 This week, the FCC announced bidding has finished for the latest Connect America Fund (CAF) broadband subsidies auction.
This week, the FCC announced bidding has finished for the latest Connect America Fund (CAF) broadband subsidies auction.
Once again, the FCC gave first priority to incumbent phone companies to bid for the subsidies, which defray the cost of expanding internet access to homes and businesses otherwise unprofitable to serve. Nearly $2 billion was left on the table by disinterested phone companies after the first round of bidding was complete, so the FCC’s second round opened up the leftover money to other telecom companies.
Winning bidders will receive their portion of $198 million annually in 120 monthly installments over the next ten years to build out rural networks. In return, providers must promise to deliver one broadband and voice service product at rates comparable to what urban residents pay for service. The winning bids, still to be publicly announced, will come from rural electric and phone cooperatives, satellite internet providers, fixed wireless companies, and possibly a handful of cable operators. But much of the money overall will be spent by independent phone companies rolling out slow, copper-based, DSL service.
Because the total committed will take a decade to reach providers, rural Americans will likely face a long wait before what purports to be “broadband” actually reaches their homes and businesses.
While many co-ops will spend the money to expand their own homegrown fiber-to-the-home services, most for-profit providers will rely on wireless or copper networks to deliver service.

Telefónica Spain
Overseas, broadband expansion is headed in another direction — expansion of fiber-to-the-home service, with little interest in investing significant sums on furthering old technology copper wire based DSL and fixed wireless services. The expansion is moving so quickly, Verizon made certain to sign long-term contracts with optical fiber suppliers like Corning in 2017 to guarantee they will not be affected by expected shortages in optical fiber some providers are already starting to experience.
Virtually everywhere in developed countries (except the United States), fiber broadband is quickly crowding out other technologies, despite the significant cost of replacing copper networks with new optical fiber cables. If a provider is brave enough to discount investor demand for quick returns and staying away from big budget upgrade efforts, the rewards include happier customers and a clear path to increased revenue and business success.
 Not every Wall Street bank is reluctant to support fiber upgrades. Credit Suisse sees a need for optical fiber today, not tomorrow among incumbent phone and cable companies.
Not every Wall Street bank is reluctant to support fiber upgrades. Credit Suisse sees a need for optical fiber today, not tomorrow among incumbent phone and cable companies.
“The cost of building fiber is less than the cost of not building fiber,” the bank advised its clients. The reason is protecting market share and revenue. Phone companies that refuse to upgrade or move at a snail’s pace to improve their broadband product (typically DSL offering 2-12 Mbps) have lost significant market share, and those losses are accelerating. Ditching copper also saves companies millions in maintenance and repair costs.
Canada’s Telus is a case in point. Its CEO, Darren Entwistle, reports Telus’ effort to expand fiber optics across its western Canada service area is already paying off.
“We see churn rates on fiber that are 25% lower than copper,” Entwistle said. “35% lower in high-speed internet access, and 15% lower on TV — 25% lower on average. We’re seeing a reduction in repair volumes to the tune of 40%. We’re seeing a nice improvement in revenue per home of close to 10%.”
Telus promotes its fiber to the home initiative in western Canada as a boost to medical care, education, the economy, and the Canadian communities it serves. (1:31)
Telus’ chief competitor is Shaw Communications, western Canada’s largest cable company. Fiber optics allows Telus to vastly expand internet speeds and reliability, an improvement over distance sensitive DSL. Shaw Cable has boosted its own broadband speeds and offers product bundles that have been largely responsible for Telus’ lost customers, until its fiber network was switched on.
In economically challenged regions, fiber optic expansion is also growing, despite the cost. In Spain, Telefónica already provides service to 20 million Spaniards, roughly 70% of the country, and plans to continue reaching an additional two million homes and businesses a year until the country is completely wired with optical fiber. In Brazil, seven million customers will have access to fiber to the home service this year, expanding to ten million by 2020.
Verizon and AT&T regularly ring alarm bells in Congress that China is outpacing the United States in 5G wireless development, but are strangely silent about China’s vast and fast expansion into fiber optic broadband that companies like Verizon stopped significantly expanding almost a decade ago. China already has 328 million homes and businesses wired for fiber and added another five million homes in the month of June alone. AT&T will take a year to bring the same number of its own customers to its fiber to the home network.
The three countries that are most closely aligned with the mentality of most U.S. providers — the United Kingdom, Australia, and Germany — are changing their collective minds about past arguments that fiber to the home service is too costly and isn’t necessary.
The government of Martin Turnbull’s cost concerns forced a modification of the ambitious proposal by the previous government to deploy fiber to the home service to most homes and businesses in the country. That decision to spend less is coming back to haunt the country after Anne Hurley, a former chief executive of the Communications Alliance involved in the National Broadband Network (NBN), admitted the cheaper NBN will face an expensive, large-scale replacement within a decade.
ABC Australia reports on findings that the country’s slimmed-down National Broadband Network is inadequate, and parts will have to be scrapped within 5-10 years (1:37)
Turnbull’s government advocated for less expensive fiber to the neighborhood technology that would still rely on a significant amount of copper wiring installed decades ago. The result, according to figures provided to a Senate committee, found only a quarter of Australians will be able to get 100 Mbps service from the NBN, with most getting top speeds between 25-50 Mbps.
Despite claims of technical advancements in DSL technology which have claimed dramatic speed improvements, Hurley was unimpressed with performance tests in the field and declared large swaths of the remaining copper network will have to be ripped up and replaced with optical fiber in just 5-10 years.
“If you look around the world other nations are not embracing fiber-to-the-[neighborhood] and copper … so yes, it’s all going to have to go and have to be replaced,” she said.
 In the United Kingdom, austerity measures from a Conservative government and a reluctant phone company proved ruinous to the government’s promise to deliver “superfast broadband” (at least 24 Mbps) over a fiber to the neighborhood network critics called inadequate from the moment it was switched on in 2012. The government had no interest in financing a fiber to the home network across the UK, and BT Openreach saw little upside from spending billions upgrading the nation’s phone lines it now was responsible for maintaining as a spun-off entity from BT. In 2015, BT Openreach’s chief technology officer called fiber to the home service in Britain “impossible” and too expensive.
In the United Kingdom, austerity measures from a Conservative government and a reluctant phone company proved ruinous to the government’s promise to deliver “superfast broadband” (at least 24 Mbps) over a fiber to the neighborhood network critics called inadequate from the moment it was switched on in 2012. The government had no interest in financing a fiber to the home network across the UK, and BT Openreach saw little upside from spending billions upgrading the nation’s phone lines it now was responsible for maintaining as a spun-off entity from BT. In 2015, BT Openreach’s chief technology officer called fiber to the home service in Britain “impossible” and too expensive.
Two years later, while the rest of Europe was accelerating deployment of fiber to the home service, the government was embarrassed to report its broadband initiative was a flop in comparison, and broke a key promise made in 2012 that the UK would have the fastest broadband in Europe by 2015. Instead, the UK has dropped in global speed rankings, and is now in mediocre 35th place, behind the United States and over a dozen poorer members of the EU.
What was “impossible” two years ago is now essential today. The latest government commitment is to promote optical fiber broadband using a mix of targeted direct funding, “incentives” for private companies to wire fiber without the government’s help, and a voucher program defraying costs for enterprising villages and communities that develop their own innovative broadband enhancements. The best the government is willing to promise is that by 2033 — 15 years from now — every home in the UK will have fiber broadband.

Deutsche Telekom echoed BT Openreach with claims it was impossible to deliver fiber optic broadband throughout an entire country.
Deutsche Telekom’s dependence on broadband-enhancements-on-the-cheap — namely speed improvements by using vectoring and bonded DSL are increasingly unpopular for offering too little, too late in the country. Deutsche Telekom applauded itself for supplying more than 2.5 million new households with VDSL service in 2017, bringing the total number served by copper wire DSL in Germany to around 30 million. The company, which handles landline, broadband and wireless phone services, is slowly being dragged into fiber broadband expansion, but on a much smaller scale.
