 Comcast is accelerating its rollout of compulsory usage caps, adding new markets in the southern U.S. to its three-year old “trial” of what it calls its “data usage plan.” DSL Reports received a tip Comcast is now sending e-mail to affected customers.
Comcast is accelerating its rollout of compulsory usage caps, adding new markets in the southern U.S. to its three-year old “trial” of what it calls its “data usage plan.” DSL Reports received a tip Comcast is now sending e-mail to affected customers.
Little Rock, Ark., Houma, LaPlace, and Shreveport, La., as well as Galax, Va., will be treated to Comcast’s 300GB usage cap with a $10 per 50GB overlimit fee beginning Dec. 1. These three states join Florida, Alabama, Kentucky, Georgia, Maine, Mississippi, South Carolina and Arizona, which now face Comcast’s form of usage rationing.
In Tennessee, Comcast is introducing its 300GB cap in Johnson City, Gray, and Greenville. The cable operator is also risking customers by introducing caps in Chattanooga, where it already faces serious competition from gigabit provider EPB, which has no usage limits, and AT&T U-verse, which doesn’t dare enforce its own 250GB cap.
Comcast began rapidly expanding its usage cap trial this fall, with new markets being announced for usage limits about once a month.
Chattanooga resident Ron Rogers called to cancel his Comcast service this afternoon. He’s giving up a good promotional discount Comcast offered to keep him a customer back in January and is headed to EPB Fiber.
“This was the last straw for Comcast,” Rogers tells Stop the Cap! “I am tired of being abused by these people. They must be crazy to think anyone who seriously uses the Internet is going to tolerate this when there are two other providers smart enough to realize usage caps are ridiculous in this day and age. Comcast can shove it.”
 Comcast’s spreading usage caps are not popular with customers. Within hours of the news Comcast would be expanding its cap “trial,” more than 900 negative comments appeared on Reddit slamming the company.
Comcast’s spreading usage caps are not popular with customers. Within hours of the news Comcast would be expanding its cap “trial,” more than 900 negative comments appeared on Reddit slamming the company.
“It is just staggering that despite all the bad press, publicity and truly awful service, Comcast is actually taking calculated measures to make things worse,” wrote one Reddit commenter.
Comcast’s frequent defense of its usage plan is that the majority of its customers will never be affected by it, consuming less than 40GB a month. But those with experience living under Comcast’s cap tell Stop the Cap! anyone playing downloadable video games or using online video are at serious risk of being charged penalty overlimit fees.
“It is very easy to hit 100GB just downloading game updates and if you watch your shows online, you will come uncomfortably close to the cap,” said Pat Kershaw in Kentucky. “Leaving a live video stream running overnight one night by mistake after I fell asleep meant a Netflix-free weekend for me last month, because it would have put me past my allowance. Hulu’s autoplay feature is also very dangerous.”
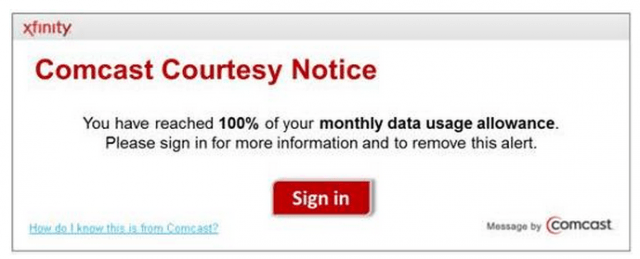 Hans says any household with kids will quickly learn Comcast isn’t being honest claiming usage caps only affect a “few customers” after they start getting warning messages injected into their web browser.
Hans says any household with kids will quickly learn Comcast isn’t being honest claiming usage caps only affect a “few customers” after they start getting warning messages injected into their web browser.
“What is worse is every time I call support about the messages that I am getting on the 18th of the month because I have already burned through my limit with my kids watching all their online content, support keeps putting me back on the queue for the next person or dropping the line,” Hans writes. “No one wants to deal with it!”
Those web warning messages also become intrusive for many customers, because some claim they never go away until the end of the billing cycle.
“I made sure to go over the 300GB cap this month to see what would happen and I received a phone call telling me I’ve went over and now I receive a popup from Comcast on my computer about every 30 seconds telling me I’ve went over as well,” writes Gldoorii. “The popups never stop. I have to deal with them until the end of the month as they keep interrupting my work.”
Other Comcast customers have grown suspicious about the company’s usage measurement tool, which in some cases reported spikes in usage only after the cap began to be enforced.
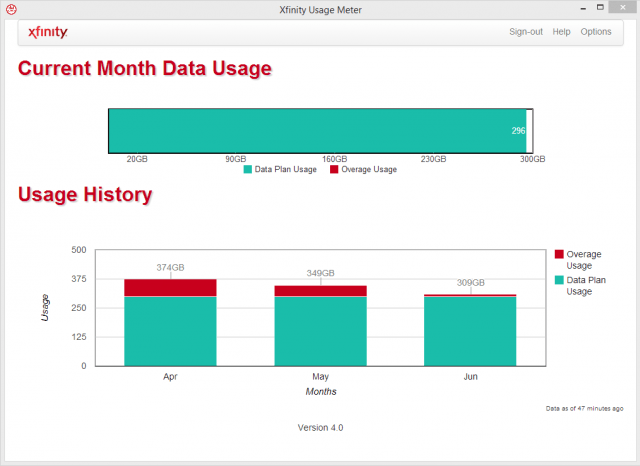 “I checked my data usage on Oct. 21 and it said I only used 162GB,” writes Sharon. “I even have [a screenshot] and saved it as I had a feeling Comcast would pull something. [On] Oct. 23, I had a pop-up on my computer that says ‘you have used 292 of 300GB’ and I went to the data usage and it shows that. Nobody in my house downloaded any huge files the past two days. So, is Comcast artificially pumping up our usage to make us go over or what? It is impossible that I only used 162GB for 21 days and then used 130GB the past two days.”
“I checked my data usage on Oct. 21 and it said I only used 162GB,” writes Sharon. “I even have [a screenshot] and saved it as I had a feeling Comcast would pull something. [On] Oct. 23, I had a pop-up on my computer that says ‘you have used 292 of 300GB’ and I went to the data usage and it shows that. Nobody in my house downloaded any huge files the past two days. So, is Comcast artificially pumping up our usage to make us go over or what? It is impossible that I only used 162GB for 21 days and then used 130GB the past two days.”
Sharon is lucky her usage meter is working. Other customers report Comcast’s meter often stops working for weeks.
“My data usage meter still does not work and it has been 19 days,” says Gldoorii. “No chat or support person has been able to figure out why it doesn’t work and that I need to call or chat whenever I want to ask what my usage is.”
Customers who want out also get the Comcast treatment as they head for the exit.
“We were charged a $150 early termination fee because Comcast does not consider imposing a usage cap to be a material change to our contract, which is unbelievable,” writes Anna Lu in Ft. Lauderdale. “These guys are nothing less than crooks and they only forgave it after my roommate complained to the Better Business Bureau. They said they were doing us a favor forgiving the charge. No wonder everyone hates Comcast.”
But not everyone is unhappy about Comcast’s usage caps.
“Our call center volumes are way up ever since Comcast brought caps to Atlanta and Florida,” reports an AT&T sales representative who agreed to talk to Stop the Cap! if we kept his identity private. “It’s common knowledge we do not enforce any caps on U-verse although we cannot tell customers that officially, but most never even ask. We’re signing up ex-Comcast customers right and left. They are not happy we cannot give them the same speeds Comcast does, but they won’t have to worry about a cap from us, at least for now.”
Other customers are waiting impatiently for Google Fiber or other competitors.
“In Atlanta Comcast now offers an unlimited data option add on to your plan for additional $35,” writes a customer on Comcast’s support forum. “So now we get to pay over $100 for 25Mbps service whereas Google Fiber [in] Atlanta [charges] $70 for one gigabit service and no data cap.”
In July, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts downplayed the impact of the company’s usage caps with investors, suggesting some customers actually supported the usage plans.
“We do have a few trials going on in different markets,” Roberts said. “The responses have been neutral to slightly positive. We don’t have any plans on expanding that to other market/bases anytime soon.”
 If you make a voice or video call over Rogers’ wireless network using Skype, you will chew into your monthly data plan. If you make the same phone call over Rogers’ Voice over LTE network, your data allowance is safe.
