Four of the nation’s largest phone companies — two former Baby Bells, two independents — have very different ideas about solving the rural broadband problem in the country. Which company serves your area could make all the difference between having basic DSL service or nothing at all.
Some blame Wall Street for the problem, others criticize the leadership at companies that only see dollars, not solutions. Some attack the federal government for interfering in the natural order of the private market, and some even hold rural residents at fault for expecting too much while choosing to live out in the country.
This four-part series will examine the attitudes of the four largest phone companies you may be doing business with in your small town.
 Today: Frontier — “Rightsizing” Our Broadband Revenue in Barely-Competitive Markets, Even When It Costs Us Customers
Today: Frontier — “Rightsizing” Our Broadband Revenue in Barely-Competitive Markets, Even When It Costs Us Customers
“We have been very disciplined with our [data] pricing and really trying to make sure that we are moving the prices up in a right direction and looking at customers who are paying way below where they should be,” Donald R. Shassian, chief financial officer and executive vice president of Frontier Communications told investors on a conference call earlier this month. “They are not a valued customer. If we can’t get them up, we are sort of letting them disconnect off, if you would, and it’s enabling us to be more disciplined.”
That “direction” has meant higher bills for some long-standing customers that suddenly lost discounts or service credits. One common example is Frontier’s mandatory broadband modem rental fee, increasingly turning up on customer bills even though they own their own equipment or had previously arranged a fee waiver. Ex-Verizon customers were particularly hard hit when Frontier switched to its own billing platform. Just about every customer has also been impacted by Frontier’s “junk fees,” including company surcharges that effectively raise the price of the service.
As a result of higher pricing and dissatisfaction with the quality of service, some customers have disconnected, and the company recently reported second quarter profits were down 44%, offset by slightly higher earnings from higher bills.
The New Frontier
Frontier Communications has enormously expanded its reach over the past few years. Frontier’s original “legacy” service areas were dwarfed in 2010 by the company’s acquisition of 4.8 million landlines from Verizon Communications.
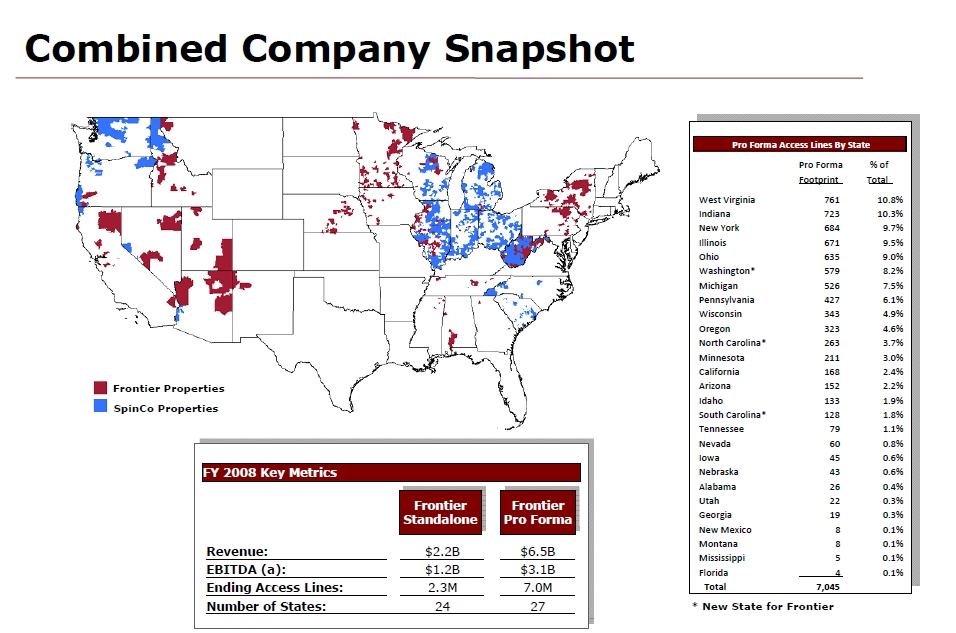
Frontier’s Combined Service Map — Areas in red are “legacy” Frontier service areas. Those in blue were acquired in 2010 from Verizon. (click to enlarge)
Frontier roughly tripled in size as a result, and the huge spike in customers delivered four straight quarters of triple-digit revenue growth. But the transition for ex-Verizon customers has not been easy. Customers endured billing errors, service plan confusion, and service quality issues as Frontier got up to speed managing Verizon’s landline network. A significant number of those customers have had enough and are switching to other providers.
West Virginia is the best place to study the contrast between Frontier’s failures and successes. A large number of service problems and lengthy outages plagued the state after Frontier took charge of a landline network Verizon treated as an afterthought. Over at least a decade, Verizon allowed its landline network to deteriorate to abysmal condition in several areas of the state. Little was invested to upgrade service, and Verizon ultimately left West Virginia with one of the lowest national broadband service penetration rates — about 60 percent.
Verizon’s priorities were elsewhere: spend millions on FiOS fiber upgrades in larger, urban markets while letting rural landline networks stagnate. Eventually, Verizon’s management team decided it was no longer worth hanging on to these low priority service areas and began selling them off. FairPoint Communications acquired Verizon customers in northern New England and Frontier bought mostly rural midwestern and western territories long struck from Verizon’s priority list.

Wilderotter
Frontier’s key argument for acquiring Verizon landlines was that the company could bank on deploying broadband to a much larger percentage of customers than Verizon ever bothered to serve.
Frontier places a very high priority on broadband, because the company can significantly boost the average revenue it earns from each customer by providing the service. With Frontier often the only home broadband choice around in its most rural markets, the company can charge whatever it wants for DSL service, tempered only by how much customers can afford to pay. Broadband is also a proven customer-keeper, an important consideration for any company facing ongoing losses from customers dumping landlines for cell phones.
Since its acquisition, Frontier has been aggressively deploying rural broadband in the former Verizon territories — typically the cheapest form it can deliver — 1-3Mbps ADSL service. Frontier considers its legacy service areas already well-covered, claiming around 93 percent of customers can already subscribe to Frontier DSL.
In states like West Virginia, the fact anyone is supplying anything resembling broadband has been well-received by those who have never had the service before. But where competition exists, Frontier has been losing ground (and customers) as cable competitors provide more consistent, higher speeds and quality of service.
The frustration is especially acute in the Mountain State. Steve Andrews, a Beckley resident complained, “This company’s idea of broadband access is up to 3Mbps DSL while nearby states like Virginia and Pennsylvania are getting fiber or cable broadband speeds ten times faster.” Andrews added that on most days his Frontier-provided broadband provides only around 800kbps, not the advertised 3Mbps.
Frontier Admits It Uses Government (Your) Money to Expand Broadband Where It Would Have Expanded Service on Its Own… Eventually
Frontier Communications was by far the most enthusiastic participant in the Federal Communications Commission’s Connect America Fund (CAF). This subsidy program currently covers $775 of the cost to extend broadband service to a currently unserved customer. Frontier agreed to accept nearly $72 million from the program, which commits the company to offering at least 4Mbps broadband service to an additional 92,877 homes and businesses around the country.
But Maggie Wilderotter, CEO of Frontier Communications, admitted Frontier would have eventually spent its own money to extend service to those rural customers without a subsidy:
“Get broadband out faster to a bunch of customers that we would have built anyway, at some point in time. And it also accomplishes the objectives of using the funds that are available from the FCC. We actually could have taken more money…. So we felt good about it. We totally understand why the other carriers made the decisions they made because we didn’t — we’re not building anything on our legacy markets. So it’s the money. It’s all in the acquired properties where we still had pretty low penetration with enough density to support the parameters that the FCC put in place.”
 The fund, paid for by telephone customers nationwide through a surcharge on customer bills, will also subsidize a lucrative business opportunity for Frontier, according to Wilderotter.
The fund, paid for by telephone customers nationwide through a surcharge on customer bills, will also subsidize a lucrative business opportunity for Frontier, according to Wilderotter.
“These are unserved locations that really are not competitive at all,” Wilderotter told investors. “So there’s no competition in those areas. So we’re pretty excited about it. We think that this is going to be good for Frontier and good overall.”
