Phillip Dampier
Lobbyists, corporate executives, and several interest groups are busy lobbying the newest additions to the Federal Communications Commission in an all-out effort to stop Net Neutrality.
The Hill newspaper today reports Mignon Clyburn, daughter of House Majority Whip James Clyburn (D-S.C.), is particularly under pressure to reject Net Neutrality. The Hill reports industry lobbyists believe that if her father is amenable to their position, his daughter might also be. To date, several hundred letters from minority groups and organizations, many opposed to Net Neutrality, have been filed with the FCC.
After reviewing dozens of those letters, it’s readily apparent many are the fruits of AT&T and Verizon lobbying labor, because several adopt both companies’ anti-Net Neutrality talking points, often word for word.
Even the newest Republican commissioner, Meredith Attwell Baker, is under a lobbying assault.
The thinking on K Street is that Baker’s views on net neutrality may not be set. Lobbyists and corporate executives have sought out Baker before the FCC votes on a final rule sometime next year.
“They are trying to get in there and remind her where she comes from to shore up her vote for the anti-net neutrality camp,” said one lobbyist working on the issue.
While the special interest blitz attempts to kill Net Neutrality, one pro-Net Neutrality advocate got into a dispute with some of the minority interest groups opposing Net Neutrality, which was gleefully covered by the broadband industry trade press. Public Knowledge got a bit too close to a nerve of several of these groups who put their logos on a letter sent to the FCC opposing Net Neutrality. The letter represents the groups’ concerns that broadband for many in America is simply not available, especially for the economically disadvantaged. They’ve been swayed by industry propaganda to characterize Net Neutrality as a threat to addressing the digital divide by making service ultimately even more expensive. Some of those groups fired back against Public Knowledge, offended by some of the language used on their blog they felt suggested minority groups were naive and possibly even “selling out” the people they represent. A few public exchanges later led to an apology from Public Knowledge if feelings were hurt and a plea from Free Press to put aside some of the personal disputes and rhetoric and argue the merits of the issue pro or con.
We agree with Free Press that personality disputes and pointless name calling don’t work and serve only to distract from the issues at hand. These groups advocating against Net Neutrality should be open to receiving additional information that doesn’t come from the broadband industry, particularly arguments that debunk those fear-mongering industry talking points. Perhaps those groups will be amenable to changing their position once they gather additional facts.
But we also feel the first rule of politics must always be to “follow the money” and that is true for non-profits, for-profits, and government interests. There must be full disclosure of the financial support and board membership of all of the groups claiming to represent consumer and minority interests. Consumers, and more importantly members of the groups themselves, deserve to know where the money is coming from and if their boards have members working for or with the telecommunications industry or its friends.
For example, in our own research of the background of 100+ members of Broadband for America, we found instances of telecommunications industry involvement in virtually every single group. If one chooses to believe that is a coincidence and still feels comfortable with that organization, so be it. However, if one is concerned to learn that in several cases those ties were being scrubbed from interest groups’ websites, or were not openly disclosed to members, learning about that could be a cause of concern. People should have the right to make an informed decision. Some of the groups complaining about Public Knowledge are also members of Broadband for America and have telecommunications industry money backing them. There is nothing wrong, in my judgment, in making sure that information is out there for readers to consider.
Be aware that while pro-Net Neutrality groups ring their hands over potentially offending one another, opponents are wasting no time mass mailing anti-Net Neutrality correspondence to the FCC. Let’s remember our first priority is to fight for Net Neutrality. If a group is offended, send them flowers, apologize quickly if you must, and be done with it. Don’t entertain the trade press.
Navarrow Wright on BlackWeb 2.0 called proponents of Net Neutrality “digital elites” and then condensed many of the industry talking points that are common to many of the anti-Net Neutrality letters heading to the FCC:
- The risk that a regressive pricing mandate that net neutrality rules could impose will shift online costs to the poor is real.
- The risk that over-regulation will depress deployment and access is real.
- The risk that restrictions on network management will reduce the quality and reliability of Internet service for light users — students, the poor on fixed incomes, the elderly, and community organizers who rely on Internet access to reach their communities – is real.
Wright doesn’t bother to provide any evidence to back up these claims. Underlining the word real does not make it reality.
We recognize these talking points from the broadband industry’s lobbying efforts against Net Neutrality. The industry scare tactic about raised prices is exactly the same one they use to justify Internet Overcharging schemes like forced consumption billing and usage caps, despite earning healthy profits and enjoying a decline in their traffic costs. Read the financial reports from the major players about broadband profits for yourself. Don’t take our word for it.
Net Neutrality simply demands the status quo — open and equal access to everyone, including the economically disadvantaged Wright is concerned about. If Wright is concerned about the cost of broadband services for the economically disadvantaged, giving the providers the right to monetize content delivery in new ways, it will lead to even higher prices than we cope with today.
