South Africa is the latest country on the way to finally discarding Internet Overcharging schemes like usage caps and usage-based billing.
South Africa is the latest country on the way to finally discarding Internet Overcharging schemes like usage caps and usage-based billing.
MWEB, one of South Africa’s largest residential broadband service providers, last week “threw down the gauntlet” and unveiled an unlimited broadband option among its various rate plans.
“We realized there’s a major gap in the market. South Africa doesn’t experience the Internet like the rest of the world does. It’s a fantastic opportunity to change the Internet in South Africa,” MWEB CEO Rudi Jansen told News24.
For a country that has never known anything but expensive, slow, usage-capped Internet, MWEB’s announcement is nothing short of a broadband revolution for 49 million South Africans.
 “This is not the end. There are still probably three or four big things that have to change in this market and for us, this is the first step. The other things that have to change are we have to get the mobile operators to offer wholesale data. The more competition there is, the better it is for the market,” said Jansen.
“This is not the end. There are still probably three or four big things that have to change in this market and for us, this is the first step. The other things that have to change are we have to get the mobile operators to offer wholesale data. The more competition there is, the better it is for the market,” said Jansen.
For $73.50US per month, MWEB offers 4Mbps DSL service that is truly unlimited, which is a radical notion in a country used to usage caps averaging 3GB per month. Customers willing to tolerate slower speeds can reduce their unlimited broadband bill considerably — 384kbps starts at $30 a month; 512kbps is priced at $41 a month. The company does admit to throttling torrent services, but customers have managed to bypass the throttle by encrypting their torrent traffic.
Although these speeds and prices are terrible in comparison to North American broadband plans, for South Africans, MWEB’s announcement was big news. That’s because the competition charges far higher prices, often for limited service:
- Telkom, South Africa’s state phone company, wants $35US monthly, five dollars more than MWEB’s lowest speed unlimited alternative, for its DSL service with a 3GB usage allowance;
- Paying $39.50US per month buys you 10GB of usage from Afrihost;
- Using 3G wireless mobile alternatives are for the deep-pocketed only. Paying $65.50US per month nets you less than a 2GB usage allowance;
- South Africa’s ‘Screamer’ offers a pricey unlimited plan at $54US per month for 384kbps service;
- Neotel offers an unlimited service package, but it’s so confusing few customers can be certain what they’re getting. (Read this South African blogger’s experience with Neotel.)
MWEB hired marketing firm Quirk to generate buzz about the company’s unlimited service option. Earlier this month, a Facebook group called Free the Web popped up asking consumers what improvements were needed in South Africa’s broadband service. It attracted more than 15,000 followers in just two weeks.
 What were South Africans complaining about? Usage caps. Broadband users despise them, especially in a country where 5-10GB allowances are considered ‘generous.’ But the lack of competition for monopoly state-owned phone company Telkom also featured prominently. Most South Africans rely on DSL service that first starts with renting a line from Telkom. Telkom prices those in accordance with its monopoly status, and requires consumers to pay line rental fees combining both data and voice services, even if a customer only intends to use the line for data. Because ADSL broadband speed is totally dependent on the phone company, and Telkom has no incentive to upgrade, few in South Africa can expect to see broadband service exceeding 4-8Mbps. Most obtain considerably less, often well below 1Mbps.
What were South Africans complaining about? Usage caps. Broadband users despise them, especially in a country where 5-10GB allowances are considered ‘generous.’ But the lack of competition for monopoly state-owned phone company Telkom also featured prominently. Most South Africans rely on DSL service that first starts with renting a line from Telkom. Telkom prices those in accordance with its monopoly status, and requires consumers to pay line rental fees combining both data and voice services, even if a customer only intends to use the line for data. Because ADSL broadband speed is totally dependent on the phone company, and Telkom has no incentive to upgrade, few in South Africa can expect to see broadband service exceeding 4-8Mbps. Most obtain considerably less, often well below 1Mbps.
“Telkom has to allow users of ADSL to split the line rental for the telephone line and the line rental for ADSL. That absolutely has to happen; then this market will grow,” Jansen said.

Jansen
MWEB hopes the unveiling of unlimited broadband will transform South Africans use of the Internet and bring prices down.
“Ubiquitous broadband is what this country needs to grow. We want to do our part in getting South Africa there,” said Jansen. “I hope [our competitors] follow us because I think as a country we desperately need it.”
