Subscription television providers should relax: Americans are not moving away from watching television on television sets. Nielsen’s Three Screen Report, issued today, finds most Americans are not fundamentally changing the way they watch TV — they are simply taking advantage of more convenient ways to watch.
The report shows considerable year over year growth in terms of time spent for Digital Video Recorder viewing (up 21.1%) and online video (up 34.9%) since the fall of 2008. Given the consistent spike in usage among the three screens of television, Internet and mobile, consumers are clearly adding video platforms to their schedule, rather than replacing them.
“Americans today have an insatiable appetite for not only content, but also choice,” says Nic Covey, director of cross-platform insights at Nielsen. “Across all age groups, we see consumers adding the Internet and mobile devices to their media diet — consuming media anytime and anywhere possible.”
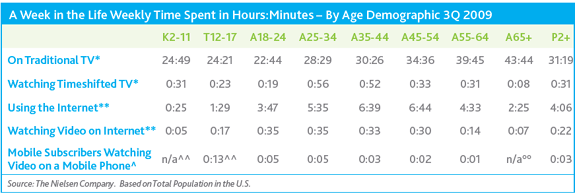
Nearly 99% of television viewing is spent watching it on a television set, according to Nielsen’s findings. But consumers are also discovering broadband and mobile viewing can add convenient new options, and are taking advantage of them:
- In 3Q09, the average American watched 31 hours of TV per week, with 31 minutes spent in playback mode with their DVR.
- In addition, each week the average consumer spent 4 hours on the Internet and 22 minutes watching online video.
- The average consumer spent 3 minutes watching mobile video each week.
The biggest fans of mobile video are teenagers, some spending just over seven hours per month watching video on their phones. Watching television on a broadband connection is a popular trend among those aged 18-44, one noticed by Comcast chief operating officer Steve Burke. Burke spoke about the trend at the recent Cable & Telecommunications Association for Marketing’s three day conference in Denver. He noted his own children now prefer to watch their shows on a laptop from one of the free online services and not on the family television.
Allowing young viewers to grow up assuming they can watch anything, anywhere, for potentially no charge is a very dangerous proposition for people in Burke’s business.
“An entire generation is growing up with that preference,” Burke said. “If we don’t do something to change that behavior so they respect copyrights on the side of content provider, and cable subscriptions or satellite subscriptions or telco subscriptions on the side of the distributors, we are going to wake up with a lot of ingrained habits going the wrong way and we will see cord-cutting.”
Comcast has two ways to make sure viewers learn their lessons about paying for what they watch:
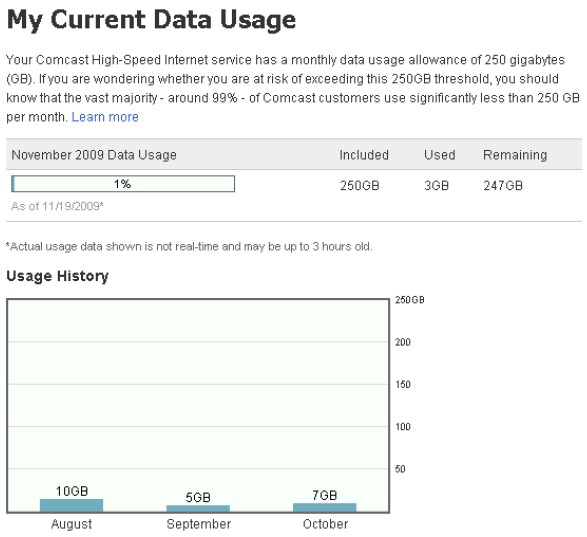
- The formalized introduction of the forthcoming usage meter, better enforcing Comcast’s 250GB monthly limit for their broadband service. Watching a lot of online video will take a major bite out of your broadband usage allowance.
- The launch of Comcast’s Fancast Xfinity TV, a service that will allow only existing Comcast cable-TV package subscribers access to many of their favorite shows online, on demand, for no additional charge. That new name comes courtesy of Comcast’s marketing gurus, to replace what readers better know as: TV Everywhere.
The usage meter and “authenticated subscribers-only” pay wall are Comcast’s one-two punch to keep subscribers from eventually dropping their cable-TV package to watch television exclusively over their broadband connection.
Cable operators already treat companies like Netflix, which use broadband to deliver an increasing number of movies and TV shows on-demand to subscribers, as a major threat. Insight Communications CEO Jamie Howard called Netflix the equivalent of the third largest cable operator in the country in terms of content delivered. That’s content not owned or directly managed by Insight or other cable providers.
Some in the industry believe who owns and controls online video will eventually decide the winners and losers in the subscription television business. Derrick Frost, founder and CEO of Invision.TV, an Internet video search engine, warned the outcome of the battle can’t come soon enough. Otherwise, consumers “will find other ways — legally or illegally — to access it.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe