 A Pennsylvania attorney that didn’t pay his $215 Comcast bill was hounded by Comcast’s collections crew despite never getting cable service at his new address.
A Pennsylvania attorney that didn’t pay his $215 Comcast bill was hounded by Comcast’s collections crew despite never getting cable service at his new address.
Wayne resident Edmond Tiryak would seem like a poor target for cable company harassment. He’s a lawyer after all. But even he withered after a month of unrelenting phone calls and letters demanding he pay his bill for non-service.
Tiryak had a peaceful 25-year relationship with Comcast until he moved last October. After three weeks of no-show appointments, waits on hold of up to 40 minutes and lots of excuses, Comcast never bothered to hook up service at his new address. But that didn’t stop the cable company from billing Tiryak $215 for his first month, in advance.
Calling Comcast to the debate the veracity of the bill turned out to be an exercise in futility. Comcast’s offshore call center insists they know best — Tiryak has cable service because the computer says he does. The fact Tiryak lives at the address and claims he doesn’t is beside the point. The only important matter is how Tiryak would like to pay – Visa, Mastercard, Discover? The fact he still doesn’t have service is, well, incidental.
A reasonable person would refuse to pay and insist on an investigation by a supervisor to verify Comcast is MIA at the Tiryak residence. But Comcast has a collections department that could wear down Vladimir Putin and they know how to use it.
Two months later, the attorney pleaded with Inquirer business columnist Jeff Gelles to help get Comcast off his back.
“By the time he contacted me in January, Tiryak had given up in frustration and was just fighting to get the $215 bill erased,” Gelles wrote. “Even four letters to Comcast’s president hadn’t done the trick.”
Some quick media attention is an excellent way to get Comcast’s attention, at least for a little while, and Tiryak was initially pleased to report the charges had been zeroed out.

Phillip “Comcast channels Genghis Khan” Dampier
But then Comcast’s collections department changed their mind after dreaming about that $215 in lost revenue, and started calling Tiryak again.
Gelles forwarded on the complaint about the resumed harassment collection calls to Comcast and received yet another promise all would be made right.
“It’s astonishing to me that they would take a really good customer, who’s been with them 25 years, and basically just treat me as if I’m nothing – as if I’m useless to them,” Tiryak told Gelles.
A long-standing pattern of Comcast customer complaints suggests Tiryak should not be surprised.
Gelles gently reminded readers in Comcast’s hometown that the free market works best when customers have an alternative when stuck in an abusive relationship with the cable company. But deregulated capitalism hands out gold stars for monopoly building consolidation. Tiryak, like so many others, landed on Comcast’s Park Place and now they have to pay.
The solution to the chronic dyspepsia resulting from repeated exposure to Comcast isn’t Verizon, which has capitulated on further expansion of its competing FiOS fiber to the home service to focus on counting Verizon Wireless coin. Instead of phantom competition that never arrives, the FCC’s recent decision to provide checks and balances for cocky, deregulated behemoth cable companies like Comcast might be the best answer for now.
Despite industry claims that an apocalypse would result from applying any “utility-style” regulation like that used to keep AT&T in check during its monopoly years, consumer advocates suggest Comcast’s passive-aggressive behavior could be managed with one phone call to a state regulator.
Geldes asked the former director of consumer services for the Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission about how the agency would handle Tiryak’s complaint, if it were empowered to do so:
Under PUC rules, he says, after a utility investigates a dispute, it has to ask whether the consumer is satisfied. “If the customer says no, the company is required to give the PUC’s number for making an informal complaint,” he says. That is usually enough to solve most issues, he says. The agency also monitors nagging problems like long hold times for calls and occasionally intervenes.
Telephone companies used to dread the prospect of dealing with a customer complaint escalated to the New York Public Service Commission. Repair crews were often dispatched within an hour and generous service credits and apologies were routine. But the impact lived on for years after that. Customer service agents looking up account information on a customer who previously complained to the PSC about anything would find their computer terminal lit up like a Christmas tree, alerting them they were dealing with a customer that doesn’t play.
Recalling that era makes one wonder if regulating the biggest bad boys on the block — cable companies running wild — might not be such a bad idea after all.
Nothing else has worked.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Time Warner (Entertainment): Not affiliated with Time Warner Cable, owning Time Warner (Entertainment) would gain Comcast important cable networks like TNT, HBO, and the Warner Bros. studio.
Time Warner (Entertainment): Not affiliated with Time Warner Cable, owning Time Warner (Entertainment) would gain Comcast important cable networks like TNT, HBO, and the Warner Bros. studio. Charter Communications has quietly dropped usage caps and allowances from the company’s terms and conditions, once again giving Charter broadband customers unlimited access to the Internet.
Charter Communications has quietly dropped usage caps and allowances from the company’s terms and conditions, once again giving Charter broadband customers unlimited access to the Internet. More than three years after Canadian regulators required Bell Canada’s northern subsidiary, Northwestel, to undertake a
More than three years after Canadian regulators required Bell Canada’s northern subsidiary, Northwestel, to undertake a 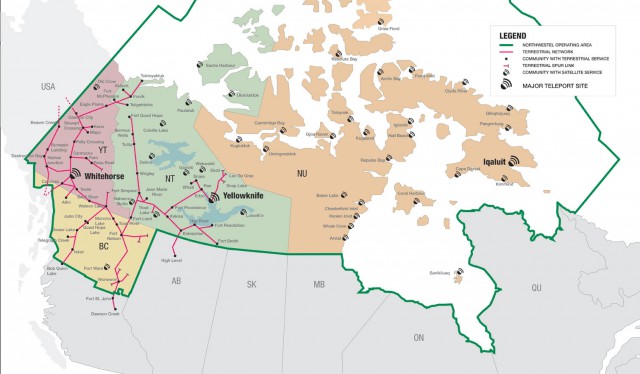
 “The DSL package that I pay for out at Lake Lebarge is absolutely ridiculous in comparison to high-speed in town,” said Jeremy Jones. “[Northwestel charges] $90 for [5Mbps DSL with a usage cap of] 125GB. The only way to increase it would be to put in another phone line and second modem and that would have ended up being another $100+ per month. We’ve decided it is cheaper just to go over it if we need to.”
“The DSL package that I pay for out at Lake Lebarge is absolutely ridiculous in comparison to high-speed in town,” said Jeremy Jones. “[Northwestel charges] $90 for [5Mbps DSL with a usage cap of] 125GB. The only way to increase it would be to put in another phone line and second modem and that would have ended up being another $100+ per month. We’ve decided it is cheaper just to go over it if we need to.”