In March, Telekom announced a fiber to the home project in north-east Germany’s Western Pomerania/Rügen district for 40,000 homes and businesses. The network will offer speeds up to 1 Gbps. In July, Telekom was back with another announcement it was building a fiber optic network for Stuttgart and five surrounding districts Böblingen, Esslingen, Göppingen, Ludwigsburg, and Rems-Murr, encompassing 179 cities and municipalities. But most of the work will focus on wiring business parks. Residents will have a 50% chance of getting fiber to the home service by 2025, with the rest by 2030.
In contrast, the chances of getting fiber optic broadband in the U.S. is largely dependent on which provider(s) offer service. In the northeast, Verizon and Altice/Cablevision will go head to head competing with all-fiber networks. Customers serviced by AT&T also have a good chance of getting fiber to the home service… eventually, if they live in an urban or suburban community. Overbuilders and community broadband networks generally offer fiber service as an alternative to incumbent phone and cable companies, but many consumers don’t know about these under-advertised competitors. The chances for fiber optic service are much lower if you live in an area served by a legacy independent phone company like Frontier, Consolidated, Windstream, or CenturyLink. Their cable competitors face little pressure to rush upgrades to compete with companies that still sell DSL service offering speeds below 6 Mbps.
CAF funding from the FCC offers some rural areas a practical path to upgrades with the help of public funding, but with limited funds, a significant amount will be spent on yesterday’s technology. In just a few short years, residents will be faced with a choice of costly upgrades or a dramatic increase in the number of underserved Americans stuck with inadequate broadband. Policymakers should not repeat the costly mistakes of the United Kingdom and Australia, which resulted in penny wise-pound foolish decisions that will cost taxpayers significant sums and further delay necessary upgrades for the 21st century digital economy. The time for fiber upgrades is now, not in the distant future.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Google may be considering renewing expansion of its fiber to the home networks with a new technology that can extend network distances and cut costs.
Google may be considering renewing expansion of its fiber to the home networks with a new technology that can extend network distances and cut costs.
 Phone companies can beat their cable competitors, but only if they invest in fiber upgrades that can deliver as-advertised broadband service and speed.
Phone companies can beat their cable competitors, but only if they invest in fiber upgrades that can deliver as-advertised broadband service and speed.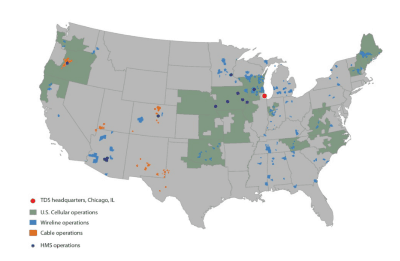 TDS has been overbuilding beyond its existing telephone service areas to deliver broadband, phone, and television service to communities evaluated as:
TDS has been overbuilding beyond its existing telephone service areas to deliver broadband, phone, and television service to communities evaluated as: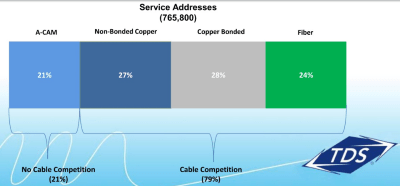 In rural areas, the company is combining federal Connect America Funds with its own money to deploy bonded DSL service in areas too unprofitable to serve with fiber. This typically delivers faster internet service than rural broadband rollouts from other phone companies like Windstream and Frontier.
In rural areas, the company is combining federal Connect America Funds with its own money to deploy bonded DSL service in areas too unprofitable to serve with fiber. This typically delivers faster internet service than rural broadband rollouts from other phone companies like Windstream and Frontier. For residents of 10 Mississippi communities, an alternative broadband option is now available delivering up to 120/50 Mbps speed with no data caps or throttling for a flat $50 a month, taxes and fees included.
For residents of 10 Mississippi communities, an alternative broadband option is now available delivering up to 120/50 Mbps speed with no data caps or throttling for a flat $50 a month, taxes and fees included.
