 In an effort to capture a major share of the $65 billion dollars becoming available for rural broadband expansion as part of the Biden Administration’s infrastructure funding program, the wireless industry’s top lobbying group is promoting the idea that 5G Fixed Wireless broadband is as future-proof as fiber to the home service.
In an effort to capture a major share of the $65 billion dollars becoming available for rural broadband expansion as part of the Biden Administration’s infrastructure funding program, the wireless industry’s top lobbying group is promoting the idea that 5G Fixed Wireless broadband is as future-proof as fiber to the home service.
Make no mistake, they are not being honest with you.
To back up their premise, the CTIA, the lobbying arm of the wireless industry, bought and paid for a report produced by Accenture that is designed to convince lawmakers and regulators that fixed wireless internet access is just as good or even better than fiber, suggesting the technology could potentially provide up to 43% of rural homes with high speed gigabit symmetrical service similar to what many fiber to the home providers offer.
Yet the same wireless industry trying to sell that idea successfully fought to water down standards in Biden’s infrastructure bill that originally required would-be funding recipients to provide customers with minimum speeds of 100/100 Mbps. Now providers can qualify by offering speeds as low as 100/20 Mbps. The CTIA report does not want to talk about that, preferring to claim providers could supply 1,000/1,000 Mbps service over traditional macro cell towers already in use today to subscribers as much as four miles away.
But look out for the fine print:
“Increased service was determined based on the potential economic feasibility of market entry. Estimates for market size, potential operating costs, and the capital investment to deploy were developed for target rural markets. The actual deployment feasibility will vary for individual FWA providers; new entrants will be influenced by the time and costs associated with factors such as market topography, construction, and permitting.”
In other words, if the required cell towers fail the same kinds of Return On Investment (ROI) formulas that have always left many rural communities behind, these 5G services will never happen either without huge concessions, subsidies, and policy changes that will further strip local control over cell tower placement and oversight. That is simply more the same failed reliance on providers to deliver service in places they never have and never will.
Ask any West Virginian about the quality of rural mobile service just to make and receive calls, and you will be told service is spotty outside of the largest communities.
T-Mobile, one of the country’s biggest advocates of fixed wireless, barely even serves West Virginia, which belies their claim that rural expansion is “one of its most promising growth opportunities.” If that growth did not materialize supplying voice, texting, and 4G LTE service in the state, it seems even less likely at materialize on spectrum that providers have always struggled with in mountainous states. To successfully reach most of West Virginia, T-Mobile would need an expensive network of traditional cell towers for which they have never believed there has been much of a business case to provide. Even then, it is inevitable that some would-be subscribers would still be without service, blocked by the terrain.
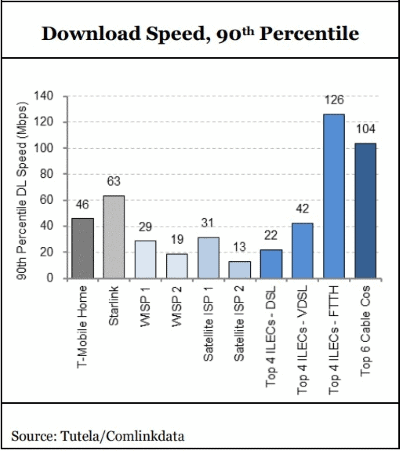
Chart also courtesy of Broadband World News.
What technology does not care about terrain? Fiber to the home service, which can deliver the same high speed performance to every customer without worrying about hills, mountains and valleys. It also has far more capacity than cell towers, which slow when congestion develops.
The report never actually promises gigabit speed service to all, but does emphasize fixed wireless is cheaper to deploy than fiber to the home service. But at least 20 years of broken and empty promises from the telecom industry to rural America should be enough to recognize that the transformational opportunity of this well-funded broadband stimulus program will allow providers to finally “do it right” with robust, infinitely upgradable fiber broadband technology that won’t slow down if a cell tower gets congested, can deliver the same speed to every subscriber, and delivers excellent customer satisfaction scores.
The wireless industry did not spend tens of millions of dollars trying to water down broadband speed requirements because they were confident fixed wireless could match fiber internet speeds. They know very well the kind of 5G networks they are envisioning for rural America cannot deliver guaranteed gigabits of speed once customers sign up in significant numbers to use it or the wireless industry deems an area unprofitable to serve. How many Americans will still be left behind with zero bars?
Wall Street analyst firm MoffettNathanson recently reviewed performance data from T-Mobile’s existing home broadband service and Starlink satellite internet — two technologies lobbyists point to as a solution for rural broadband dead zones. It found the median download speed for T-Mobile’s fixed wireless service is just 20Mbps. Starlink performed slightly better at 35Mbps. That is a long way away from 1,000 Mbps. Will these technologies threaten to be the dead-end DSL of the 21st century?
