
Kansas House Bill 2563 would require content providers that sell products and services in Kansas to pay into the state’s rural broadband fund.
ISPs and any website that generates at least $500,000 in revenue from Kansas residents would be required to pay into a state fund to subsidize rural broadband, if a bill introduced by a Lawrence Republican becomes law.
Rep. Thomas Sloan’s House Bill 2563 — a bill requiring broadband and content providers to pay into the Kansas Universal Service Fund (KUSF), drew immediate fire from cable and telephone companies across the state, and Sprint Corp. told state officials the bill was illegal.
“Rural residents lack the same broadband opportunities as urban residents because of the high cost to serve low-population density areas,” Sloan said. “We have a classic case of rising customer expectations for capabilities delivered through a broadband communications system and a fiscally stressed telecommunications provider network’s ability to serve high-cost rural customers.”
As in many rural states, finding the funding to solve the rural broadband problem gets more difficult as those hardest to serve are also the most expensive to reach. Kansas currently spends about $40 million annually to reach homes and businesses that are still using dial-up or forced to invest in satellite internet service. Most KUSF money is given to incumbent rural telephone, wireless or cable providers to subsidize expansion, keeping costs in line with each company’s Return On Investment expectations.
But as demand for faster and more robust broadband accelerates, and as the definition of broadband itself has evolved, rural providers are increasingly challenged reaching both unserved customers and those now considered underserved because older technologies like DSL often do not meet the current FCC definition of broadband: 25/3 Mbps service.
Sloan said his bill is designed to address both problems by wiring unserved areas and improving access to reliable, high-speed internet service where only slower alternatives now exist. The bill would provide funding to more than 90 Kansas counties with a population density of less than 100 people per square mile (excepting the county seat). In an agricultural state like Kansas, that would directly inject cash for upgrades into large sections of the state. Sloan says his law would cover at least 40% of a provider’s wiring and upgrade costs.

Rep. Sloan
House Bill 2563 would fund a rural broadband project that:
- is capable of minimum download speeds of 25 Mbps and minimum upload speeds of three megabits per second;
- provides an average latency of less than 100 milliseconds to enable the use of real time communications; and
- provides subscribers with a minimum monthly data allowance of 150 gigabytes per month.
“Poor connectivity to the internet undermines operation of businesses, filing of government documents, school research projects, viewing of entertainment and other day-to-day activities,” Sloan said.
ISPs would likely pass along the costs of the new broadband universal service fund charge to subscribers, which means urban Kansans will be contributing a portion of their monthly internet bill to benefit their rural neighbors.
Sloan’s bill would also take the unprecedented step of taxing internet content companies and for-profit websites that generate at least $500,000 in revenue attributable to Kansas customers and use the money for rural broadband expansion as well. Websites like Amazon.com, Netflix, and Hulu would certainly be liable, but so would thousands of other smaller website ventures, including porn websites and online publishers like newspapers.
Telecom industry lobbyists quickly descended on state lawmakers in Topeka to encourage them to kill Sloan’s bill:
- Catherine Moyer, chief executive officer of Pioneer Communications in Ulysses, represents the interests of the State Independent Telephone Association for Kansas and the Kansas Rural Independent Telecommunications Coalition. She is strongly opposed to the bill because she claims it would weaken the current Kansas Universal Service Fund (KUSF) model that has given rural companies confidence and certainty their rural expansion investments will be backed with adequate state subsidies. Under Sloan’s bill, the disbursement formula and the areas entitled to receive state support would be expanded, potentially reducing funds that were payable to projects under the old KUSF subsidy system.
- Patrick Fucik, national director of legislative affairs for Sprint Corp. in Overland Park, is concerned about broadening the universal service fund to tax content providers and other websites, claiming the state lacks the legal authority under federal law to impose such taxes.
- John Idoux, a lobbyist with CenturyLink, which serves more than 100 Kansas communities with fewer than 1,000 residents, said the bill would likely make lawyers rich from the “prolonged” and inevitable legal challenges that will begin if the bill becomes law, “all while creating false hope of rural broadband availability.” Idoux also wants to make sure none of the KUSF money will be spent in areas already served by a fixed broadband provider (like CenturyLink). He does not want to see public money competing with private investment, even if it results in better service.
An audio-only hearing of the Committee on Energy, Utilities and Telecommunications of the Kansas State Legislature on HB2563, held Feb. 5, 2018. (35:53)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
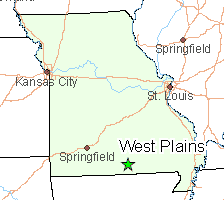 West Plains’ fiber network has grown carefully over the last few years, both in terms of its reach and its capabilities. At the outset, the network offered 25/25 Mbps dedicated connections primarily to business customers. But where West Plains’ fiber loop passes residential homes, the city has also been willing to provide service to local homeowners as well.
West Plains’ fiber network has grown carefully over the last few years, both in terms of its reach and its capabilities. At the outset, the network offered 25/25 Mbps dedicated connections primarily to business customers. But where West Plains’ fiber loop passes residential homes, the city has also been willing to provide service to local homeowners as well.


 It will take until 2019 to fully integrate all of Charter’s customers onto a single platform that will no longer distinguish if a customer was a long-standing Charter customer or a former TWC or BH subscriber.
It will take until 2019 to fully integrate all of Charter’s customers onto a single platform that will no longer distinguish if a customer was a long-standing Charter customer or a former TWC or BH subscriber. Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.
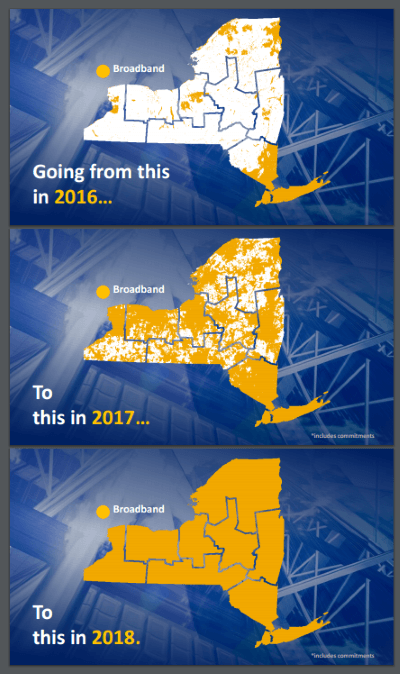
Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible. New York’s Broadband for All Program yesterday
New York’s Broadband for All Program yesterday 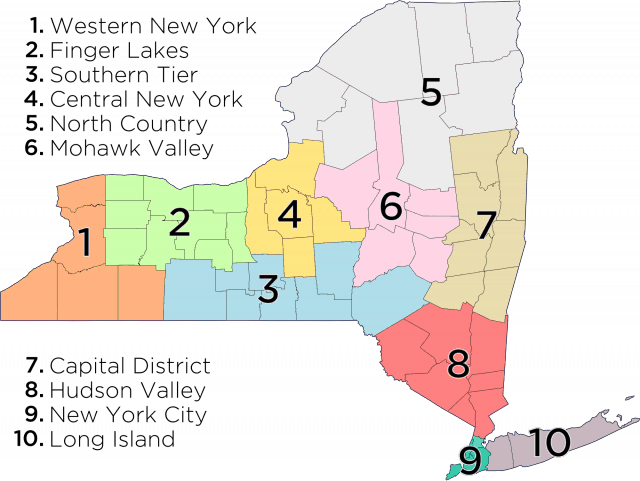 Central New York Region
Central New York Region

 “This is a huge disappointment for us,” Pat added. “We were counting on this happening. Told numerous times it would. Now we have to debate moving, we can’t continue not having internet. My oldest son just graduated high school never having internet at home.”
“This is a huge disappointment for us,” Pat added. “We were counting on this happening. Told numerous times it would. Now we have to debate moving, we can’t continue not having internet. My oldest son just graduated high school never having internet at home.”