 Frontier Communications spent more time working on ways to keep Minnesota customers from turning up at upcoming public hearings to discuss their poor service than actually resolving those customers’ service troubles.
Frontier Communications spent more time working on ways to keep Minnesota customers from turning up at upcoming public hearings to discuss their poor service than actually resolving those customers’ service troubles.
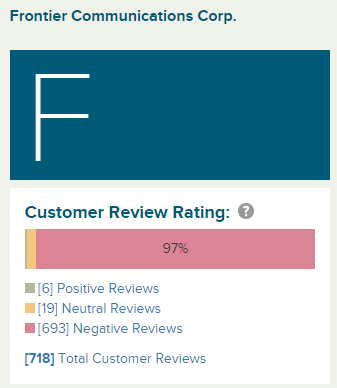
Minnesota has a big problem with Frontier. The company has been the subject of an unprecedented number of customer complaints and negative comments — 439 in just a five-week period from Feb. 12 – March 19, 2018 about poor service, repair crews that don’t show up, woefully inadequate internet service, poor billing and customer service practices, and false advertising. As a result, the Minnesota Public Utilities Commission (PUC) launched an investigation into Frontier’s service performance in the state (Note: most links in this article will require a free account at the Minnesota Department of Commerce to read. Register here.), which is about the same time Frontier’s top executives in the state began a campaign of damage control focused primarily on keeping internet complaints out of the public record.
The complaints, summarized below by the Minnesota PUC, are familiar to many Frontier Communications customers around the country:
Some parties allege being without telephone service for about a week’s time on multiple occasions. Such instances resulted in customers being unable to access 911 or connect medical devices dependent on land telephone lines. Missed incoming calls, noise on phone lines and other phone quality complaints are not infrequent. Nearly all comments mention that they are being charged for service product(s) not being provided as promised, often with related billing and cancellation disputes as a consequence.
Nearly all parties complain that Frontier’s customer service representatives provide inconsistent information on available service in the customer’s area and its price. Many report routinely being sold higher level (more costly) service or hardware as a remedy for service problems that remain or return after the recommended solution is in place. Customers often note being told later that the upgraded service they were sold is not available at their location.
Many complaints concern home service visits that require subsequent visits to correct or augment earlier actions, often with charges but no resulting remedy. Often customers say they experience long delays in getting repairs scheduled, must take lengthy time from work to await for service representatives to arrive only to find problems cannot be remedied. Missed service appointments, mistaken disconnections, unrequested service additions, installation and wiring errors are common complaints.
Customers frequently report discovering they are allegedly on a contract with penalties for ending service early even if they had explicitly refused to accept long term contracts. Apparently such contracts automatically renew without customer notice upon payment of the first month of the new period. Customers indicate being warned of damaging credit reports in addition to accumulating penalties if they do not pay disputed bills. Billing disputes also include promised discounts not being provided, penalties accumulating on disputed amounts, and checks being sent but not being credited to accounts.
 Based on decades of experience, the PUC staff knew trouble when they saw it, and found the complaints about Frontier credible and serious.
Based on decades of experience, the PUC staff knew trouble when they saw it, and found the complaints about Frontier credible and serious.
“The total number of comments and complaints, often with detailed documentation, appears to indicate that widespread problems with service quality, customer service and billing exist,” PUC staffers wrote. “Customers express the very highest levels of frustration over service quality and over their interactions with Frontier representatives. Customers express despair over their billing and lack of alternatives. Finally, they express outright ‘gratitude for the hope that someone might come to their aid.”
Customers hoping for rescue discovered Frontier’s legal team instead, on a mission to do everything possible to limit the scope of the state’s investigation and discourage public participation by suggesting customers with internet complaints would not be welcome at the hearings.
Frontier, joined by fellow independent phone company CenturyLink, immediately realized the implications of holding public hearings about the performance of their DSL service in Minnesota. Both companies likely receive an even larger number of service complaints than regulators do, and here is just a sampling:
‘If you don’t like our service in the countryside, move to town!’
Graham Adams: “We have had Frontier for a little over 2 years and have had nothing but problems. Internet is constantly out for days sometimes weeks at a time. I think it’s preposterous they can charge me $42 a month for 5 Mbps service that is inconsistent at best. Because we live outside city limits Frontier is the only internet service available.”
