
Pai
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai has gone all out to defend internet service providers and his plan to jettison Net Neutrality, claiming companies like Twitter and other “edge providers” that offer a platform to a diversity of voices are a much bigger threat to an open internet than companies like AT&T and Comcast.
Speaking at the Future of Internet Freedom conference in Washington, Pai faced down the torrent of criticism that has been expressed about his plans to roll back Title II enforcement of ISPs and Net Neutrality rules that protect internet content from discriminatory behavior. In remarks to the audience, Pai used partisan framing to criticize companies like Twitter that he claims have targeted bans on conservative users who violate its terms and conditions and removes tweets for political reasons.
“Now look, I love Twitter, and I use it all the time,” Pai said. “But let’s not kid ourselves; when it comes to an open internet, Twitter is part of the problem. The company has a viewpoint and uses that viewpoint to discriminate. As just one of many examples, two months ago, Twitter blocked Rep. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.) from advertising her Senate campaign launch video because it featured a pro-life message. Before that, during the so-called Day of Action [to preserve Net Neutrality], Twitter warned users that a link to a statement by one company on the topic of internet regulation ‘may be unsafe.’ And to say the least, the company appears to have a double standard when it comes to suspending or de-verifying conservative users’ accounts as opposed to those of liberal users. This conduct is many things, but it isn’t fighting for an open internet.”
Pai also used additional examples of “edge provider” censorship that he claims targets conservatives far more often than liberals:
- Apple’s app store bars apps from cigar aficionados as promoting tobacco use
- YouTube “restricts videos from the likes of conservative commentator Dennis Prager on subjects he considers ‘important to understanding American values.'”
- Mysterious algorithms target content to specific users but without transparency and disclosure
- Edge providers champion their own free speech while supporting online censorship at the behest of foreign governments for business reasons.
But Pai’s own statements lacked transparency:
- Twitter blocked, then rescinded its block, on one sponsored Tweet from Blackburn that claimed in the ad she ‘stopped the sale of baby body parts.’ Twitter declared the ad was inflammatory and violated Twitter’s advertising standards. Other media fact-checkers were less polite, calling her claim false advertising. “No investigation ever found proof of actual tissue sales. The only criminal charges stemming from the videos were filed against antiabortion activist David Daleiden and another activist in California for violations of privacy. Yet to this day, ‘baby body parts’ remain a rallying cry in conservative and antiabortion circles,” according to a Washington Post story. Twitter’s advertising standards differ from its general code of user conduct.
- Apple’s app store does indeed block apps promoting products deemed harmful to users. There is no financial incentive to block these apps, however. The specific language: “Apps that encourage consumption of tobacco products, illegal drugs, or excessive amounts of alcohol are not permitted on the App Store. Apps that encourage minors to consume any of these substances will be rejected. Facilitating the sale of marijuana, tobacco, or controlled substances (except for licensed pharmacies) isn’t allowed.”
- Pai suggests YouTube is unfairly restricting Mr. Prager’s videos, but in fact it is only placing advisories on some of his more inflammatory content warning the video may not be suitable for some audiences. YouTube also demonetized certain videos, making them ineligible for pre-roll advertisements, primarily because advertisers do not want to be associated with inflammatory content. But no videos have been censored, blocked, or removed. Anyone can view them by acknowledging the content advisory. Members of the LGBTQ community have also been upset with YouTube for similar actions, so there is scant evidence YouTube’s motives are political and target conservatives.
- Pai’s ‘mysterious algorithms’ have existed across the internet for years, including Verizon’s “super cookie” and AT&T that extracted more money from customers to switch off its monitoring and tracking software following customers’ internet usage. Pai was highly instrumental in blocking internet privacy regulations that would have forced the kind of disclosure of practices he suddenly objects to now.
- Pai’s claims about American companies caving in to foreign governments’ censorship policies seem to echo his similar 2015 claim that Net Neutrality also helps authoritarian regimes, as long as one interprets Net Neutrality as a “government takeover” of the internet. “If in the United States we adopt regulations that assert more government control over how the internet operates… it becomes a lot more difficult for us to go on the international stage and tell governments: ‘Look, we want you to keep your hands off the internet. Even if the ideas aren’t completely identical, you can appreciate the optical difficult[y] in trying to make that case,” Pai said. But that argument distorts like a fun house mirror. Pai’s declaration that Net Neutrality is a bad thing is based on his premise it would hand the keys to information control to the government to act as gatekeeper. He prefers trusting private companies to be more reliable and safer gatekeepers than the FCC or the Trump Administration. But that argument puts Pai at war with himself, considering his attacks on edge providers — private companies — for bias and censorship. Incidentally and ironically, he raised many of his 2015 objections on RT — the external television service of Russian State Television.
Pai reserved much of his remarks to attack Hollywood celebrities that occasionally inelegantly promote Net Neutrality with inexact language Pai loves to exploit. Among his targets were Mark Ruffalo, who played Hulk, Cher, and George “Sulu” Takei.

Takei
Pai called out Mr. Takei for his suggestion eliminating Net Neutrality would allow internet companies to further monetize the internet by selling additional packages of services to access certain internet content.
“The complaint by Mr. Takei and others doesn’t hold water. They’re arguing that if the plan is adopted, Internet Service Providers would suddenly start doing something that Net Neutrality rules already allow them to do. But the reason that Internet service providers aren’t offering such packages now, and likely won’t offer such packages in the future, is that American consumers by and large don’t want them.”
But of course that didn’t prevent ISPs like Comcast and AT&T to impose data caps on their customers with scant evidence of their necessity and with purely arbitrary allowances. From this regime of data caps, Wall Street analysts push providers to further monetize internet usage to raise revenue to return to shareholders. What customers want has not had much impact on Comcast’s business decisions, as the record on data caps illustrates. The threat of regulation like Net Neutrality enforcement has cooled enthusiasm for these pricing schemes, however, until recently. In April, after Mr. Pai introduced his Net Neutrality repeal plan, Comcast quietly repealed its self-ban on paid prioritization — internet fast lanes.
In a barely competitive marketplace, what customers want may not count for much if they have few, if any alternatives.
Chip Pickering, CEO of INCOMPAS, which includes as member major Silicon Valley edge providers, called Pai’s speech a diversion from the real issues.
“Chairman Pai’s attack on Twitter is like a boxer losing a fight and taking wild and erratic swings,” Pickering said. “Preventing hate speech and bullying behavior online is not the same thing as allowing cable companies to block, throttle and extort money from consumers and the websites they love. Twitter is an amazing platform for left, right and center. Donald Trump might not be President without it, and Chairman Pai’s plan to kill Net Neutrality will put Comcast and AT&T in charge of his Twitter account.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Defenders of FCC Chairman Ajit Pai are rushing to defend the Republican majority’s likely support for an initiative to roll back the FCC’s 25/3Mbps speed standard embraced by his predecessor, Thomas Wheeler.
Defenders of FCC Chairman Ajit Pai are rushing to defend the Republican majority’s likely support for an initiative to roll back the FCC’s 25/3Mbps speed standard embraced by his predecessor, Thomas Wheeler. Kampis’ piece, like many of those published on Watchdog.org, distorts reality with suggestions that communities with 50Mbps broadband service will now be ripe for government handouts. He depends on an unnamed source from
Kampis’ piece, like many of those published on Watchdog.org, distorts reality with suggestions that communities with 50Mbps broadband service will now be ripe for government handouts. He depends on an unnamed source from 
 Kampis claims to be an investigative reporter, but he didn’t venture too far beyond regurgitating press releases and talking points from big phone companies and opponents of municipal broadband. If he had spent time reviewing correspondence sent to the FCC in response to the question of easing broadband speed standards, he would have discovered the biggest advocates for that are large phone companies and wireless carriers that stand to benefit the most from the change.
Kampis claims to be an investigative reporter, but he didn’t venture too far beyond regurgitating press releases and talking points from big phone companies and opponents of municipal broadband. If he had spent time reviewing correspondence sent to the FCC in response to the question of easing broadband speed standards, he would have discovered the biggest advocates for that are large phone companies and wireless carriers that stand to benefit the most from the change.


 Alphabet, the parent company of Google Fiber, has lost interest in expanding its fiber to the home service and is showing signs of pulling the plug on its cable television alternative while it drags its feet on keeping promised rollout commitments.
Alphabet, the parent company of Google Fiber, has lost interest in expanding its fiber to the home service and is showing signs of pulling the plug on its cable television alternative while it drags its feet on keeping promised rollout commitments.


 Porat also had a major hand in slashing the budget at Google’s Nest Labs division. Google spent $3.2 billion acquiring the home thermostat and smoke alarm company in 2014. Nest CEO Tony Fadell came along as part of the deal and was initially considered a major asset, having been the former Apple engineer who built the original iPod prototype. But Fadell clashed with Google’s culture and
Porat also had a major hand in slashing the budget at Google’s Nest Labs division. Google spent $3.2 billion acquiring the home thermostat and smoke alarm company in 2014. Nest CEO Tony Fadell came along as part of the deal and was initially considered a major asset, having been the former Apple engineer who built the original iPod prototype. But Fadell clashed with Google’s culture and 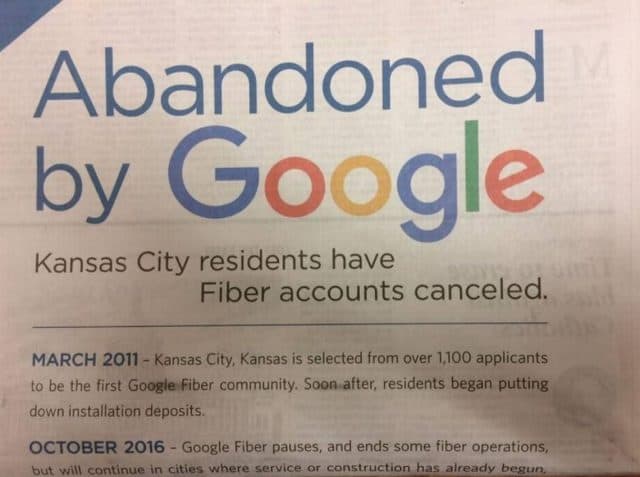
 Porat has been defending Alphabet’s increasingly conservative spending plans and pull-backs.
Porat has been defending Alphabet’s increasingly conservative spending plans and pull-backs.