 Canadian telecom regulators have announced new rules that will limit “gotcha” fees for mobile customers caught exceeding their data allowance, push for an end to the ubiquitous three-year service contract, and force carriers to unlock cell phones after 90 days.
Canadian telecom regulators have announced new rules that will limit “gotcha” fees for mobile customers caught exceeding their data allowance, push for an end to the ubiquitous three-year service contract, and force carriers to unlock cell phones after 90 days.
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) this week unveiled a new consumer’s Wireless Code governing wireless service. The new rules were introduced in response to more than 5,000 consumer comments received by the regulator over service pricing, opaque wireless contract language, and policies that kept customers locked into long service contracts with expensive exit penalties.
On the surface, the new rules seem to aggressively rein in Bell, Rogers, and Telus — Canada’s three dominant carriers. Among the new provisions taking effect Dec. 2:
- cancel your contract at no cost after a maximum of two years;
- cancel your contract and return your phone at no cost, within 15 days and specific usage limits, if you are unhappy with your service;
- have your phone unlocked after 90 days, or immediately if you paid in full for your phone;
- have your service suspended at no cost if your phone is lost or stolen;
- receive a Critical Information Summary, which explains your contract in under two pages;
- receive a notification when you are roaming in a different country, telling you what the rates are for voice services, text messages, and data usage;
- limit your data overage charges to $50 a month and your data roaming charges to $100 a month;
- pay no extra charges for a service described as “unlimited”;
- you can refuse a change to the key terms and conditions of your contract, including the services in your contract, the price for those services, and the duration of your contract; and
- all cell contracts must use plain language and clearly describe the services customers receive and include information on when and why customers may be charged extra.
[flv width=”480″ height=”290″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC New CRTC wireless rules ban contract break fees after 2 years 6-3-13.flv[/flv]
CBC Television’s “The National” explains the CRTC’s new Wireless Code and how it will impact Canadian cell phone customers. Many are skeptical the CRTC will outwit the wireless industry. (4 minutes)

“Every day, Canadians rely on wireless devices while in their homes, at their jobs, at school or traveling abroad,” said Jean-Pierre Blais, chairman of the CRTC. “The wireless code will contribute to a more dynamic marketplace by making it possible for Canadians to discuss their needs with service providers at least every two years. The code is a tool that will empower consumers and help them make informed choices about the service options that best meet their needs. To make the most of this tool, consumers also have a responsibility to educate themselves.”
Canadians pay among the world’s highest wireless charges and most are offered contracts lasting three years. In the United States, two-year contracts are standard. But in both countries, once the contract is fulfilled customers do not receive a discount on services going forward.
“The biggest scam of all is still allowed under the new rules: wireless companies don’t lower your bill if you buy your own phone or fulfill your contract, so you are still paying their subsidy-recovery phone rates either way,” complains Thomas Harcourt in Toronto. “Once again, the wireless companies got the ears of the commissioners and despite thousands of angry Canadians, they watered down our ‘Bill of Rights’ into more bait and switch. You can almost see where the wireless lobbyists had their way with the language.”
Most Canadian wireless carriers welcomed the new rules and the industry participated in hearings contemplating their creation. The new federal rules will supersede conflicting, sometimes stronger provincial regulations, which some observers suggest is a decision in the carriers’ favor.
A closer review of the new regulations exposes several that were tempered, perhaps after industry objections.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/BNN Wireless Code of Conduct CWTA 2-11-13.flv[/flv]
Back in February, BNN talked with Bernard Lord, a representative of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association about what policies they hoped to see in a national wireless “code of conduct.” The industry got most of what it wanted in the final Wireless Code. (8 minutes)
The CRTC did not ban 3-year contracts outright. Instead, they tied contract termination policies and fees to the device subsidy phone companies give customers to cheapen the upfront cost of equipment.

Blais
In Canada, a new smartphone selling for $699 might be discounted to $99 with a three-year contract. For the next 36 months, customers gradually pay back that discount, called a device subsidy, in the form of an artificially inflated rate plan. Most companies amortize that payback rate over the life of the contract. Under the new CRTC rules, companies must recoup their device subsidy within 24 months.
“We didn’t focus on the length of the contract, we focused on the economic relation,” CRTC chairman Blais said. “So, in effect, it’s equivalent to those asking for a ban of a three-year contract without us actually banning three-year contracts, because what we’re saying is the contract’s amortization period can only be for a maximum period of 24 months.”
Carriers can still charge early termination fees during the first two years and can also recoup any remaining unpaid subsidy during the third year as the regulations begin to cover more customers already under three year contracts. Customers who bring or buy their own device can also be charged an early termination fee up to $50 during the first two years of the contract.
Since the rules will apply only to new cellular contracts signed after Dec. 2, 2013, current customers will have to wait before the new Wireless Code fully applies to them. That means wireless carriers can lock you to the old rules if you buy a new phone before December until your contract ends or is amended.
“I think a lot of consumers, if they were thinking of going to the mall and picking up a new phone and signing a contract, they should think twice about doing so,” Michael Geist, the Canada Research Chair in Internet and e-commerce law at the University of Ottawa, told CTV News.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC 3-year contracts to end 6-3-13.flv[/flv]
The CBC tells you when you can rip up your three-year contract. But be careful. The new rules don’t take effect until December. Many complain cell phone service is far too expensive in Canada. (4 minutes)
Wireless carriers claim consumers may eventually pay the price for the rules changes, with some hinting they will increase the upfront price for devices or raise rates to cover the shortened window of time they can recoup a device subsidy.
 “This requirement does limit consumer choice in the marketplace, and could make a customer’s up-front purchase price of a smartphone more expensive than current offerings,” said Bernard Lord, head of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association (CWTA).
“This requirement does limit consumer choice in the marketplace, and could make a customer’s up-front purchase price of a smartphone more expensive than current offerings,” said Bernard Lord, head of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association (CWTA).
The CWTA also hinted rates may also increase to cover the “major technology development and costs associated with implementing and complying with the new code.”
Ken Engelhart, senior vice president for regulatory affairs at Rogers told BNN a new smartphone under the old three-year contract was typically priced at around $100. Under a two-year contract, that smartphone might cost $300 upfront.
The CRTC’s language banning overage charges for “unlimited” service does not offer consumers any relief from speed throttling. The CRTC says speed limits are acceptable as long as they are “clearly explained” in what the regulator calls a “fair use” policy.
Language that covers contract changes also leaves some wiggle room for carriers to make changes and in certain cases, even increase customer rates while the contract is in effect. The new rules specify customers must make “informed and express consent” to approve a contract change. But the rules might allow a carrier to consider those changes as accepted if a customer does not expressly complain and/or continues to use the phone after a specified deadline. Carriers can also make changes without consumer consent if they involve reducing the rate for a single service or increasing the customer’s usage allowance for a single service.
The limit of data overage charges ($50) and international data roaming charges ($100) are welcomed by most Canadians to avoid bill shock. But most wireless carriers will likely impose usage “toll booths” to avoid uncollectable customer overages. When a customer reaches their limit, they will be given a choice of having their service cut off, opting to cover the overlimit fees, or upgrade their plan.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/BNN Wireless Code of Conduct PIAC 2-11-13.flv[/flv]
BNN talked with John Lawford, executive director of the Public Interest Advocacy Centre about the things Canadians hate most about their wireless phone companies. (February 11, 2013) (4 minutes)
 AT&T has once again followed Verizon Wireless’ lead by ending early upgrades for contract customers, making it impossible to upgrade a handset with a full device subsidy until 24 months have passed.
AT&T has once again followed Verizon Wireless’ lead by ending early upgrades for contract customers, making it impossible to upgrade a handset with a full device subsidy until 24 months have passed.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Still waiting for Verizon FiOS in New York City? Are you annoyed that your neighbors have impressive broadband speeds from an all-fiber network while you suffer with DSL or cable broadband from Time Warner or Cablevision? Your landlord may be the problem.
Still waiting for Verizon FiOS in New York City? Are you annoyed that your neighbors have impressive broadband speeds from an all-fiber network while you suffer with DSL or cable broadband from Time Warner or Cablevision? Your landlord may be the problem. In April, Verizon was criticized by New York City public advocate Bill de Blasio for falling behind schedule providing access to FiOS in low-income communities.
In April, Verizon was criticized by New York City public advocate Bill de Blasio for falling behind schedule providing access to FiOS in low-income communities.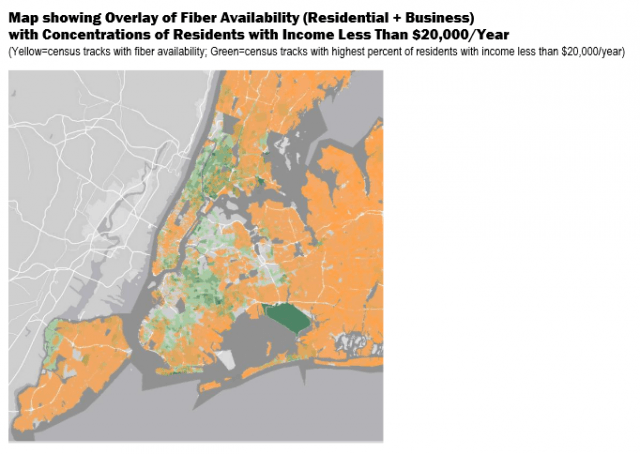

 Canadian telecom regulators have announced new rules that will limit “gotcha” fees for mobile customers caught exceeding their data allowance, push for an end to the ubiquitous three-year service contract, and force carriers to unlock cell phones after 90 days.
Canadian telecom regulators have announced new rules that will limit “gotcha” fees for mobile customers caught exceeding their data allowance, push for an end to the ubiquitous three-year service contract, and force carriers to unlock cell phones after 90 days.

 “This requirement does limit consumer choice in the marketplace, and could make a customer’s up-front purchase price of a smartphone more expensive than current offerings,” said Bernard Lord, head of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association (CWTA).
“This requirement does limit consumer choice in the marketplace, and could make a customer’s up-front purchase price of a smartphone more expensive than current offerings,” said Bernard Lord, head of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association (CWTA).

 More than a year ago, Comcast
More than a year ago, Comcast  But if Comcast brings back the cap, Cox will downgrade his service back to where he started.
But if Comcast brings back the cap, Cox will downgrade his service back to where he started.