 A company is testing a solution to video subscription password abuse that will register each device authorized to access streaming video, while giving customers a Forever Login, ending the need to regularly re-enter usernames and passwords to watch.
A company is testing a solution to video subscription password abuse that will register each device authorized to access streaming video, while giving customers a Forever Login, ending the need to regularly re-enter usernames and passwords to watch.
Synacor is responding to growing concerns from some in the cable industry that subscription television password sharing is allowing unauthorized access to content viewers did not pay to view. The new system is an attempt to upgrade the authenticated TV Everywhere experience to reduce subscriber inconvenience while locking down the number of concurrent devices allowed to view online content.
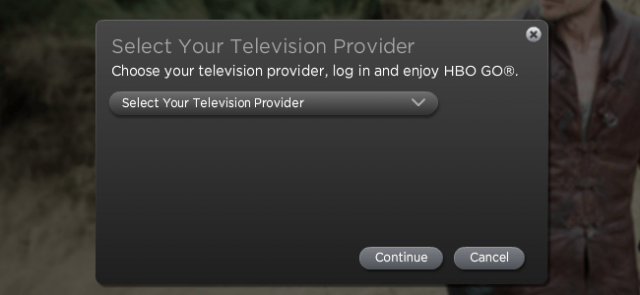
Currently, when a customer accesses subscription-required content online, they are asked to select their TV provider and then enter their assigned username and password to verify they are a current subscriber to a video package that includes that network. Once authenticated, the network’s website controls how long user credentials are kept before they must be re-entered, as well as how many concurrent viewing sessions from multiple family members are permitted.
TV Everywhere services were originally designed to allow the subscriber and anyone else living within the home to be able to access networks like CNN, HBO, ESPN, and others on portable devices in-home and while on the go. But many customers also share their user credentials with extended family members and friends who do not live at the same address. Unauthorized third parties also occasionally obtain user credentials through brute force hacking and sell them on the black market. The subscriber usually only discovers a security problem with their account when they reach the concurrent viewing limit, which displays as an on-screen message stating the maximum number of viewers are already watching content through a subscription and at least one must disconnect before a new stream can be viewed.
Cable company executives hold a variety of opinions about the seriousness of password sharing. Altice and Comcast, and programmers like Time Warner, Inc., which owns HBO and Cinemax, have not shown much concern about the practice, but Charter/Spectrum executives have, and are leading the charge to lock down subscriber authentication.
Synacor’s new system introduces a new layer of cable company-defined limits on streaming: registering each device allowed to view content as well as checking how many people are attempting to stream content simultaneously.
 Under the new system, a customer will be permitted to register a limited number of “trusted devices” allowed access to streamed video content. A cable company, for example, could limit subscribers to two smartphones, one tablet, and one smart/internet-enabled TV or Roku box. Even if the subscriber has other devices, they would have to unregister an existing device before being allowed to register a new one. Additionally, a cable operator could limit concurrent streams to two or three, either per network or per account, regardless of what networks are being watched. That would mean, in one example, a family of four would designate a maximum of five “trusted devices” and be allowed to watch up to three concurrent streams per account. “Bill” could watch ESPN on the bedroom television, “Mary” could watch a murder-mystery on the Hallmark Channel on her tablet on the patio, and “Dylan” could watch a movie on HBO on his phone at the same time. But if “Sara” decided to watch a show on Lifetime on her phone, the system would block the request.
Under the new system, a customer will be permitted to register a limited number of “trusted devices” allowed access to streamed video content. A cable company, for example, could limit subscribers to two smartphones, one tablet, and one smart/internet-enabled TV or Roku box. Even if the subscriber has other devices, they would have to unregister an existing device before being allowed to register a new one. Additionally, a cable operator could limit concurrent streams to two or three, either per network or per account, regardless of what networks are being watched. That would mean, in one example, a family of four would designate a maximum of five “trusted devices” and be allowed to watch up to three concurrent streams per account. “Bill” could watch ESPN on the bedroom television, “Mary” could watch a murder-mystery on the Hallmark Channel on her tablet on the patio, and “Dylan” could watch a movie on HBO on his phone at the same time. But if “Sara” decided to watch a show on Lifetime on her phone, the system would block the request.
In the past, it was likely all four family members could watch concurrent streams of their shows on virtually any device they like, and they could also share login credentials with “Jeff” — a family member at college, who in turn shared his username and password with the other people living in his dorm room — exactly the kind of thing Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge would like to stop.
Synacor claims its new system is still a positive for consumers because it allows user credentials to be stored in perpetuity, ending the need for frequent logins to re-verify and re-authenticate one’s account, regardless of where they are. Synacor’s executive director of identity services, John Kavanagh, suggests it is a win-win for companies and consumers.
“They wanted to deliver the same user experience benefit…and we brought the trust along with it with device registration,” Kavanagh said. “The end-user experience of home-based authentication really set a high bar. They wanted to take that high bar and extend it elsewhere.”
 But many subscribers, especially those with larger families, are likely to balk at the new restrictions, especially if cable operators offer to ease them in return for additional fees. The process of registering devices is also likely to be seen as cumbersome by those not technically proficient, as well as those who own a large assortment of electronic devices.
