 The days of the wireless phone subsidy are numbered with today’s announcement Verizon Wireless will end all smartphone subsidies and service contracts next week. It’s a path we’ve predicted at Stop the Cap! since at least 2013.
The days of the wireless phone subsidy are numbered with today’s announcement Verizon Wireless will end all smartphone subsidies and service contracts next week. It’s a path we’ve predicted at Stop the Cap! since at least 2013.
In an effort to “simplify” wireless pricing, Verizon Wireless is radically shaking up its wireless plans starting Aug. 13 — raising prices for its lightest users, ending the two-year phone contract, and requiring customers buy or finance their devices at the full retail price. Instead, customers will pay $650 up front for a phone like Apple’s iPhone 6, or finance it for around $27 a month for the next two years.
Phone plans are changing as well. Eliminated are “individual” and “family plans.” In their place, there is just one plan with four data options:
- Access Fee (includes unlimited voice/text): $20/mo per phone, $10/mo per tablet or portable hotspot, $5 for connected devices (eg. watches)
- Shareable Data Option: $30 (Small – 1GB), $45 (Medium – 3GB), $60 (Large – 6GB), or $80 (X-Large – 12GB) — Overlimit Fee is $15/GB
Average and heavier users will save a few dollars with Verizon’s new plans. The “Medium” plan is $5 less than Verizon used to charge and the “Large” plan is $10 less. You get 2GB of extra data for your $80 comparing Verizon’s older plan and its newer one. The benefits seem less compelling when you realize just a few years ago Verizon charged $30 for unlimited use data plans.
Budget customers will find Verizon’s new plans the least attractive. Customers with 6GB or less data plans used to pay a $15 access fee. Now they will pay $5 more per phone. Those who want Verizon’s cheapest 500MB plan for $20 are out of luck. That plan is being dropped, according to Verizon, because customers were confused over the difference between MB and GB. Customers now on that low-end plan will probably be able to keep it, but may eventually have to choose a “Small” data plan for $10 more per month. Budget customers used to pay around $35 a month. Now they will pay at least $50.
Heavy data users may be concerned Verizon’s top data plan tops out at 12GB. The company plans to privately offer bigger data buckets to customers, but only if they visit a Verizon Wireless store to discuss their needs.
Current customers still on contract will not see any changes immediately. Verizon will continue to charge the $40 a month access fee for contract customers until the contract expires, after which the fee will drop to $20. Customers on More Everything plans can stick with their existing plans for now, as well as add lines. There are no plans to force customers to change service plans at this point.
Expect AT&T to take a similar path towards the elimination of subsidized devices. Because customers will likely finance their $600+ smartphones, it isn’t likely consumers will face dramatically changed pricing as a result of Verizon’s plan changes. But device manufacturers can no longer get away with promoting their phones at a $200 price point. In fact, the sticker shock of the retail price of smartphones may eventually force manufacturers to produce more affordable phones for the marketplace.


 Subscribe
Subscribe “Must-have” ESPN is not as must-have as the pay television business once believed as the costly basic cable network reported more subscriber losses as consumers cut the cord.
“Must-have” ESPN is not as must-have as the pay television business once believed as the costly basic cable network reported more subscriber losses as consumers cut the cord.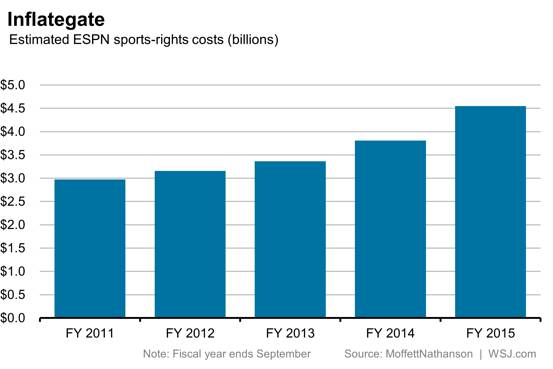
 The network has been a safe bet for investors for years, at least until this week when the company lowered its expectations for cable operating income growth from 2013-2016. Instead of growth between 7-9 percent, ESPN is now predicting only 4-6 percent. Although some might see that as a modest adjustment, Wall Street didn’t think so and Disney shares tanked 8.4% Wednesday. That was nothing compared to
The network has been a safe bet for investors for years, at least until this week when the company lowered its expectations for cable operating income growth from 2013-2016. Instead of growth between 7-9 percent, ESPN is now predicting only 4-6 percent. Although some might see that as a modest adjustment, Wall Street didn’t think so and Disney shares tanked 8.4% Wednesday. That was nothing compared to 

 Among those that do, Comcast’s Xfinity takes first prize:
Among those that do, Comcast’s Xfinity takes first prize:
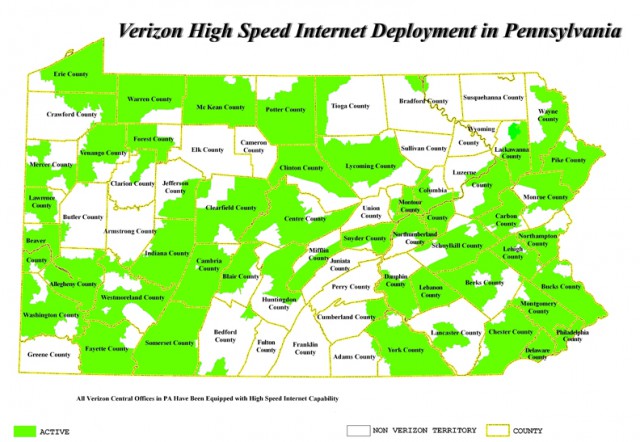
 After
After 