Jansen may have his wish. Hours after MWEB announced unlimited broadband, its competitors began to follow suit, meaning South Africans can finally follow Australians and New Zealanders discarding hated Internet Overcharging schemes.
Mybroadband.co.za took note of several broadband package changes coming as a direct result of MWEB’s new service (One South African Rand = 13.6 US cents):
Vox Telecom responded quickly and announced that @lantic will be launching bundled ADSL offerings – which include both ADSL access and an uncapped ISP account. Pricing starts at R339 for a DSL384 bundle while a 512 Kbps service will cost R589 and a 4 Mbps solution R889. This undercuts MWEB’s bundled pricing by R10 per month.
Openweb also joined the price war by announcing that they will resell MWEB accounts at the same rates as MWEB.
This is however not where it ends. Afrihost said that consumers can look forward to their uncapped ADSL services next week, and G-Connect also indicated that they will respond to MWEB’s recent announcement with a competing service.
Even the state monopoly phone company Telkom has started talking about offering unlimited service.
“Uncapped speed-locked ADSL service consumer offerings are in development. However, no time-frames, offering specifications or price points can be disclosed at this stage. In the development process, Telkom is striving for optimal quality, reliability and affordability,” said Ajith Bridgraj, Telkom Senior Specialist for Media Relations.
MWEB expects a surge of new customers, which leads some to worry if the company can sustain its network under the burden of throngs of new customers. Jansen says they can, noting their connectivity ultimately comes from Seacom, which is an important provider of international connectivity between Africa, Europe, and beyond.
Early tests by Mybroadband appear positive:
MyBroadband got its hands on an uncapped 4 Mbps test account to take the service through its paces – and early test results are very promising.
For basic email and surfing the MWEB uncapped account performed well, and results from Speedtest.net were on par with SAIX and IS based offerings.
Local Speedtest.net downlink speeds ranged between 3.28 Mbps and 4.13 Mbps while local uplink speeds ranged between 0.26 Mbps and 0.42 Mbps.
International Speedtest.net results – tested with servers in London, New York and Brussels – ranged between 2.96 Mbps and 3.61 Mbps while international uplink speeds were fairly steady at between 0.3 Mbps and 0.32 Mbps.
Local latency was fairly consistent and ranged between 17 ms and 41 ms in tests to Johannesburg and Cape Town based servers. International latency was however less consistent, and ranged between 285 ms and 528 ms to the UK and US.
The MWEB uncapped account performed well with all bandwidth intensive applications.
YouTube videos streamed without any buffering, but some buffering was needed when moving to high definition video streaming (480p and more specifically 720p).
Standard file download speeds were quite consistent at between 2 Mbps and 3.4 Mbps while multi-threaded FTP and HTTP downloads sat at around 3.2 Mbps.
Good news for those keen on torrent services is that the MWEB uncapped account seems torrent friendly. We selected 10 of the most popular torrents, and total download speeds ranged between 2.8 Mbps and 3.2 Mbps.
American broadband providers contemplating Internet Overcharging schemes of their own often point to usage limits and usage-based billing schemes that exist in other countries, implying they are well-tolerated by consumers abroad and should be likewise domestically. The truth is, such pricing schemes are as despised abroad as they are domestically, and most countries seeking to improve broadband consider eliminating them a top priority.