But many subscribers, especially those with larger families, are likely to balk at the new restrictions, especially if cable operators offer to ease them in return for additional fees. The process of registering devices is also likely to be seen as cumbersome by those not technically proficient, as well as those who own a large assortment of electronic devices.
Multichannel News reports a recent study from Hub Research and CTAM that monitors the TV Everywhere market surveyed 3,491 TV subscribers who watch at least five hours of television a week and discovered 28% claimed that password sharing with friends and family members was okay and permitted by their provider, although generally it is not. Another 33% believed password sharing was allowed for family members who have since moved out of the family home and live elsewhere. No provider authorizes such viewing.
The cable industry generally does not mind password sharing for family members who are traveling or attending school and live outside of the home in a dorm, or watching on a device that belongs to a friend. They do mind if that friend keeps the user credentials and watches programming without their own subscription.
Kavanagh claims the biggest concern is “commercial-level” black market sales of user credentials to third parties who have no relationship to the account owner.
“Once we’re able to register that device securely as part of the sign-in flow, we then connect that with a complete list of devices that have been used with a given subscription,” Kavanagh said. “We not only expose that master list to the end user for their own benefit on things that might be suspicious, but on the operator side, it gives them a depth of awareness they haven’t had before. It allows them to have a fine instrument to enforce their business rules and security policies.”
Both customers and cable operators can see who is currently accessing content using their account and cancel authorization for device(s) they no longer own, lost, or are being used by those who do not have an association with the account holder at all.
The new system is being introduced on an experimental basis to some current customers, starting with Service Electric Cablevision. It is likely similar rollouts will happen with Synacor’s other clients, which include:
- Streaming Services: Sling TV, PlayStation Vue, HBO
- Telco TV: AT&T, Cincinnati Bell, Verizon, Windstream, CenturyLink
- Fiber/Cable TV: WOW!, Armstrong Cable, Atlantic Broadband, Cable One, Mediacom, GCI, Hotwire Communications, Charter/Spectrum, Grande Communications


 Subscribe
Subscribe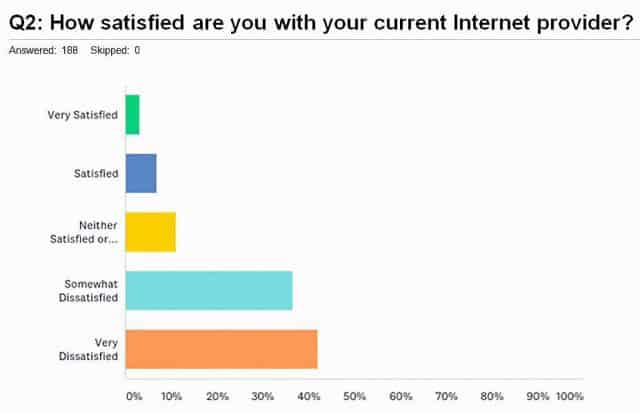
 Frontier representatives responded to the survey results at a March 27 Elko City Council meeting.
Frontier representatives responded to the survey results at a March 27 Elko City Council meeting. Frontier also noted internet traffic was up 25% in the Elko area, primarily as a result of video streaming, social media, and cloud services.
Frontier also noted internet traffic was up 25% in the Elko area, primarily as a result of video streaming, social media, and cloud services. The Federal Communications Commission is pushing hard to free up additional spectrum in some unlikely extremely high frequency ranges — some at 95 GHz or higher, for the next generation of wireless services.
The Federal Communications Commission is pushing hard to free up additional spectrum in some unlikely extremely high frequency ranges — some at 95 GHz or higher, for the next generation of wireless services. There are proposals and counter proposals from the satellite industry and wireless companies over how to manage sharing this band. Most are coalescing around the idea of sequestering 100 MHz of spectrum at the low-end of the band and using 3700-3800 MHz for high-speed wireless broadband. Some want satellite operators to clear out of this section of frequencies voluntarily, others propose compensation similar to what was given to television stations to relocate their channel positions. Google is pushing for a plan that would offer mobile 5G service in large urban areas and 25 Mbps – 1 Gbps fixed wireless broadband in rural and residential areas.
There are proposals and counter proposals from the satellite industry and wireless companies over how to manage sharing this band. Most are coalescing around the idea of sequestering 100 MHz of spectrum at the low-end of the band and using 3700-3800 MHz for high-speed wireless broadband. Some want satellite operators to clear out of this section of frequencies voluntarily, others propose compensation similar to what was given to television stations to relocate their channel positions. Google is pushing for a plan that would offer mobile 5G service in large urban areas and 25 Mbps – 1 Gbps fixed wireless broadband in rural and residential areas. Many agencies contemplating use of this band discovered equipment that supported 4.9 GHz was hard to find and extremely expensive. Most public safety agencies seeking grants or other funding to improve their communications equipment opted to transition to digital P25 networks that operate on much lower frequencies and use equipment that is now widely available and, in comparison, much cheaper. Many agencies are conservative about using new technology as well, concerned a communications failure could cost the life of a fire or police responder. As a result, of the 90,000 organizations certified for licenses in this band, only 3,174 have been granted. That represents a take rate of just 3.5%. The band, as one might expect, is effectively dead in most areas, underutilized in others.