 Christopher Krolak: “I have been a Frontier Communications customer for about 4.5 years. I live in an area where there isn’t a lot of competition for high speed internet. I pay $30 per month for “up to 6 Mbps” service but real world speeds are best case 2 Mbps and fall to 0.3 Mbps during peak times. When I’ve called about the large discrepancy between advertised speed and actual speed, Frontier has responded that the area I live in is only provisioned for about 2 Mbps speed and an infrastructure upgrade is required. Frontier is unwilling to give any timeline forecast for when such upgrade will be made.”
Christopher Krolak: “I have been a Frontier Communications customer for about 4.5 years. I live in an area where there isn’t a lot of competition for high speed internet. I pay $30 per month for “up to 6 Mbps” service but real world speeds are best case 2 Mbps and fall to 0.3 Mbps during peak times. When I’ve called about the large discrepancy between advertised speed and actual speed, Frontier has responded that the area I live in is only provisioned for about 2 Mbps speed and an infrastructure upgrade is required. Frontier is unwilling to give any timeline forecast for when such upgrade will be made.”
Sylvia Svihel: “We have been a customer of Frontier’s for 41 years as it has been the only land line in our area. Our phone, internet and Dish service are tied into the same package. The prices keep going up. We did upgrade our service for a faster speed but we see zero improvement on the speed…just an even higher bill. I have lost track of how many times we have contacted Frontier on lost service. They usually just say it’s the modem and to reboot it and everything will be OK. I reboot the modem, sometimes multiple times a day.”
Jay Johnson: “I have been a Frontier customer for internet for a long time. The service I pay for is “up to 6 Mbps” but I’d be lucky to get 1.2 Mbps. They have a monopoly in this part of Mille Lacs County. There are really no other options other than satellite or cellular and those are not really any better speed and certainly not price.”
Roger Wikstrom: “We have had Frontier service for 32 years. Beginning about 20 years ago we added internet service, which has always been unreliable. […]We complained many times and had dozens of service calls over the years. At one point, the technician told us we were out in the country, the brass at Frontier did not really care about our service, and that if we wanted good service from Frontier, we should move to town.”
Based on a growing record of complaints, the PUC sought to hold public hearings to gather more information from consumers and to better understand the problems being experienced by Frontier customers. Almost immediately, Frontier began to claim the complaints were few and far between, and most of the complaints seen on the record pertain to the company’s DSL internet service, which Frontier claims is not subject to oversight by the PUC and cannot be a subject on the agenda of the public hearings.
Frontier’s Lawyers: It would confuse customers and give them false hope if they believed the Commission can force Frontier to improve DSL service.

Frontier’s attorneys lecture the Minnesota Department of Commerce
Frontier’s attorneys have repeatedly objected to any investigation or hearings that cover anything beyond the performance of Frontier’s landline telephone service. Frontier was joined by CenturyLink, which also argues Minnesota no longer has any jurisdiction over broadband issues, noting a state court recently ruled telecommunications services are subject to state regulation and oversight, while “information services” like internet access are not.
Frontier was particularly irritated that the hearings could stray into an open mic session filled with consumers upset about Frontier’s DSL service. Unless customers were warned in advance the public meetings were not to include discussions about internet service, it “would create false expectations and confusion for customers.” In fact, if regulators permitted this, Frontier claims it would “violate federal law.”
“Holding public hearings directed to internet access service complaints would not be constructive because the Commission would be precluded from taking action concerning internet service rates or service quality using any information it may collect during the public hearings,” Frontier added.
Here is where the Republican-dominated FCC comes to the aid of Frontier and CenturyLink. At the insistence of FCC Chairman Ajit Pai, stripping away state oversight of poorly performing telecom companies was a key industry benefit gained with the implementation of Pai’s “Restoring Internet Freedom Order,” implemented on Jan. 8, 2018. That FCC Order swept away former FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler’s favored classification of broadband as a “telecommunications service,” which is subject to oversight, and instead put it firmly back in unregulated territory as an “information service.” That proved helpful to CenturyLink’s argument:
In making its decision the FCC broadly preempted state regulation and decided that “regulation of broadband Internet access service should be governed principally by a uniform set of federal regulations, rather than by a patchwork that includes separate state and local requirements.” The FCC expressly preempted any ‘public utility-type’ regulations, . . . akin to those found in Title II of the Act and its implementing rules . . .”
Frontier’s lawyers made so much noise about the prospect of internet complaints being heard at public hearings, the Commission elected to allow Frontier to draft the public hearing notices that would be inserted into customer bills and published in newspapers around the state. The Commission also allowed Frontier to clarify the limits of the Commission’s jurisdiction over internet service — a decision it would soon regret.
Minnesota is unusual because it is served by dozens of smaller, typically independent telephone companies, which include Frontier and its subsidiary Citizens Telecommunications of Minnesota.
Give Frontier an inch, and they take a mile, according to some company critics who told Stop the Cap! were astonished on April 30th when Frontier shared its draft notice with the public. The Minnesota attorney general’s office politely characterized Frontier’s notice as a “very narrow reading of the Commission’s jurisdiction over internet service.”
Here it is, as originally proposed by Frontier in April:
The jurisdiction of the MPUC includes telephone services, but does not include Internet services or the speed or quality of access or connections to the Internet or the communications services, such as Voice Over IP, that are provided using only the Internet.
The attorney general’s office objected to Frontier’s characterization of VoIP phone service as completely unregulated. A subsequent proposed revision by Frontier was not welcomed by the attorney general’s office either:
The jurisdiction of the MPUC includes telephone services, but does not include Internet access services or the rates, speed, quality, or availability of Internet services.
After motions to reconsider, the Commission ultimately reversed its earlier decision allowing Frontier to write its own text:
While the Commission does not want to mislead the public into believing the Commission has jurisdiction over matters that are solely within the province of federal entities, neither does the Commission want to erroneously disavow any aspect of the jurisdiction it does have over the goods and services that Frontier provides to its Minnesota customers.
Given the tension between these two objectives—and the fact that this dispute is arising in the context of drafting the language of a public notice—the Commission will resolve this matter by simply eliminating the requirement that the notice address the topic of the Commission’s jurisdiction over aspects of internet services.
Frontier DSL in Watertown: “47 minutes to upload one small photo to Facebook.”
While Frontier argues about jurisdiction issues, customers like Dr. Kathleen McCann — a dentist serving rural Watertown Township in Carver County, share their stories about how inadequate internet access directly harms local communities, and in her case, her patients.

Dr. McCann
“Frontier Communications is my only option for internet,” McCann told regulators. “My internet service is worse than dial-up. I am charged for ‘DSL High Speed Broadband’ on my monthly bill, but my download speeds are only averaging 2 Mbps and the upload speeds average 0.28 Mbps. As a dentist, I am not able to email dental X-rays. It took me 47 minutes to upload one small photo to Facebook recently.”
McCann added what is even worse than her DSL speed is Frontier’s service. She claims there are “frequent drops” every day, and a technician from Frontier measured an average of 20 small service outages a day. One day her service dropped 400 times. Outages can last days.
“The most recent Frontier internet outage began March 3 and as of March 7, there are at least 27 homes in my neighborhood still without internet service,” McCann added. “This is unacceptable, especially since many of these 27 Frontier customers are running their businesses entirely from home. Calls to Frontier, when finally answered after sometimes 40 minutes on hold, are ineffective.”
Public meetings to discuss Frontier service are scheduled in these areas of Minnesota (exact locations to be determined):
- Ely: September 4, 2018, at 6:00 p.m.
- McGregor: September 5, 2018, at 6:00 p.m.
- Wyoming: September 12, 2018, at 6:00 p.m.
- Slayton: September 25, 2018, at 6:00 p.m.
- Lakeville: September 26, 2018, at 2:00 p.m. and 6:00 p.m.
 As gigabit internet becomes more common across the United States, some ISPs are seeking a speed advantage by offering even faster speeds to residential and business customers. On Tuesday, Nokia announced Frontier Communications and Rochester, N.Y.-based Greenlight Networks would be upgrading their fiber networks to the company’s XGS-PON solution, which can handle 10 Gbps upload and download speeds.
As gigabit internet becomes more common across the United States, some ISPs are seeking a speed advantage by offering even faster speeds to residential and business customers. On Tuesday, Nokia announced Frontier Communications and Rochester, N.Y.-based Greenlight Networks would be upgrading their fiber networks to the company’s XGS-PON solution, which can handle 10 Gbps upload and download speeds. Next generation XGS-PON allows up to 10 Gbps in both directions over existing fiber networks. In fact, the technology is future proof, allowing operators to immediately upgrade to faster speeds and later move towards Full TWDM-PON, an even more robust technology, without expensive network upgrades.
Next generation XGS-PON allows up to 10 Gbps in both directions over existing fiber networks. In fact, the technology is future proof, allowing operators to immediately upgrade to faster speeds and later move towards Full TWDM-PON, an even more robust technology, without expensive network upgrades. Frontier intends to deploy Nokia’s technology in ex-Verizon markets in California, Texas, and Florida, beginning in Dallas-Fort Worth. It will allow Frontier to beef up its FiOS network and market stronger broadband products to Texas businesses. In Rochester, Greenlight will use the technology to upgrade its fiber service, which competes locally with Frontier DSL and Charter/Spectrum. Spectrum recently introduced gigabit download speed in Rochester. Greenlight can now expand beyond its 1 Gbps offering, but more importantly, increase its maximum upload speed beyond 100 Mbps.
Frontier intends to deploy Nokia’s technology in ex-Verizon markets in California, Texas, and Florida, beginning in Dallas-Fort Worth. It will allow Frontier to beef up its FiOS network and market stronger broadband products to Texas businesses. In Rochester, Greenlight will use the technology to upgrade its fiber service, which competes locally with Frontier DSL and Charter/Spectrum. Spectrum recently introduced gigabit download speed in Rochester. Greenlight can now expand beyond its 1 Gbps offering, but more importantly, increase its maximum upload speed beyond 100 Mbps.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Frontier Communications spent more time working on ways to keep Minnesota customers from turning up at upcoming public hearings to discuss their poor service than actually resolving those customers’ service troubles.
Frontier Communications spent more time working on ways to keep Minnesota customers from turning up at upcoming public hearings to discuss their poor service than actually resolving those customers’ service troubles. Based on decades of experience, the PUC staff knew trouble when they saw it, and found the complaints about Frontier credible and serious.
Based on decades of experience, the PUC staff knew trouble when they saw it, and found the complaints about Frontier credible and serious. Christopher Krolak: “I have been a Frontier Communications customer for about 4.5 years. I live in an area where there isn’t a lot of competition for high speed internet. I pay $30 per month for “up to 6 Mbps” service but real world speeds are best case 2 Mbps and fall to 0.3 Mbps during peak times. When I’ve called about the large discrepancy between advertised speed and actual speed, Frontier has responded that the area I live in is only provisioned for about 2 Mbps speed and an infrastructure upgrade is required. Frontier is unwilling to give any timeline forecast for when such upgrade will be made.”
Christopher Krolak: “I have been a Frontier Communications customer for about 4.5 years. I live in an area where there isn’t a lot of competition for high speed internet. I pay $30 per month for “up to 6 Mbps” service but real world speeds are best case 2 Mbps and fall to 0.3 Mbps during peak times. When I’ve called about the large discrepancy between advertised speed and actual speed, Frontier has responded that the area I live in is only provisioned for about 2 Mbps speed and an infrastructure upgrade is required. Frontier is unwilling to give any timeline forecast for when such upgrade will be made.”


 Last week, AT&T announced its intention to abandon an appeal of a decision of the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals granting the Federal Trade Commission the right to continue its lawsuit against AT&T for speed throttling its “unlimited data” wireless customers.
Last week, AT&T announced its intention to abandon an appeal of a decision of the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals granting the Federal Trade Commission the right to continue its lawsuit against AT&T for speed throttling its “unlimited data” wireless customers.
 While AT&T publicly expressed confidence about its appeal right up to the day it abandoned it,
While AT&T publicly expressed confidence about its appeal right up to the day it abandoned it, 
 AT&T does not see fixed wireless millimeter wave broadband in your future if you live in or around a major city.
AT&T does not see fixed wireless millimeter wave broadband in your future if you live in or around a major city.


