get bad DSL service, despite the fact the Federal Communications Commission marks many of those addresses as well-served. According to a new report by the company Broadband Now, the FCC could be claiming at least 20 million Americans have access to robust internet service that, in fact, does not exist, especially in rural counties.
Citylab:
To get its estimate, the Broadband Now team manually ran 11,663 randomly selected addresses through the “check availability” tool of nine large internet service providers that claim to serve those areas. All in all, the team analyzed 20,000 provider-address combinations. A fifth of them indicated that no service was available, suggesting to the researchers that companies may be overstating their availability by 20%, said John Busby, the managing director of Broadband Now. The results also show that 13% of the addresses served by multiple providers didn’t actually have available service through any of them. They then applied these rates across the country to get their final estimate of 42 million people without broadband.
The disparity between their estimate and the FCC’s largely comes from the agency’s reliance on Form 477 reports, in which internet providers self-report the locations they serve. Providers can claim to serve the population of an entire census block if service is provided to just one household in that block. After the release of FCC’s May report, the agency’s Democratic commissioners dismissed the report, berating their colleagues for “blindly accepting incorrect data” and using the numbers to “clap its hands and pronounce our broadband job done.”
Across DSL-heavy rural Ohio, weary residents have nothing to clap about as they desperately look for something better than slow speed DSL from the local phone company.
“It’s a good day when Frontier DSL breaks 2 Mbps, although they advertise (and we pay for) 10 Mbps,” said Fred Phelps, a Frontier DSL customer for more than a decade. “In rural Ohio, it is take it or leave it internet access and we have no choice other than Frontier.”
Phelps has longed for Charter Spectrum to wire his area, next to a large farm operation, but the nearest Spectrum-connected home is a half-mile down the road. Phelps was lucky to get DSL at all. That aforementioned farm paid Frontier a handsome sum to extend its commercial DSL service to the farm’s office, putting Phelps in range for a residential DSL connection.
“It is always slow and frequently goes offline on rainy and snowy days because water is getting into the phone cable somewhere,” Phelps told Stop the Cap! “Service calls are a waste of time because the problem always disappears by the time the repair crew shows up.”
Cindy B (last name withheld at request) is in a similar situation in Ohio. She has a CenturyLink DSL line that averages 1 Mbps, although some of her relatives have managed to get almost 12 Mbps from CenturyLink closer to town.
Warren County, Ky.
“CenturyLink treats you like they are doing you a favor even offering DSL service in this part of Ohio. There is no cable TV service for at least 20 miles, so cable internet is out of the question,” Cindy tells us. “They have also made it crystal clear there are no plans to upgrade service in our area.”
She used to be a Viasat satellite internet customer but quickly canceled service.
“Satellite internet should be considered torture and banned as illegal,” Cindy said. “You can spend five minutes just trying to open an email, and the only time we could download a file was overnight, but even that failed all the time.”
Cindy and Fred are collateral damage of the country’s broadband dilemma. They are stuck with DSL, a service that often wildly over-claims advertised speed that it actually cannot deliver in rural areas. In much of rural Ohio, DSL speeds are usually under 6 Mbps, although companies often claim much faster speed on reports sent to the FCC.
“According to the FCC website, we should be getting 24 Mbps internet from Frontier and two other companies, but that simply does not exist,” said Phelps. “I really don’t understand how the FCC can rely on its own database for broadband speed that is not available and never has been.”
Cindy said her children cannot depend on their DSL line and have to do their homework at school or in the library, where a more dependable Wi-Fi connection exists.
“The problem is getting worse because websites are becoming more elaborate and are designed for people who have real internet connections, so often they won’t even load for us,” she said.
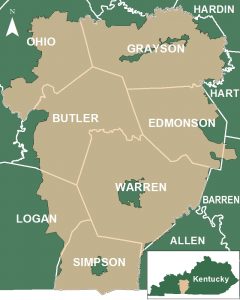
Warren Rural Electric Co-Op’s service area.
But according to the FCC, neither Cindy nor Fred live in a broadband-deprived area. For this reason, public funding to improve internet access is hard to come by because the FCC deems both areas well-served.
South of Ohio, in Warren County, Ky., a local rural electric co-op is not waiting for the State of Kentucky or the federal government to fix inaccurate data about broadband service in the rural exurbs around Bowling Green, usually stuck with slow DSL or no internet access at all. Warren Rural Electric Cooperative and Lafayette, Tenn.-based North Central Telephone Co-Op are working together to lay fiber optic cables to bring fiber to the home internet service to some broadband-deprived communities in the county. Warren RECC serves eight counties in south central Kentucky with over 5,700 miles of electric transmission and distribution lines, mostly in rural parts of the state. Two communities chosen for service as part of a pilot project — Boyce and September Lakes, are more than a little excited to get connected.
The Bowling Green Daily News reports that an informational meeting held in early February drew 300 residents (out of nearly 800) ready to hear more information about the project. Almost 150 signed up for future fiber service on the spot. Many more have subsequently signed up online. The new service will charge $64.95/mo for 100 Mbps service or $94.95 for 1,000 Mbps service. That is about $5 less than what Charter Spectrum charges city folks and is many times faster than what most phone companies are offering in rural Kentucky.
![]() Spectrum Mobile customers enrolled in an unlimited data plan will get free access to Verizon’s millimeter wave 5G network, if they own a device that supports 5G service.
Spectrum Mobile customers enrolled in an unlimited data plan will get free access to Verizon’s millimeter wave 5G network, if they own a device that supports 5G service.


 Subscribe
Subscribe With the average speed of DSL service under 10 Mbps in rural counties across the United States, this legacy technology is disenfranchising a growing number of rural Americans and is largely responsible for dragging down overall U.S. internet speed scores. Only satellite internet offers overall lower speed and poor customer satisfaction, according to consumer surveys.
With the average speed of DSL service under 10 Mbps in rural counties across the United States, this legacy technology is disenfranchising a growing number of rural Americans and is largely responsible for dragging down overall U.S. internet speed scores. Only satellite internet offers overall lower speed and poor customer satisfaction, according to consumer surveys.

 Rose said she contacted at least five Mediacom employees, including a supervisor, and none were apparently familiar with this policy.
Rose said she contacted at least five Mediacom employees, including a supervisor, and none were apparently familiar with this policy. AT&T has created a streaming television bundle that cable and satellite subscribers can appreciate. Replicating the kind of promotions familiar to DirecTV subscribers, AT&T debuted its new streaming TV service nationwide this morning with three promotionally priced packages that start at a relatively low price and end with a very high one.
AT&T has created a streaming television bundle that cable and satellite subscribers can appreciate. Replicating the kind of promotions familiar to DirecTV subscribers, AT&T debuted its new streaming TV service nationwide this morning with three promotionally priced packages that start at a relatively low price and end with a very high one.
 The Federal Communications Commission will seek hundreds of millions of dollars in fines from America’s four largest wireless companies after company officials apparently lied to Congress and regulators about ending the lucrative sale of customer locations to third parties in early 2019.
The Federal Communications Commission will seek hundreds of millions of dollars in fines from America’s four largest wireless companies after company officials apparently lied to Congress and regulators about ending the lucrative sale of customer locations to third parties in early 2019.