Speeds slow down on congested cell towers, and providers have implemented network management technologies that can selectively throttle speeds to all but their most preferred premium customers when they consider it necessary.
 Wave7 Research also reported that T-Mobile is already concerned about network congestion on its existing fixed wireless service and that T-Mobile is moving “very cautiously with respect to network loading, in an attempt to limit the number of subscribers per cell, and even per cell sector.” That does not sound “future proof” to us if customer limits are already being enforced.
Wave7 Research also reported that T-Mobile is already concerned about network congestion on its existing fixed wireless service and that T-Mobile is moving “very cautiously with respect to network loading, in an attempt to limit the number of subscribers per cell, and even per cell sector.” That does not sound “future proof” to us if customer limits are already being enforced.
The wireless industry itself seems to hint at future capacity issues in a report that heavily emphasizes the need for the federal government to clear more spectrum that can eventually supply more wireless capacity.
MoffettNathanson’s Craig Moffett seems convinced any fixed wireless or satellite provider is going to be more capacity and performance-limited than wired alternatives like fiber to the home service. In Moffett’s view, these wireless technologies are best suited to extremely rural areas where fiber or cable deployment is simply untenable, even with the much larger amount of subsidy funding soon to be made available.
The biggest benefit of the Biden infrastructure program is that it actually does allow the country to “build back better” instead of offering the usual incremental upgrades delivering “good enough for you” internet access that has left millions stuck with slow speed DSL or low capacity rationed satellite internet. Now that funds are finally becoming available, why divert them to a technology that “may” one day provide unguaranteed gigabit service when fiber to the home technology is available today that can meet and exceed those speeds comfortably and has sufficient capacity to serve rural America’s needs for decades to come.
 Rogers’ attitude towards loyal customers seems to be summed up by what people encounter when visiting some of their retail locations: a locked door.
Rogers’ attitude towards loyal customers seems to be summed up by what people encounter when visiting some of their retail locations: a locked door.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Effective March 18, 2022 the cost of Spectrum’s “Broadcast TV Fee,” charged to cable television customers, will increase $3, reaching an unprecedented $21 a month, just to cover the carriage of local, over the air television stations. The Broadcast TV Fee was last raised to $17.99 in June 2021. The summer before that, the fee increased by nearly $3 a month as well. This means the average surcharge for local, over the air stations, is going up an average of $36 a year at Spectrum.
Effective March 18, 2022 the cost of Spectrum’s “Broadcast TV Fee,” charged to cable television customers, will increase $3, reaching an unprecedented $21 a month, just to cover the carriage of local, over the air television stations. The Broadcast TV Fee was last raised to $17.99 in June 2021. The summer before that, the fee increased by nearly $3 a month as well. This means the average surcharge for local, over the air stations, is going up an average of $36 a year at Spectrum.
 In an effort to capture a major share of the $65 billion dollars becoming available for rural broadband expansion as part of the Biden Administration’s infrastructure funding program, the wireless industry’s top lobbying group is promoting the idea that 5G Fixed Wireless broadband is as future-proof as fiber to the home service.
In an effort to capture a major share of the $65 billion dollars becoming available for rural broadband expansion as part of the Biden Administration’s infrastructure funding program, the wireless industry’s top lobbying group is promoting the idea that 5G Fixed Wireless broadband is as future-proof as fiber to the home service.
 Wave7 Research also reported that T-Mobile is already concerned about network congestion on its existing fixed wireless service and that T-Mobile is moving “very cautiously with respect to network loading, in an attempt to limit the number of subscribers per cell, and even per cell sector.” That does not sound “future proof” to us if customer limits are already being enforced.
Wave7 Research also reported that T-Mobile is already concerned about network congestion on its existing fixed wireless service and that T-Mobile is moving “very cautiously with respect to network loading, in an attempt to limit the number of subscribers per cell, and even per cell sector.” That does not sound “future proof” to us if customer limits are already being enforced. The Federal Communications Commission today approved Verizon’s acquisition of low-cost carrier TracFone Wireless, which will bring a familiar brand for prepaid wireless service under the wireless giant’s corporate umbrella.
The Federal Communications Commission today approved Verizon’s acquisition of low-cost carrier TracFone Wireless, which will bring a familiar brand for prepaid wireless service under the wireless giant’s corporate umbrella. Hulu’s live streaming TV service, known as Hulu Live,
Hulu’s live streaming TV service, known as Hulu Live, 