Industry rate hikes come in spite of Net Neutrality, and we call on Wright to join our effort to demand increased competition so these kinds of price increases become untenable. Time Warner Cable, the nation’s second largest provider, is busily increasing prices for Road Runner service right now in several regions, even without the “imminent threat” of Net Neutrality.
Net Neutrality is hardly “over regulation,” and the empty rhetoric about it depressing investment, deployment, and access has been made every time this industry has faced the prospect of some oversight. Wright should remember the industry used the same arguments to resist universal wiring requirements made in franchise agreements to guarantee that income challenged neighborhoods had the same access to cable and telephone broadband services as wealthy suburbs. In their fight to obtain quick and simple statewide video franchising, they argued that without it, it would discourage investment, deployment, and access to competition. Regulating rates? Same argument. The Discovery Institute, which has produced suspect studies on demand for the industry, paid for by the industry, provides an excellent example of “we’ve heard this song before” in comments they made to the FCC back in 2006 to try and reform cable franchising:
V. LEVEL-PLAYING-FIELD REQUIREMENTS ARE ANTICOMPETITIVE
Build-out requirements were an appropriate quid pro quo for the telephone, cable and wireless companies who received an exclusive franchise. An exclusive franchise ensured the viability of average pricing by eliminating the risk of cherry-picking by a competitive entrant, and allowed providers to serve the most profitable customers first who could then, in turn, subsidize the cost of serving everyone else.
Competitive entrants already have an incentive to expand their networks: They must produce consistent revenue gains, and the cost of adding additional users declines as a network grows. But unless flexibly and intelligently applied, a build-out requirement threatens the entire undertaking by creating the possibility that the initial investment will be effectively lost if, for whatever reason, it just isn’t possible to meet the deadline. The evidence that cities possess the inclination to perform this thoughtful and delicate task is entirely conjectural.
Build-out is typically not required of competitive entrants, because it imposes costs that may not be recoverable in a competitive market. Exceptions are Personal Communications Service (PCS) providers and Eligible Telecommunications Carriers (ETCs). However, these examples are clearly distinguishable. As the Commission has noted in another context, the grant of a PCS license confers on the licensee an exclusive right to use a designated portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. In that decision, the Commission rejected a Texas build-out requirement applicable to competitive entrants in the local exchange market.
ETCs are required to provide service and advertise their rates throughout the area for which they seek Universal Service support, but an ETC has the right to resell another carrier’s services. There is no suggestion in the current proceeding that telephone companies seeking to offer video services should have the right to resell the services of the incumbent cable operator, nor should there be. However, in view of the fact that telephone companies cannot be assured of the capital needed to build out their advanced services networks, a resale requirement would probably be the only practical way ensure that a competitive entrant could serve every household.
Build-out is not the same thing as redlining. Redlining is illegal, but by its terms, 47 U.S.C. 621(a)(4)(A) does not require build-out. It merely imposes a reasonableness requirement on the amount of time locally-enacted build-out requirements provide for the competitive entrant to serve every household. There is no Congressional mandate for build-out.
Since cable operators are not required to offer voice services to every household, it is not clear why telephone companies should be required to offer video services throughout their service area. There is no way to predict whether competitive entrants will have access to sufficient capital or be able to gain enough market share to make build-out requirements objectively reasonable. These risk factors suggest that build-out requirements would be anticompetitive.
It is also utter nonsense to suggest network management restrictions will reduce the quality and reliability of Internet service for light users. In fact, the industry’s proposed “light user” solution is a consumption billing scheme that includes usage allowances and limits, overlimit penalties for exceeding them, and consumers forced into limited use plans, often for little or no savings over existing under-marketed “lite” plans.
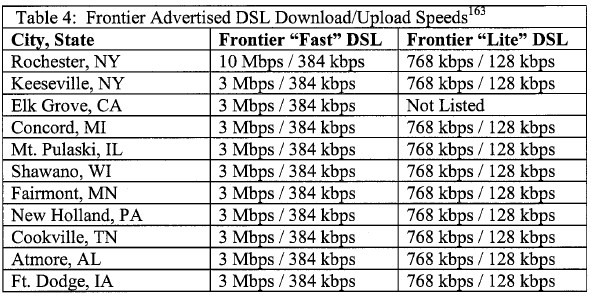
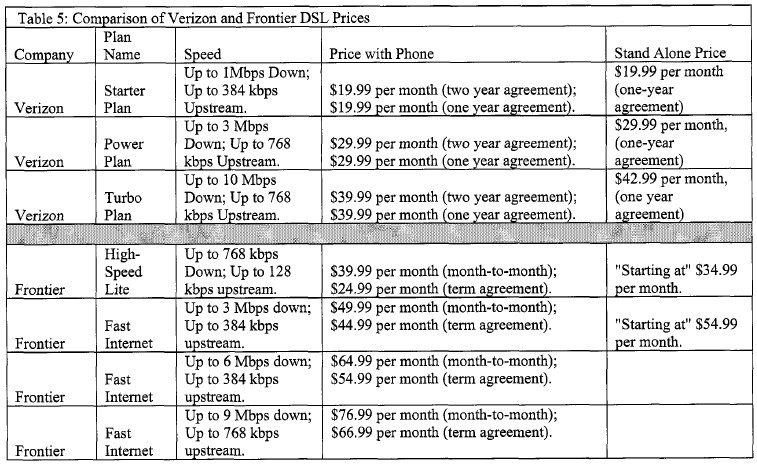
Most providers currently tier broadband based on speed. If a consumer wants to get “light service,” they can purchase a discounted lower speed package perfectly adequate for most web use, and never have to worry about how much they choose to use it. They want to continue offering speed tiers, but also limit customers’ use of their accounts, giving them a paltry usage allowance and then subjecting them to steep penalties for exceeding it. Residents in Rochester, New York fought back against two such schemes advocated by Time Warner Cable and Frontier Communications, the local phone company. It is under the guise of “network management” that these Internet Overcharging schemes were born. A word to the wise – this price gouging hurts the economically disadvantaged far more than wealthy suburbanites.
I also point Wright’s attention to the broadband situation in Canada, which has adopted the viewpoint of our provider friends. There, Internet usage is limited by allowances, with fees of $1-5 per gigabyte for exceeding them. Net Neutrality is not protected, and certain Internet services are “network managed” with speed throttles, reducing their speed by 90% or more, making their use untenable. Yet, Canadian broadband dropped in global broadband rankings, service providers increased prices anyway, and the digital divide Wright is worried about has not been addressed. In fact, it’s arguably worse, because the industry won efforts to also limit and ration wholesale broadband access used by independent service providers to create competitive, lower-priced alternatives.
Does that make Wright stupid or a “sell-out?” Of course not. It means we have a lot of information to share with Mr. Wright and others like him. As consumers ourselves, we believe in getting affordable broadband access to disadvantaged communities, and support Universal Service Fund reform and appropriate stimulus funding, or providing municipally built networks to introduce needed competition to get quality, affordable broadband service into urban and rural homes that are woefully underserved. The industry advocated “don’t regulate us” approach has been in place since the 1990s and has not come close to solving the problem.
It’s our view broadband service is rapidly becoming as important as water, gas and electric, and telephone service, and must be provided to every American that wants a connection, at an affordable price. When private providers won’t do that, it’s time to follow the same path we took to assure electrification of this country decades earlier, with public projects to get the job done.
We think every person should check out these issues for themselves. As a consumer, confronting Internet Overcharging schemes was what got this site started, and once I examined the facts about the profitable state of broadband, and the quest to make it even more profitable at consumer expense, I got angry and involved. That doesn’t make me an “elitist.” It makes me an informed and involved citizen.
We have always told providers this isn’t personal and we respect the work done by the employees to serve their customers. Most of us are customers ourselves. We will debate policy matters and advocate for our position, and try and bring supporting evidence to the table, and let the best argument win. Along the way, disclosing who represents who and where they money comes from is part of that debate.
It will remain our policy to expose industry connections in organizations that purport to advocate for consumer interests, particularly when those connections are not routinely disclosed. Consumers have a right to know whether the industry is writing checks to ostensibly independent groups, or have executives seated on their governing boards, potentially influencing their public policy positions. To not provide this needed information would sell out our readers, and not living up to the standards we set for ourselves.
For the record, Stop the Cap! has zero industry money backing us. We are 100% consumer-funded and have no involvement in any online business or telecommunications company.
 Last spring, consumers across North Carolina banded together to oppose legislation custom-written by the telecommunications industry to keep municipal broadband networks from competing with cable and telephone companies. Your efforts made a dramatic impact on state legislators and the bill was set aside. One representative that helped push it has since resigned after being caught up in a campaign contribution scandal. But we always knew the industry would be back. The threat of competition, and a reduction in their fat profits, is too great to ignore.
Last spring, consumers across North Carolina banded together to oppose legislation custom-written by the telecommunications industry to keep municipal broadband networks from competing with cable and telephone companies. Your efforts made a dramatic impact on state legislators and the bill was set aside. One representative that helped push it has since resigned after being caught up in a campaign contribution scandal. But we always knew the industry would be back. The threat of competition, and a reduction in their fat profits, is too great to ignore.

 Subscribe
Subscribe