 The Federal Trade Commission today filed a lawsuit against AT&T for its practice of subjecting grandfathered unlimited data customers to speed throttles that dramatically cut speeds up to 90 percent after customers use more than 3GB of data on AT&T’s 3G network or 5GB on its 4G network. Thus far, according to the FTC, AT&T has throttled at least 3.5 million unique customers a total of more than 25 million times.
The Federal Trade Commission today filed a lawsuit against AT&T for its practice of subjecting grandfathered unlimited data customers to speed throttles that dramatically cut speeds up to 90 percent after customers use more than 3GB of data on AT&T’s 3G network or 5GB on its 4G network. Thus far, according to the FTC, AT&T has throttled at least 3.5 million unique customers a total of more than 25 million times.
The FTC’s complaint alleges that the company failed to adequately disclose to its customers on unlimited data plans that, if they reach a certain amount of data use in a given billing cycle, AT&T reduces – or “throttles” – their data speeds to the point that many common mobile phone applications – like web browsing, GPS navigation and watching streaming video – become difficult or nearly impossible to use.
“AT&T promised its customers ‘unlimited’ data, and in many instances, it has failed to deliver on that promise,” said FTC Chairwoman Edith Ramirez. “The issue here is simple: ‘unlimited’ means unlimited.”
FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler publicly complained about Verizon’s plans to start a similar throttling program on its wireless network, questioning the fairness of cutting speeds for certain customers while exempting others. Both Verizon and AT&T have claimed speed throttles are part of a fair usage policy that allows all customers to share its wireless resources. Broadband providers have often painted a picture of a “bandwidth hog” taking a disproportionate share of network resources away from other customers, but there is no evidence heavier users are creating conflicts for other users, especially as wireless carriers encourage customers to use more data.
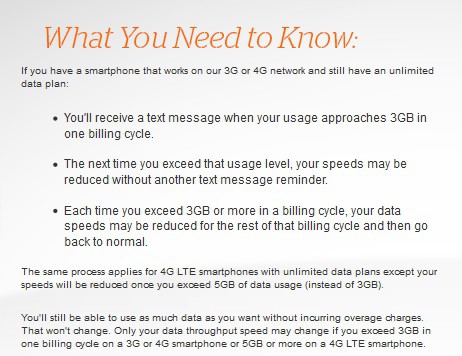
From AT&Ts website
The logic of rationing Internet use for unlimited customers while providing unlimited access to those willing to pay usage-based charges escaped the FTC, which is what brought the suit.
According to the FTC’s complaint, AT&T’s marketing materials emphasized the “unlimited” amount of data that would be available to consumers who signed up for its unlimited plans. The complaint alleges that, even as unlimited plan consumers renewed their contracts, the company still failed to inform them of the throttling program. When customers canceled their contracts after being throttled, AT&T charged those customers early termination fees, which typically amount to hundreds of dollars.
The FTC alleges that AT&T, despite its unequivocal promises of unlimited data, began throttling data speeds in 2011 for its unlimited data plan customers after they used as little as 2 gigabytes of data in a billing period. According to the complaint, the throttling program has been severe, often resulting in speed reductions of 80 to 90 percent for affected users.
According to the FTC’s complaint, consumers in AT&T focus groups strongly objected to the idea of a throttling program and felt “unlimited should mean unlimited.” AT&T documents also showed that the company received thousands of complaints about the slow data speeds under the throttling program. Some consumers quoted the definition of the word “unlimited,” while others called AT&T’s throttling program a “bait and switch.” Many consumers also complained about the effect the throttling program had on their ability to use GPS navigation, watch streaming videos, listen to streaming music and browse the web.
The complaint charges that AT&T violated the FTC Act by changing the terms of customers’ unlimited data plans while those customers were still under contract, and by failing to adequately disclose the nature of the throttling program to consumers who renewed their unlimited data plans.
FTC staff worked closely on this matter with the staff of the Federal Communications Commission.