More than $38 million of the total broadband subsidy Frontier received will be spent in 30 counties in just one state: Wisconsin. Among other locations where Frontier will spend the money:
- 1 Arizona county
- 2 California counties
- 1 Florida county
- 5 Idaho counties
- 25 Illinois counties
- 2 Indiana counties
- 26 Michigan counties
- 2 Nevada counties
- 8 New York counties
- 1 North Carolina county
- 8 Ohio counties
- 5 Oregon counties
- 2 Tennessee counties
- 7 Washington counties
- 25 West Virginia counties
Trying to Hang Onto Customers Frontier Already Has… With Serious Speed Boosts
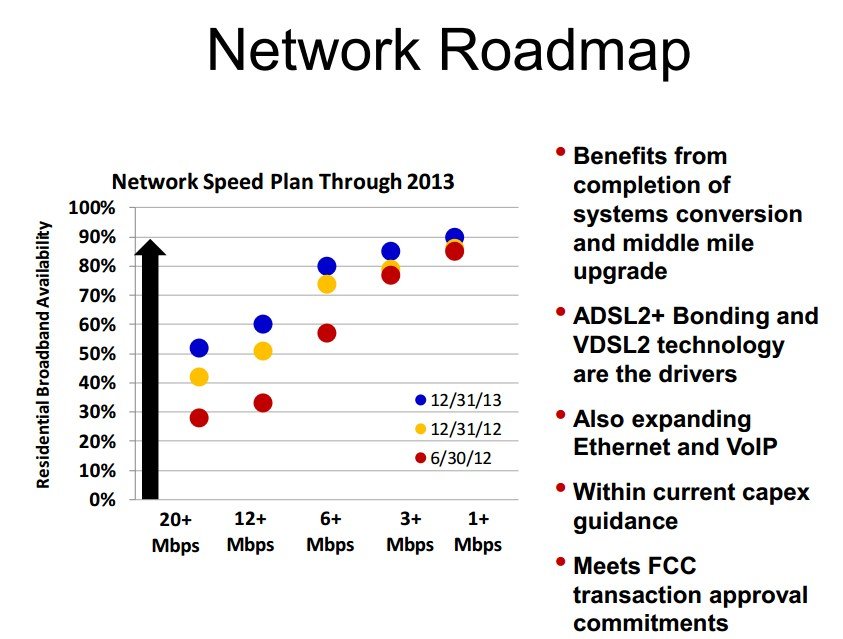
Frontier’s speed plans through 2013.
One of the loudest and most consistent complaints Frontier broadband customers mention is the slow speeds they receive from Frontier’s DSL. Frontier traditionally offers 1-3Mbps in rural areas, up to 10Mbps in urban areas. But in fact many customers report their speeds are much lower than advertised. Data from the FCC’s national broadband speed measurement program bears this out. Frontier was the only measured provider in the United States that has been losing ground in promised broadband speed and performance.
Frontier officials announced earlier this month the company was shifting some of its capital investments away from broadband expansion towards improving the performance of its broadband service for current customers.
In highly competitive, urban markets Frontier will deploy VDSL2 technology which can support significantly faster and more reliable Internet speeds. In more rural markets, bonded ADSL 2+ will deliver speeds of 10Mbps or better to customers currently stuck with around 1-2Mbps speed.
Daniel J. McCarthy, president and chief operating officer:
- We expect our 20Mbps service to move from 28% of residential households today to 42% by year-end and then 52% by the end of 2013;
- The 12Mbps services planned to increase from 33% of homes today to 51% by year-end and 60% by 2013;
- And the 6Mbps service is planned to increase from 57% of homes today to 74% by year-end and 80% by 2013.
The new speeds will not come free of charge. Customers will be marketed speed upgrades for additional monthly fees.
Customers will also discover Frontier has been simplifying its packages and moving away from high-value promotional offers that bundled a free laptop, television, or satellite dish in return for a lengthy contract. Today, the company is emphasizing increasing discounts for customers subscribing to two or more services that include telephone/long distance, broadband, and satellite television.
Speeds Going Up, Employees (and their salaries) Going Down
 Finally, Frontier executives told investors they are scouring the company looking for cost savings. They appear to have identified around $100 million worth, a good portion of which will come from employees facing job cuts or salary reductions.
Finally, Frontier executives told investors they are scouring the company looking for cost savings. They appear to have identified around $100 million worth, a good portion of which will come from employees facing job cuts or salary reductions.
Wilderotter said she is focusing on call center workers, retiree positions, and “tech op” savings.
“We still have some bubble workforce in the call centers that will continue to go away,” Wilderotter told Wall Street. “We have a number of employees, too, that are going to be retiring over these next several months. And our goal is not to replace any of those retirees either.”
One of the best examples of this cost savings, according to unions representing Frontier employees, is the forthcoming closure of an Idaho-based call center in Coeur d’Alene. More than 100 workers, average age 55, will lose their $15-21/hour jobs Sept. 18 while Frontier prepares to leverage cheaper labor in South Carolina.
Frontier’s new call center employees in Myrtle Beach will receive $11 an hour while training, $12/hour after training — with a five year wage freeze. Benefits will be considerably leaner for South Carolina employees as well, according to union officials.
 Dish Network is planning to introduce 5Mbps nationwide satellite broadband service after its partner company EchoStar successfully launched the satellite that will host the new service.
Dish Network is planning to introduce 5Mbps nationwide satellite broadband service after its partner company EchoStar successfully launched the satellite that will host the new service.

 Subscribe
Subscribe