 CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.
CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.
“FDX DOCSIS 3.1 is an extension of the DOCSIS 3.1 specification that will significantly increase upstream capacity and enable symmetric multi-Gbps services over existing HFC networks,” CableLabs wrote. “Full Duplex DOCSIS 3.1 technology builds on the successful completion of the DOCSIS 3.1 specification, which has made deployments of 10Gbps downstream and 1Gbps upstream broadband speeds a reality.”
Cable operators that adopt FDX will be able to sell identical upstream and downstream speeds to customers. The new standard concurrently uses the same spectrum reserved for broadband service for uploads and downloads. The technology was developed using Time Division Duplexing (TDD).
The new standard is 100% compatible with DOCSIS 3.1, which is slowly being implemented by cable operators around the country. However, it is not compatible with DOCSIS 3.0, which is still the predominate cable broadband technology standard in use in North America. As DOCSIS 3.1 gradually gets introduced, some cable modem manufacturers are building modems compatible with both DOCSIS 3.0 and 3.1, so equipment is not rendered obsolete in the next few years. But early adopters will likely not find modems supporting FDX DOCSIS 3.1 for up to two years.
The prerequisites for cable operators interested in deploying the new standard are significant. The most important requirement is the adoption of “node+0” architecture, which requires deploying fiber optics deep into the cable company’s network.
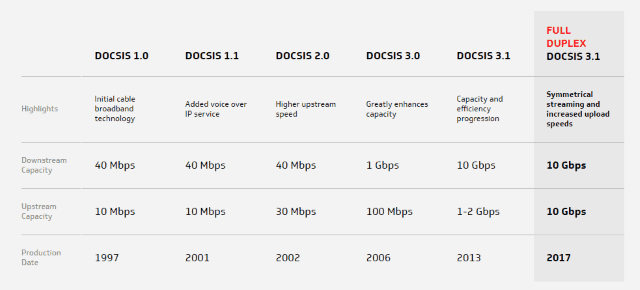
The history of the DOCSIS standard powering cable broadband.
How cable systems work
In the early days of cable, companies relied primarily on coaxial cable between its “headend” — often its main office, and customers. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, cable companies began replacing sections of its copper coaxial cable with fiber optics, a more reliable technology with fewer failure points. There was considerable debate about how much copper cable should be scrapped, based primarily on the cost to deploy fiber. More fiber = more money, less fiber = less reliability. Anyone who subscribed to cable in the 1970s and 1980s was well acquainted with frequent outages, often caused by a failure in one of the many amplifiers cable system operators used to get signals from their office to individual customers.
Many cable companies eventually settled on plotting each fiber optic route to the center of a circle on a map with a 1-kilometer radius. In most suburban areas, this meant that each fiber “node” would serve around 500 customers. The cable company would continue to use its existing coaxial cable to extend into neighborhoods and reach subscribers. Over the last 5-10 years, some cable companies have invested to push fiber optics “deeper” into their networks, which means further reducing the amount of copper coaxial cable still in use.
Today, in many cities, the average cable subscriber can theoretically find the location where a cable company’s fiber connection interfaces with coaxial cable somewhere within a three block radius.
To make FDX DOCSIS 3.1 work, cable companies need enough fiber pushed towards customers to completely eliminate the use of amplifiers. That is what “node+0” means: from the fiber node to the customer, there are zero amplifiers.
Timeline
Because of the cost implications, some cable operators may initially offer FDX DOCSIS 3.1 only to their commercial clients, especially in areas where a fiber competitor does not exist.
Although many cable operators doubt symmetrical broadband is attractive to residential customers, it does offer the cable industry the talking point its networks will be gigabit-capable without an investment in fiber to the home service.
The cable industry expects to test the technology in late 2018 or early 2019, with the expectation it will be introduced for sale starting in 2020.


 Subscribe
Subscribe