 Verizon and T-Mobile are redlining their up and coming 5G wireless services to target wealthy neighborhoods and business districts while shunning the urban poor.
Verizon and T-Mobile are redlining their up and coming 5G wireless services to target wealthy neighborhoods and business districts while shunning the urban poor.
Dave Burstein examined the coverage maps of both carriers in cities like Manhattan and found a distinction in the service available in wealthy southern Manhattan and what upper Manhattan neighborhoods including Harlem and the mostly Latino Washington Heights are getting. For both companies, 5G is not much of a priority for Brooklyn either.
“I do not think T-Mobile specifically intended to exclude people of color, but that seems to be the practical effect,” Burstein wrote.
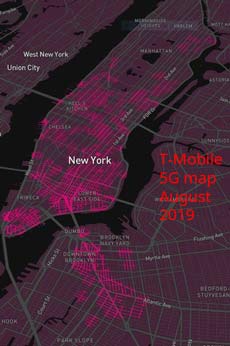
(Image: Dave Burstein)
Ronan Dunne, executive vice president & group CEO of Verizon Consumer confirmed that Verizon will be targeting 5G service to areas where it makes the most economic sense. He said that more than half of Verizon Wireless customers will continue to get 4G LTE-like speeds, with the rest eventually upgraded to 5G service.
“So we’ve taken a very clear view that we want to have both a coverage strategy and a capability strategy. And a very large majority of the volume of data that we carry on our networks goes to large, dense urban environments,” Dunne told investors recently. “So from a population point of view, it’ll be significantly less than half of the customers [getting 5G]. But from a data traffic point of view, it’s significantly more than half. So when it comes to the ability to use 5G as a significant capacity enhancement, there’s more of an opportunity to leverage that in the urban areas.”
In other words, Verizon plans to target population dense urban areas for 5G service the most, because that is where most of its data-loving customers live and where they network’s cost effectiveness may be the highest. Although the geographic coverage of 5G will seem relatively small, the population density of areas targeted for 5G service is not.

Dunne
Verizon has been touting its forthcoming nationwide 5G network, but Dunne has hinted to investors that the devil will be in the details. Not every customer will have access to Verizon’s super fast millimeter wave 5G service. In fact, at least half the country will be serviced by existing 4G LTE cell towers upgraded to provide 5G service on lower frequencies capable of reaching far beyond the coverage area offered by millimeter wave service. But that will also mean a much larger number of customers will share the same 5G network connection, potentially dramatically reducing speed and performance. Dunne said the performance of this type of 5G service “will approximate a good 4G service.”
Burstein notes in real terms, this will mean a significant difference in network speed. Verizon’s millimeter wave service will be capable of delivering 1-2 Gbps, while Verizon’s 5G upgrade of its existing 4G cell towers will deliver speeds in the low hundreds of megabits per second, potentially even slower on crowded cell sites.


 Subscribe
Subscribe