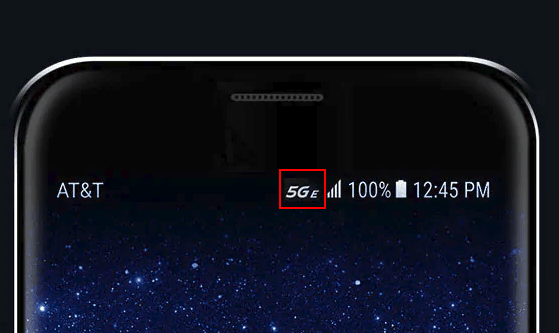
 AT&T customers with Samsung Galaxy 8 Active or LG’s V30 or V40 smartphones began noticing a new icon on their phones starting last weekend: an italicized 5GE, leading some to believe 5G wireless service has now reached AT&T’s network.
AT&T customers with Samsung Galaxy 8 Active or LG’s V30 or V40 smartphones began noticing a new icon on their phones starting last weekend: an italicized 5GE, leading some to believe 5G wireless service has now reached AT&T’s network.
Not so fast, AT&T.
AT&T’s use of 5GE, which stands for “5G Evolution” in AT&T’s techie parlance, is another example of how wireless carriers exploit up and coming technology upgrades that are unprotected from overzealous marketing misuse. The actual 5G standard is different from 5GE, and customers using 5G on millimeter wave frequencies can expect very different performance in comparison to today’s 4G LTE experience. But with 5G being hyped in the media, AT&T is attempting to capture some of that excitement for itself.
The company’s marketing division managed to accomplish a speed and technology upgrade without spending millions of dollars on actual 5G network upgrades — just by changing an icon on customers’ phones and making them believe they are getting a 5G experience. In fact, 5GE is actually just the latest evolution of 4G LTE already known to Verizon customers as LTE-Advanced or LTE Plus on Sprint’s network — technology including carrier aggregation, 256 QAM, and 4×4 MIMO that has been in use on competing cellular networks in the U.S. since at least 2016. But just as Verizon customers saw significant speed improvements from Verizon’s updates to the 4G LTE standard, as AT&T deploys similar upgrades in each of its markets, customers should notice similar performance improvements.
AT&T claims 5GE is already live in 400+ markets with more to come. In the short term, the “upgrade” that was pushed to AT&T network devices last weekend only switched on the 5GE icon, which will mean little to AT&T customers already reached by 5GE and never knew it until this past weekend, and nothing to those still waiting for the upgrade to arrive.
 Walter Piecyk, an analyst at BTIG Research, says AT&T’s latest spectrum deployments will matter more than whatever the company brands its latest upgrade, and could eventually allow AT&T to surpass Verizon Wireless in network performance.
Walter Piecyk, an analyst at BTIG Research, says AT&T’s latest spectrum deployments will matter more than whatever the company brands its latest upgrade, and could eventually allow AT&T to surpass Verizon Wireless in network performance.
AT&T’s recent effort to improve its network by deploying more wireless spectrum — up to 60 MHz in many areas, is not the 5G upgrade customers might expect, but it will deliver faster speeds and more performance on today’s smartphones.
AT&T calls its forthcoming actual 5G network 5G+, and the company is launching a modest but authentic 5G experience in limited “innovation zones” in Jacksonville, Fla., Atlanta, Ga., Indianapolis, Ind., Louisville, Ky., New Orleans, La., Charlotte and Raleigh, N.C., Oklahoma City, Okla., as well as Dallas, Houston, San Antonio, and Waco, Tex.
In a money-saving maneuver, AT&T’s combined spectrum upgrades include 20 MHz of FirstNet first responder spectrum (prime 700 MHz spectrum shared with AT&T customers except during emergencies) it received in 2017, 20 MHz of AWS-3 spectrum (1755-1780 MHz for uplink operations and 2155-2180 MHz for downlink) it acquired for $18 billion in 2015, and 20 MHz of WCS spectrum (2300 MHz) it acquired from NextWave for $650 million back in 2012. All of this spectrum is expected to be activated at the same time as technicians work to upgrade each AT&T cell tower. This dramatically cuts AT&T’s costs and truck rolls for incremental upgrades.

AT&T calls its improved 4G LTE network “5G Evolution”
“We’re turning up not only the FirstNet spectrum that we got, but all of this other spectrum that we’ve acquired over the last few years,” AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson told investors at a December conference. “So as we climb these cell towers, we turn up the spectrum. By the time we get to end of 2019, we will have increased the capacity on AT&T’s network by 50%. I mean, you just have to pause and think about this. The entire AT&T wireless network capacity is going to increase over the next 14 months by 50%. I mean, that’s huge.”
Some areas have already received partial upgrades, others may find newly improved rural coverage as AT&T meets its commitments to the government’s FirstNet platform, which calls for more robust rural coverage. Some areas that never had AT&T coverage before may get it for the first time.
AT&T’s biggest competitor, Verizon, has commanded a lead in 4G LTE coverage from 2010 forward after utilizing a considerable amount of its available spectrum for the faster standard. But Verizon has not been a robust bidder for new spectrum recently, except for the millimeter wave frequencies it bought for its emerging 5G network. It has some additional unused AWS-3 spectrum it can use for expansion, but Piecyk believes Verizon may already be using those frequencies in many markets where it is likely facing a spectrum crunch.
While AT&T lights up 60 MHz of additional spectrum, Verizon is primarily depending on the ongoing conversion of 10-15 MHz of existing spectrum it now uses for 3G service to LTE each year. But the company is reportedly running out of frequencies in areas where data demand requires that extra spectrum the most.
The only short term solution for Verizon, which is not participating in marketing hoopla like 5GE, is to make its current spectrum more efficient. That means more cell towers sharing the same frequencies to reduce the load on each tower, improved antenna technology, and using newly available spectrum in the CBRS and millimeter wave bands to manage network traffic. Verizon may even use unlicensed shared spectrum to handle some of the load. Unfortunately, smartphones equipped to take advantage of these new bands are not yet available and may not be until 2020.
For AT&T, improved network performance is seen as a key to resume robust growth in new subscribers. After Verizon dramatically improved its LTE network in 2014, AT&T stopped growing its lucrative post-paid phone subscriber base, according to Piecyk. Now it may be AT&T’s chance to turn the tables on Verizon.
This AT&T produced video helps consumers understand what 5G, beam forming, small cells, and coverage differences between 4G and 5G are all about. Notice the 5G trial speed test showed download speeds topping out at around 137 Mbps. (4:26)


 Subscribe
Subscribe By the year 2022, 60% of the world’s population will be connected to the internet and 82% of online traffic will come from streaming video.
By the year 2022, 60% of the world’s population will be connected to the internet and 82% of online traffic will come from streaming video. A snowstorm, in winter, in Upstate New York, was the excuse Frontier Communications gave for leaving scores of residents in the Minerva-Johnsburg area without phone or internet service for as long as 10 days this month.
A snowstorm, in winter, in Upstate New York, was the excuse Frontier Communications gave for leaving scores of residents in the Minerva-Johnsburg area without phone or internet service for as long as 10 days this month.
 Pearsall pays Frontier for internet speeds advertised at 6-10+ Mbps, but receives 0.69 Mbps for downloads and 0.08 Mbps for uploads at his home in Garnet Lake. A typical Microsoft Office software update takes approximately 48 hours to arrive, assuming one of many frequent service outages does not force the upgrade to start anew.
Pearsall pays Frontier for internet speeds advertised at 6-10+ Mbps, but receives 0.69 Mbps for downloads and 0.08 Mbps for uploads at his home in Garnet Lake. A typical Microsoft Office software update takes approximately 48 hours to arrive, assuming one of many frequent service outages does not force the upgrade to start anew.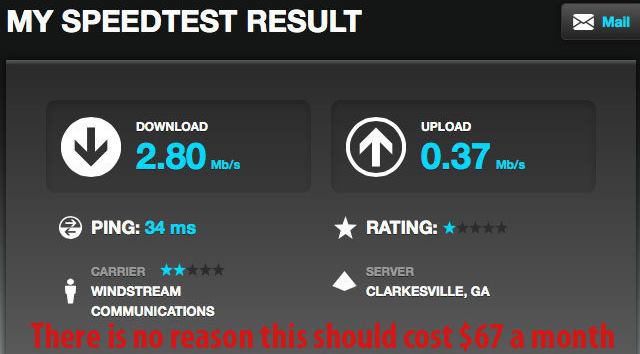
 “It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.”
“It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.” “We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.”
“We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.” Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.
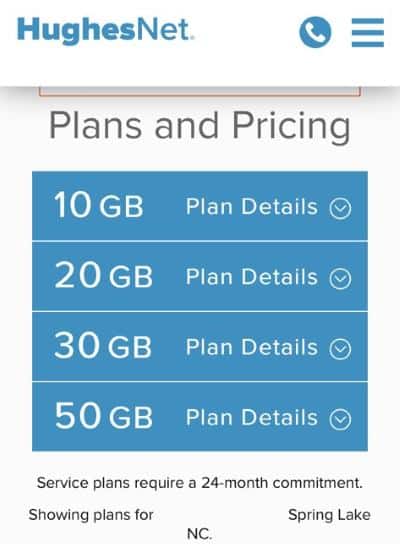
Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before. For 76,783 homes and businesses in upstate New York, the future of internet access will be a satellite dish and as little as a 20 GB data allowance per month, courtesy of the New York State Broadband Program Office’s decision to partner with HughesNet, a satellite internet provider, instead of finding a provider willing to extend wired internet access to every New Yorker.
For 76,783 homes and businesses in upstate New York, the future of internet access will be a satellite dish and as little as a 20 GB data allowance per month, courtesy of the New York State Broadband Program Office’s decision to partner with HughesNet, a satellite internet provider, instead of finding a provider willing to extend wired internet access to every New Yorker.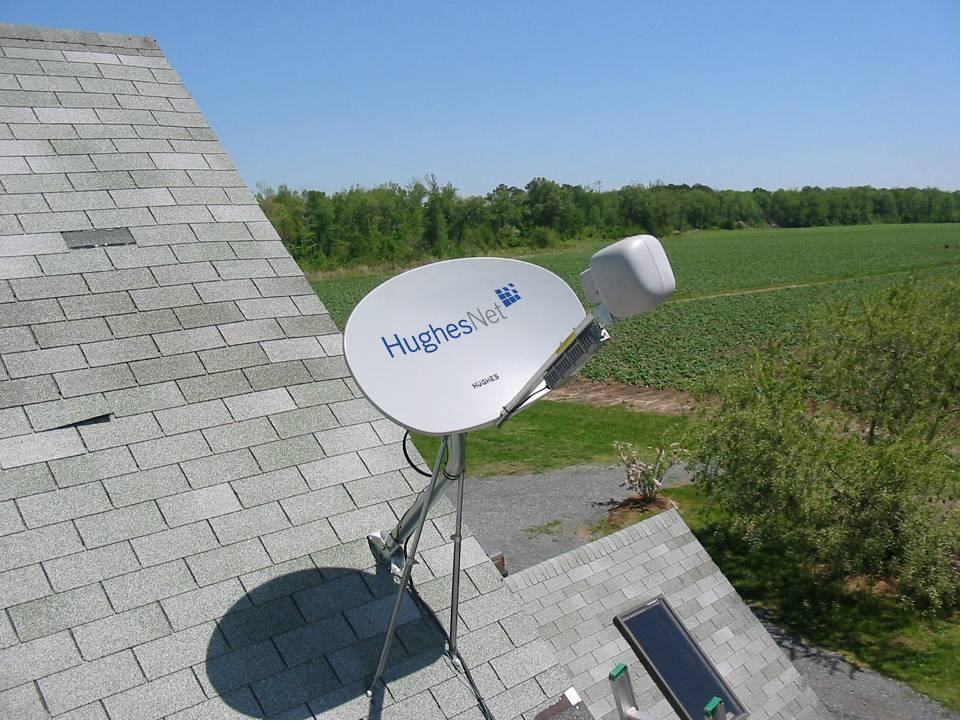 “Definitely broken promises there,” Harte says.
“Definitely broken promises there,” Harte says.
 HughesNet isn’t the only provider attracting crowds armed with pitchforks and torches. Frontier Communications, which was recently awarded $9.7 million to extend DSL service to 2,735 more rural customers in the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier and North Country, attracts scorn from its existing customers.
HughesNet isn’t the only provider attracting crowds armed with pitchforks and torches. Frontier Communications, which was recently awarded $9.7 million to extend DSL service to 2,735 more rural customers in the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier and North Country, attracts scorn from its existing customers.