[flv width=”448″ height=”356″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Carte Blanche Consumer – No Broader Than a Band.flv[/flv]
South African news program ‘Carte Blanche’ provides this general overview of the current state of broadband in South Africa, and the challenges that must be faced to improve it. (10 minutes)
[flv width=”384″ height=”308″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/News24 MWEB Unveils Unlimited Broadband 3-19-10.mp4[/flv]
South Africa’s News24 network reported on MWEB’s unlimited broadband package including an interview with MWEB CEO Rudi Jansen. (3 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/South African Broadband.flv[/flv]
As part of MWEB’s social marketing campaign, ordinary South Africans talk about their broadband experiences, what the Internet has done for them, and the things they hate the most about South African Internet Service Providers. (9 minutes)
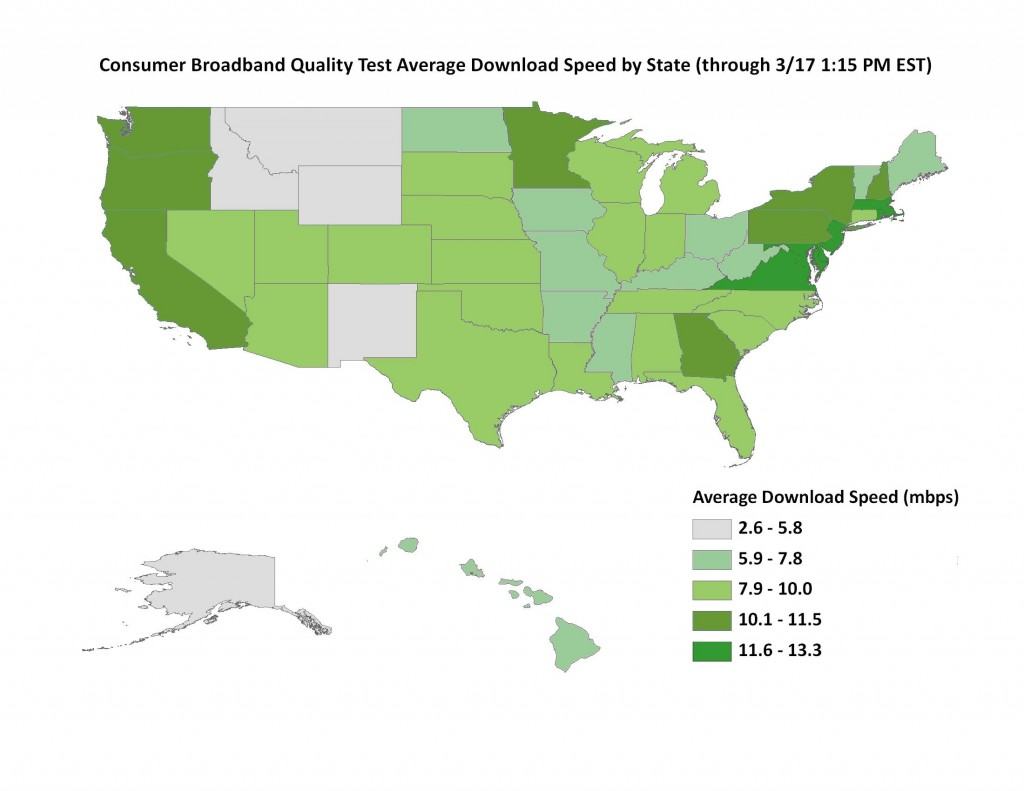
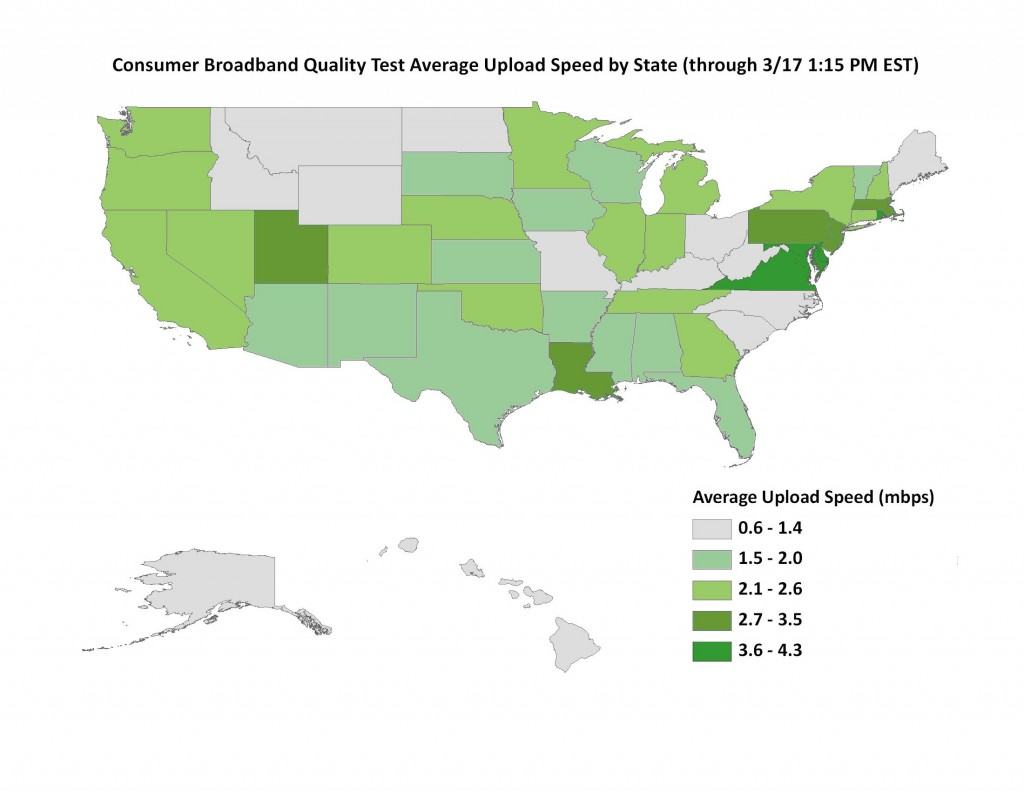
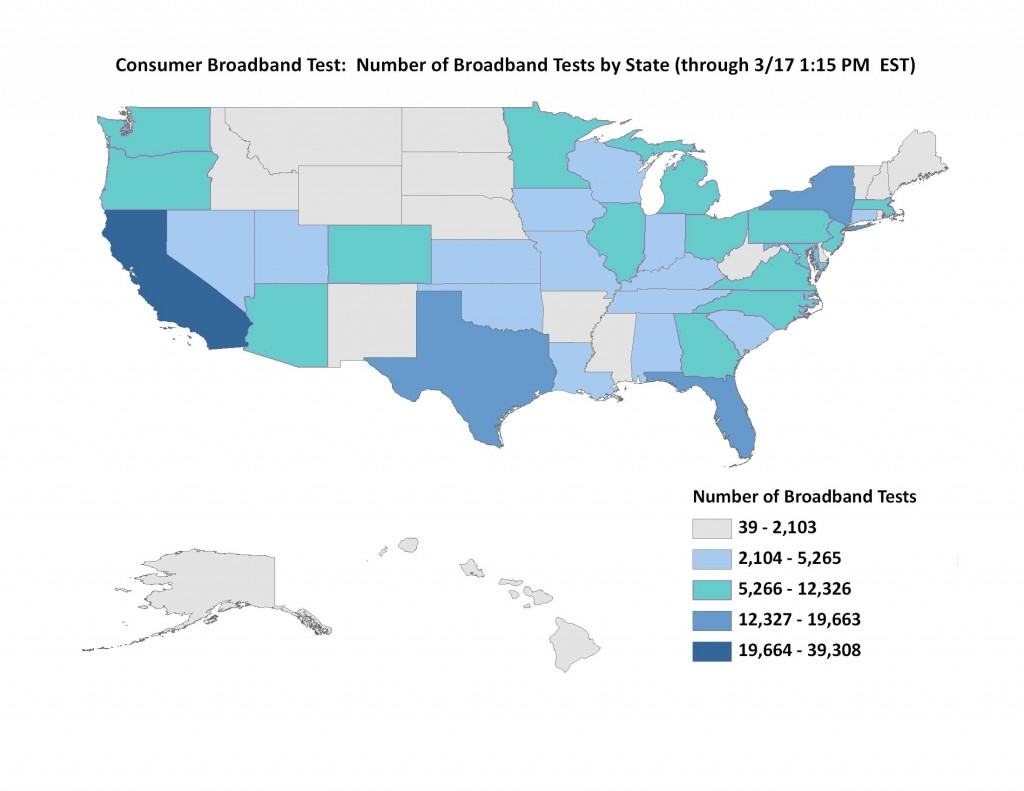 The Federal Communications Commission is catching on to a long-known telecommunications industry secret — always provide top quality, showcase service in areas where the movers and shakers of power and politics can make your life easy or hard. Early results from the Broadband.gov national speed test project confirm this is still the case. After a few weeks of testing, the FCC reports America’s best broadband speeds are available in and near two cities – Washington, DC and New York, NY.
The Federal Communications Commission is catching on to a long-known telecommunications industry secret — always provide top quality, showcase service in areas where the movers and shakers of power and politics can make your life easy or hard. Early results from the Broadband.gov national speed test project confirm this is still the case. After a few weeks of testing, the FCC reports America’s best broadband speeds are available in and near two cities – Washington, DC and New York, NY.

 Subscribe
Subscribe