The Commission vote authorizing the staff to file the complaint was 5-0. The complaint was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California, San Francisco Division.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Federal Communications Commission announced Friday it will
The Federal Communications Commission announced Friday it will 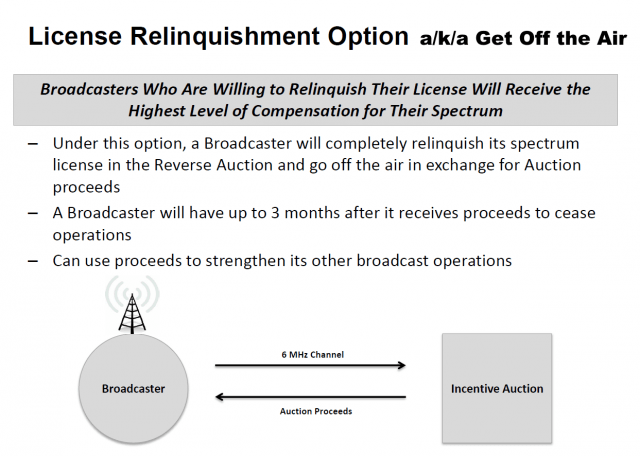 There is so much money to be made buying and selling the public airwaves — at least twice as much as broadcasters originally anticipated– spectrum speculators have also jumped on board, snapping up low power television station construction permits and existing stations with hopes of selling them off the air in return for millions in compensation. Wireless customers are effectively footing the bill for the auction as wireless companies bid for the additional spectrum. Television stations will receive 85% of the proceeds, the FCC will keep 15%.
There is so much money to be made buying and selling the public airwaves — at least twice as much as broadcasters originally anticipated– spectrum speculators have also jumped on board, snapping up low power television station construction permits and existing stations with hopes of selling them off the air in return for millions in compensation. Wireless customers are effectively footing the bill for the auction as wireless companies bid for the additional spectrum. Television stations will receive 85% of the proceeds, the FCC will keep 15%. Major network-affiliated or owned stations in major cities are unlikely to take the deal. But in medium and smaller-sized markets where conglomerates own and operate most television stations, there is a greater chance some will be closed down, moved to a lower channel, or transferred to a digital sub-channel of a co-owned-and-operated station in the same city. The most likely targets for shutdown will be independent, CW and MyNetworkTV affiliates. In smaller cities, multiple network affiliates owned by one company could be combined, relinquishing one or more channels in return for tens of millions in cash compensation.
Major network-affiliated or owned stations in major cities are unlikely to take the deal. But in medium and smaller-sized markets where conglomerates own and operate most television stations, there is a greater chance some will be closed down, moved to a lower channel, or transferred to a digital sub-channel of a co-owned-and-operated station in the same city. The most likely targets for shutdown will be independent, CW and MyNetworkTV affiliates. In smaller cities, multiple network affiliates owned by one company could be combined, relinquishing one or more channels in return for tens of millions in cash compensation.


 “Marriott has a strong interest in ensuring that when our guests use our Wi-Fi service, they will be protected from rogue wireless hot spots that can cause degraded service, insidious cyber-attacks and identity theft,” Marriott said in a statement. “Like many other institutions and companies in a wide variety of industries, including hospitals and universities, the Gaylord Opryland protected its Wi-Fi network by using FCC-authorized equipment provided by well-known, reputable manufacturers. We believe that the Opryland’s actions were lawful. We will continue to encourage the FCC to pursue a rule making in order to eliminate the ongoing confusion resulting from today’s action and to assess the merits of its underlying policy.”
“Marriott has a strong interest in ensuring that when our guests use our Wi-Fi service, they will be protected from rogue wireless hot spots that can cause degraded service, insidious cyber-attacks and identity theft,” Marriott said in a statement. “Like many other institutions and companies in a wide variety of industries, including hospitals and universities, the Gaylord Opryland protected its Wi-Fi network by using FCC-authorized equipment provided by well-known, reputable manufacturers. We believe that the Opryland’s actions were lawful. We will continue to encourage the FCC to pursue a rule making in order to eliminate the ongoing confusion resulting from today’s action and to assess the merits of its underlying policy.”
 Wheeler also questioned how Verizon could justify its planned speed throttling under the conditions it agreed to after winning the 700MHz “C Block.” That spectrum was accompanied by a special FCC mandate – open platform rules which prohibits Verizon Wireless from denying, limiting, or restricting the ability of end users to download and use applications of their choosing on the C Block networks. A speed throttle would make using some applications impossible.
Wheeler also questioned how Verizon could justify its planned speed throttling under the conditions it agreed to after winning the 700MHz “C Block.” That spectrum was accompanied by a special FCC mandate – open platform rules which prohibits Verizon Wireless from denying, limiting, or restricting the ability of end users to download and use applications of their choosing on the C Block networks. A speed throttle would make using some applications impossible.