Many agencies contemplating use of this band discovered equipment that supported 4.9 GHz was hard to find and extremely expensive. Most public safety agencies seeking grants or other funding to improve their communications equipment opted to transition to digital P25 networks that operate on much lower frequencies and use equipment that is now widely available and, in comparison, much cheaper. Many agencies are conservative about using new technology as well, concerned a communications failure could cost the life of a fire or police responder. As a result, of the 90,000 organizations certified for licenses in this band, only 3,174 have been granted. That represents a take rate of just 3.5%. The band, as one might expect, is effectively dead in most areas, underutilized in others. Although the 28 GHz band has many licensed users already, the 24 GHz band does not, and the wireless industry is interested in grabbing vast swaths of spectrum in this band for 5G home broadband. Known as “millimeter wave spectrum,” these two bands are expected to be a big part of the 5G fixed wireless services being planned by some carriers. Verizon acquired Straight Path late in 2017, which had collected a large number of licenses for this frequency range. Today, Verizon holds almost 30% of all currently licensed millimeter wave spectrum, an untenable situation if you are AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint. T-Mobile has been the most aggressive seeking more spectrum to compete with Verizon in this frequency range, and has purchased almost 1,150 MHz covering Ohio for use with a 5G project the company is working on.
Although the 28 GHz band has many licensed users already, the 24 GHz band does not, and the wireless industry is interested in grabbing vast swaths of spectrum in this band for 5G home broadband. Known as “millimeter wave spectrum,” these two bands are expected to be a big part of the 5G fixed wireless services being planned by some carriers. Verizon acquired Straight Path late in 2017, which had collected a large number of licenses for this frequency range. Today, Verizon holds almost 30% of all currently licensed millimeter wave spectrum, an untenable situation if you are AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint. T-Mobile has been the most aggressive seeking more spectrum to compete with Verizon in this frequency range, and has purchased almost 1,150 MHz covering Ohio for use with a 5G project the company is working on.

 PBS TV stations in smaller communities and secondary PBS affiliates and public stations in large ones are ending their free, over-the-air television broadcasts after decades of service because of politics, budget cuts and repacking the TV dial to give up more spectrum for wireless providers.
PBS TV stations in smaller communities and secondary PBS affiliates and public stations in large ones are ending their free, over-the-air television broadcasts after decades of service because of politics, budget cuts and repacking the TV dial to give up more spectrum for wireless providers.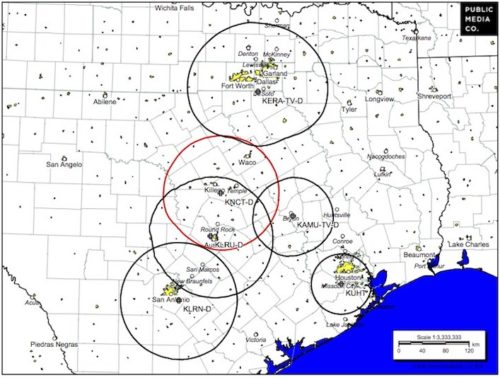
 KNCT-TV serves the Belton/Killeen/Temple/Waco, Tex. market, although KNCT’s signal struggles to reach into the northeastern part of its service area near Waco, where public TV station KAMU-TV in more distant College Station strangely provides a better signal.
KNCT-TV serves the Belton/Killeen/Temple/Waco, Tex. market, although KNCT’s signal struggles to reach into the northeastern part of its service area near Waco, where public TV station KAMU-TV in more distant College Station strangely provides a better signal. KMTP, San Francisco’s youngest multicultural public television station,
KMTP, San Francisco’s youngest multicultural public television station,  Its best chance to survive is dependent on an acquisition or arrangement with Poquito Mas Communications LLC, the licensee of low-power KCNZ in San Francisco, which is best known for carrying Creation TV, a Chinese language religious network. KMTP can either occupy several of KCNZ’s subchannels, or potentially buy the station outright. As a low power outlet, KMTP can hope to keep carriage on cable television, giving it perfect reception in areas where KCNZ’s low-power UHF transmitter cannot reach. But that means cord-cutters may have no access to the channel unless they live near the transmitter.
Its best chance to survive is dependent on an acquisition or arrangement with Poquito Mas Communications LLC, the licensee of low-power KCNZ in San Francisco, which is best known for carrying Creation TV, a Chinese language religious network. KMTP can either occupy several of KCNZ’s subchannels, or potentially buy the station outright. As a low power outlet, KMTP can hope to keep carriage on cable television, giving it perfect reception in areas where KCNZ’s low-power UHF transmitter cannot reach. But that means cord-cutters may have no access to the channel unless they live near the transmitter. WYCC in Chicago was the city’s second PBS affiliate, behind the larger and better known WTTW. Licensed by City Colleges of Chicago, the trustees
WYCC in Chicago was the city’s second PBS affiliate, behind the larger and better known WTTW. Licensed by City Colleges of Chicago, the trustees 