If you make a voice or video call over Rogers’ wireless network using Skype, you will chew into your monthly data plan. If you make the same phone call over Rogers’ Voice over LTE network, your data allowance is safe. That could suggest a potential Net Neutrality violation for one of Canada’s largest cellular providers because Section 27 (2) of the Telecommunications Act makes it clear unjust discrimination is illegal:
That could suggest a potential Net Neutrality violation for one of Canada’s largest cellular providers because Section 27 (2) of the Telecommunications Act makes it clear unjust discrimination is illegal:

 Subscribe
Subscribe An expert hired by Charter Communications to offer “qualified” views on the competitive impact of a merger involving Charter, Bright House Networks, and Time Warner Cable got his facts wrong about Charter’s data cap policy, a mistake that calls into question his analysis about the company’s potential to abuse broadband customers by imposing data caps after its three-year commitment not to expires.
An expert hired by Charter Communications to offer “qualified” views on the competitive impact of a merger involving Charter, Bright House Networks, and Time Warner Cable got his facts wrong about Charter’s data cap policy, a mistake that calls into question his analysis about the company’s potential to abuse broadband customers by imposing data caps after its three-year commitment not to expires. But his facts are in error. The same company that believed usage caps were an essential part of its broadband service between
But his facts are in error. The same company that believed usage caps were an essential part of its broadband service between 
 Since Malone sold TCI, the multi-billionaire has built a significant cable empire in Europe and is today the largest private landowner in the United States. In the U.S., he is best known as the current owner of SiriusXM satellite radio. The two satellite companies merged with an agreement not to raise rates for a few years. As soon as that agreement expired, Malone’s combined Sirius/XM operation began a series of rate hikes and maintain a satellite radio monopoly in the U.S.
Since Malone sold TCI, the multi-billionaire has built a significant cable empire in Europe and is today the largest private landowner in the United States. In the U.S., he is best known as the current owner of SiriusXM satellite radio. The two satellite companies merged with an agreement not to raise rates for a few years. As soon as that agreement expired, Malone’s combined Sirius/XM operation began a series of rate hikes and maintain a satellite radio monopoly in the U.S. Comcast is accelerating its rollout of compulsory usage caps, adding new markets in the southern U.S. to its three-year old “trial” of what it calls its “data usage plan.” DSL Reports
Comcast is accelerating its rollout of compulsory usage caps, adding new markets in the southern U.S. to its three-year old “trial” of what it calls its “data usage plan.” DSL Reports  Comcast’s spreading usage caps are not popular with customers. Within hours of the news Comcast would be expanding its cap “trial,”
Comcast’s spreading usage caps are not popular with customers. Within hours of the news Comcast would be expanding its cap “trial,”  Hans says any household with kids will quickly learn Comcast isn’t being honest claiming usage caps only affect a “few customers” after they start getting warning messages injected into their web browser.
Hans says any household with kids will quickly learn Comcast isn’t being honest claiming usage caps only affect a “few customers” after they start getting warning messages injected into their web browser. “I checked my data usage on Oct. 21 and it said I only used 162GB,” writes Sharon. “I even have [a screenshot] and saved it as I had a feeling Comcast would pull something. [On] Oct. 23, I had a pop-up on my computer that says ‘you have used 292 of 300GB’ and I went to the data usage and it shows that. Nobody in my house downloaded any huge files the past two days. So, is Comcast artificially pumping up our usage to make us go over or what? It is impossible that I only used 162GB for 21 days and then used 130GB the past two days.”
“I checked my data usage on Oct. 21 and it said I only used 162GB,” writes Sharon. “I even have [a screenshot] and saved it as I had a feeling Comcast would pull something. [On] Oct. 23, I had a pop-up on my computer that says ‘you have used 292 of 300GB’ and I went to the data usage and it shows that. Nobody in my house downloaded any huge files the past two days. So, is Comcast artificially pumping up our usage to make us go over or what? It is impossible that I only used 162GB for 21 days and then used 130GB the past two days.” Frontier Communications continues to face challenges keeping customers in its legacy copper wire service areas, where only modest investments in network upgrades have proved insufficient to stop customers shopping around for better service.
Frontier Communications continues to face challenges keeping customers in its legacy copper wire service areas, where only modest investments in network upgrades have proved insufficient to stop customers shopping around for better service.