The FCC is preparing to pay about 1,000 TV stations and cable operators $1 billion dollars to subsidize necessary expenses to change over-the-air channels to make room for cell phone companies.
The FCC is preparing to pay about 1,000 TV stations and cable operators $1 billion dollars to subsidize necessary expenses to change over-the-air channels to make room for cell phone companies.
The channel changes are a result of a now-complete spectrum auction that will reallocate part of the UHF TV dial for use by cell phone companies for wireless broadband. Part of the auction proceeds will be used to reimburse TV stations and cable operators for the expenses associated with changing channel positions and equipment needed to receive those signals.
The move will significantly compress the UHF TV dial, requiring viewers to rescan their local channel lineups in what the industry is calling a “repack” of stations to closer dial positions. When complete, the UHF TV band will shrink from channels 14-51 to 14-36. Channels 38-51 are being reallocated to the wireless industry (channel 37 remains reserved for radio astronomy use only).
Some stations will need to buy a new antenna or transmitter, others may require interim or larger facilities to manage the change. The National Association of Broadcasters complains the FCC is not allocating enough money to cover what it estimates will eventually cost TV station owners $2.139 billion. TV tower rigging crews, who climb antenna towers and perform installation and maintenance services, are booked well in advance and are charging prices consistent with the urgent need to prepare for the biggest TV transition since the switch to digital broadcasting.
Because nobody is certain exactly how much the free TV repack and transition will eventually cost, the FCC intends to partly reimburse commercial stations about 52% of their costs (62% for non-commercial stations) during the first round of funding. Another $750 million is expected to be allocated for the second round of funding to cover the rest.
The agency also intends to scrutinize receipts to make certain stations are not dipping into the fund to help pay for the forthcoming transition to ATSC 3.0 broadcasting, which will eventually make current TV sets and some station equipment functionally obsolete. TV stations can only recoup expenses directly related to the repack. The FCC suspects as repack deadlines near, TV tower rigging crews could raise prices further and take a bigger percentage of the fund than station owners may realize. If costs rise out of proportion to what is now deemed reasonable, some stations may face out-of-pocket expenses the FCC will not reimburse if the fund is exhausted.
The FCC did not account for cell companies stepping in and directly assisting TV stations to vacate their existing channel positions faster than the FCC initially planned. T-Mobile, which won a large number of licenses that cannot be used until certain TV stations make channel changes, is reaching agreements with stations directly, offering incentives to move faster. In New York City, an agreement between FOX and T-Mobile will save the FCC fund almost $80 million. FOX-owned stations WWOR and WNYW will move their transmitters from the Empire State Building to One World Trade Center, allowing them to switch channel positions and make room for T-Mobile more than a year ahead of schedule.
When the repack is complete, viewers watching over-the-air will need to rescan their televisions to find their local stations once again.
A Public Service Announcement from the FCC explains the “rescanning” process to keep or receive new digital over-the-air stations. (1 minute)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 The Daily News
The Daily News 
 Charter Communications will have 30 days to fix alleged problems affecting Lexington, Ky.’s cable subscribers or the company could face fines of $500 a day for each violation.
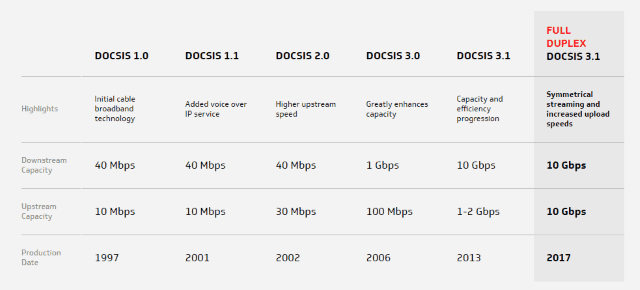
Charter Communications will have 30 days to fix alleged problems affecting Lexington, Ky.’s cable subscribers or the company could face fines of $500 a day for each violation. CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.
CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.