 With an estimated 90,000 New Yorkers stranded without broadband service, a proposal from Charter Communications to block funding for future projects is coming under fire from a bipartisan group of rural legislators.
With an estimated 90,000 New Yorkers stranded without broadband service, a proposal from Charter Communications to block funding for future projects is coming under fire from a bipartisan group of rural legislators.
Charter, which does business as Spectrum, filed a request with the Federal Communications Commission to exclude certain census blocks for funding under the agency’s new $20.4 billion Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF). The cable company claims it intends to privately fund expansion of internet service in those areas, and does not welcome government-subsidized competition.
“Good cause plainly exists to grant the waiver to avoid overbuilding areas in which Charter has already begun the process of deploying service and is investing private capital well in excess of $600 million,” company officials wrote. “This will ensure scarce universal service support is deployed to close the gap/digital divide in actually unserved areas. The commission has previously granted rule waivers where, as here, the purposes of the rule would be disserved by its strict application, and where waiver would affirmatively serve the public interest.”
Many of the rural homes Charter claims it intends to serve have been waiting for internet access for well over a decade. Many were hopeful that wait would end shortly after the cable company agreed to expand service to an additional 145,000 rural New York households as part of an agreement with state regulators approving its merger with Time Warner Cable. But a March 2020 audit conducted by the Comptroller of New York found Charter was not meeting its commitments:
“[…] It has been over three years since the merger was approved. Network expansion should have already been provided to approximately 126,875 unserved or underserved premises based on the 2016 Commission Order approving the merger. As of July 2019, Charter had only extended its network to 64,827 premises. Based on the original Order, 62,048 additional customers should have received access to these services. Charter now has until September 2021 to complete the network expansion of 145,000 premises previously scheduled to be completed by May 2020.”

Barrett
Some New York legislators believe Charter is out of line asking the FCC to exclude funding for other rural broadband projects while taking its time meeting its own commitments.
“Charter’s waiver request is simply self-serving and will in no way benefit the residents of upstate New York who, even in the year 2020, are struggling to access adequate broadband by any provider,” Rep. Didi Barrett (D-Hudson) wrote in a letter to the FCC. “Charter’s petition is a blatant attempt to reduce competition and leave consumers with no choice but to wait around for Charter to finish a job that should already be complete. In Upstate New York, tens of thousands of residents and businesses are still waiting for internet service because of Charter’s years-long effort to renege on their obligations to New York State and the people who live in rural communities. We must continue to call Charter out until every household and business is served as planned under their agreement with New York State.”
Republican congresswoman Elise Stefanik from Schuylerville agrees with many of Barrett’s views, blasting Spectrum for seriously delaying its rural rollout commitments. Stefanik worked with FCC Chairman Ajit Pai to change the qualification requirements for the RDOF program, which originally would have excluded New York from receiving funding. If the FCC adopts Charter’s request, it would block much of her district from receiving broadband funds, either because Charter previously indicated it would (eventually) offer service or because the state previously supplied broadband subsidies, which would also seem to disqualify RDOF grants.
“I have heard directly from constituents and local elected officials that this decision would have a severe impact on their ability to gain rural broadband access, which is essential, especially during this time of crisis,” Stefanik said. “Charter’s request would exclude parts of the North Country from this critical federal funding, and I will work with my upstate colleagues and the FCC to keep it available.”
WNYT in Albany reports rural New York communities like Stillwater have waited years for Charter Spectrum to provide broadband service. The addresses Spectrum grudgingly will serve in the area are routinely quoted installation fees starting at $8,000. (2:16)
 Russian satellite television provider Tricolor, in collaboration with Eutelsat Networks, has launched satellite broadband service throughout Siberia, with data plans offering speeds up to 100 Mbps.
Russian satellite television provider Tricolor, in collaboration with Eutelsat Networks, has launched satellite broadband service throughout Siberia, with data plans offering speeds up to 100 Mbps.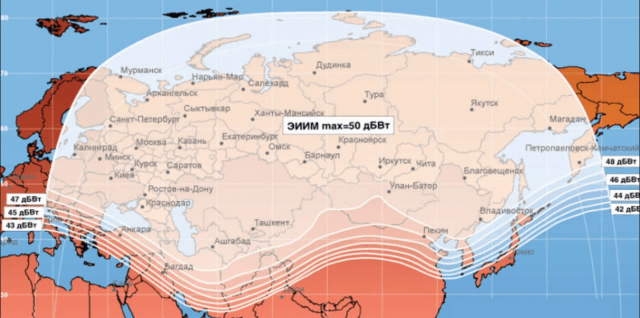


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Internet access in rural states like Idaho is mostly a mixture of cable internet in larger cities and towns and DSL service in suburban areas. Rural communities often have to rely on wireless internet, where available, or satellite internet access. A few communities have a co-op utility that doubles as a broadband provider, but in most cases rural Idaho only gets what CenturyLink, Frontier, and other telephone companies are willing to provide.
Internet access in rural states like Idaho is mostly a mixture of cable internet in larger cities and towns and DSL service in suburban areas. Rural communities often have to rely on wireless internet, where available, or satellite internet access. A few communities have a co-op utility that doubles as a broadband provider, but in most cases rural Idaho only gets what CenturyLink, Frontier, and other telephone companies are willing to provide.
 Stankey’s predecessor, Randall Stephenson, will exit as AT&T’s CEO in July. He leaves a much larger conglomerate than what he started with. AT&T has diversified from its telephone and wireless portfolio with several major acquisitions, including DirecTV — the satellite TV service, and Time Warner (Entertainment), a Hollywood studio and entertainment giant. The result is a company loaded with debt and a revolt by activist investors that question the wisdom of creating the 2010s version of AOL-Time Warner.
Stankey’s predecessor, Randall Stephenson, will exit as AT&T’s CEO in July. He leaves a much larger conglomerate than what he started with. AT&T has diversified from its telephone and wireless portfolio with several major acquisitions, including DirecTV — the satellite TV service, and Time Warner (Entertainment), a Hollywood studio and entertainment giant. The result is a company loaded with debt and a revolt by activist investors that question the wisdom of creating the 2010s version of AOL-Time Warner. Comcast today announced it will extend its COVID-19 crisis commitments until the end of June, including a continued suspension of its 1 TB data cap.
Comcast today announced it will extend its COVID-19 crisis commitments until the end of June, including a continued suspension of its 1 TB data cap. With an estimated 90,000 New Yorkers stranded without broadband service, a proposal from Charter Communications to block funding for future projects is coming under fire from a bipartisan group of rural legislators.
With an estimated 90,000 New Yorkers stranded without broadband service, a proposal from Charter Communications to block funding for future projects is coming under fire from a bipartisan group of rural legislators.
