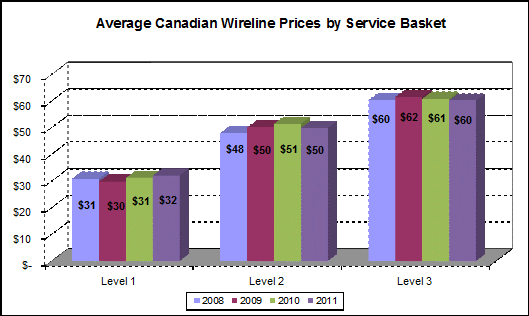
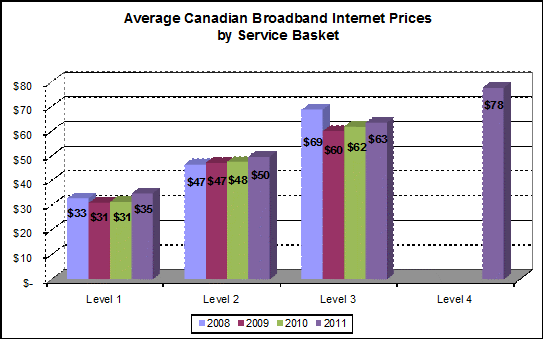
Rogers Communications has announced usage cap and speed adjustments for many of its Internet service plans — changes that will bring increased allowances for some of the company’s most premium customers.
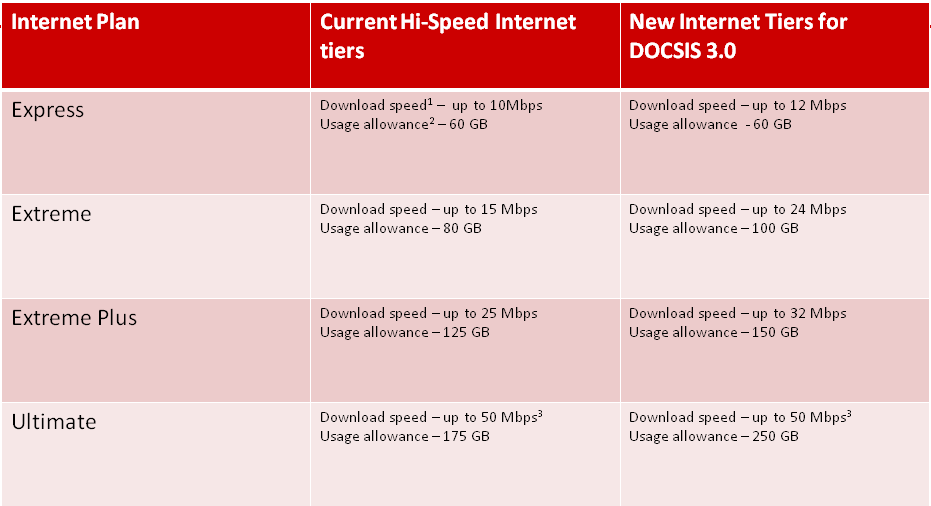
Rogers has modestly adjusted usage caps on its popular Extreme Internet Plan a year after slashing them, and brings dramatic increases for the company’s most expensive service tiers, even as it leaves usage caps unchanged for the bulk of their customers subscribed to the basic Express service plan:
 A Rogers spokesman explained the changes.
A Rogers spokesman explained the changes.
“With the rapid rise of online video, social media and online gaming, the way Canadians use the Internet is changing dramatically. We’re always reviewing our plans to ensure they meet your changing needs so starting later this month, our Hi-Speed Internet tiers are being upgraded with faster download speeds and higher data allowances for customers on Rogers DOCSIS 3.0, our best and fastest wireline network,” wrote RogersMarina on the company’s RedBoard blog.
Apparently the way Canadians use the Internet with Rogers’ most-popular Express plan hasn’t changed much, because Rogers leaves that cap unchanged at 60GB of usage per month. Rogers previously reduced its usage cap for its Extreme level of service from 95 to 80GB, days after Netflix announced it was bringing its streamed video service to Canada. Rogers’ latest increase amounts to just 5GB more usage than customers had during the spring of 2010.
The increased speeds that some usage tiers are gaining with the introduction of DOCSIS 3 technology come “at no additional cost” according to Rogers, but the company also mentions it charges higher prices — $1.50-$3 more per month — for the required DOCSIS 3 modem.
For customers certain to exceed their allowance, Rogers will sell you an insurance plan to protect your wallet from their $0.50-5.00/GB overlimit fees:
“Also starting later this month, you’ll be able to add a data assurance option if you’re currently using the Express and Extreme tiers. For an extra $20 per month, you’ll receive an extra 80 GB of data on top of your existing allowances. If you don’t need quite as much data, you can also get an additional 20 GB for an extra $5 per month.”
Most customers were not impressed. Take Matt, for example:
“Speed increases are great but all they allow us to do is to get to our low data caps faster. These days with YouTube, Netflix, VOIP, and work VPN (heavy work from home user) $60 for 100 GB of data is pretty expensive, especially when a GB of data probably costs Rogers pennies per user. Competitors are starting to offer higher data caps for a similar price. In Toronto you can get a plan for same or slightly cheaper starting with 200GB. In Vancouver you can get 50Mbps for $29 a month with a 400 GB data cap!”
Cambo notes the usage upgrades come easy for higher-priced tiers, but customers on the most popular Express tier have no increase in their usage allowance at all.
“You guys just don’t get it,” he writes on RedBoard. “Speed isn’t the issue. Usage is. Why is it every tier gets a usage bump except the most popular Express? What is the point of bumping the speeds up and not significantly increasing usage, so we can get to the caps even faster I suppose. Sounds like a ploy to get people to spend more, to me.”
Andrew agreed:
“I also agree with this. I would rather get a larger usage bump than a speed bump — I don’t see a point in raising speeds when the data cap is still extremely restrictive. After all, I’d want to enjoy using the Internet, rather than monitoring my usage restrictions every day. If Rogers really listened to the customers, they’d know that most of us are more critical of their plans’ usage restrictions than their speeds.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe