 Despite perennial claims of an unmanageable wireless data traffic tsunami threatening the future of the wireless industry, there is strong evidence wireless data traffic growth has actually flattened, increasing mostly as a result of new customers signing up for service for the first time.
Despite perennial claims of an unmanageable wireless data traffic tsunami threatening the future of the wireless industry, there is strong evidence wireless data traffic growth has actually flattened, increasing mostly as a result of new customers signing up for service for the first time.
Expensive wireless data plans and usage caps have left consumers more cautious about how they use wireless data, reducing the demand on wireless networks and allowing carriers to defer plans for aggressive network densification they claim is needed to keep up with demand.
Analysys Mason discovered some of the biggest victims of the myth of the traffic tidal wave are the manufacturers and dealers of small cell equipment hoping to make a killing selling solutions to the wireless traffic jam. Vendors attending the ‘Small Cell, Carrier Wi-Fi and Small Cells Backhaul World’ event will have no trouble filling the modest amount of orders they likely received this year. While there is money to made selling small cells to manage data usage in very high traffic locations including shopping and sports venues, AT&T dropped plans to deploy 40,000 small cells on its network by the end of 2015, a goal that had been a key element of its Project Velocity IP (VIP) network initiative, and no other U.S. carrier has shown as much interest in small cell technology as AT&T once did.
It turns out, Rupert Wood, principal analyst at Analysys Mason writes, most operators admit they are not experiencing much “pain” managing data growth. As a result, rapid public small-cell densification, an important indicator of heavy traffic growth, is continuously deferred.
As customers confront costly, usage-limited data plans, they are deterred from the kind of usage that might actually create widespread traffic issues for wireless carriers. Instead, carriers are primarily relying on a mix of data caps, incremental upgrades, and gradual expansion of their traditional cell tower networks to keep 4G performance stable and expand coverage areas to improve customer satisfaction. AT&T claims most of its traffic concerns were abated with the 2014 acquisition of Leap Wireless’ Cricket network, which added to AT&T’s network capacity. The Cricket network never came close to offering nationwide coverage, however.
 When pressed for specifics, many wireless carriers eventually admit they have enough spectrum to handle today’s traffic demand, but will face overburdened and insufficient capacity tomorrow. But that is not what the evidence shows.
When pressed for specifics, many wireless carriers eventually admit they have enough spectrum to handle today’s traffic demand, but will face overburdened and insufficient capacity tomorrow. But that is not what the evidence shows.
Analysys Mason:
Nations where the use of 4G is highest are not experiencing exponential growth in mobile data traffic. In fact, they have not been doing so for some time – even in developed Asia–Pacific. In the US, the CTIA recently recorded 26% traffic growth in 2014. If this figure is correct, the average usage per US mobile data subscriber barely changed at all in 2014: the recorded number of data subscribers grew by 22%, and the expected exponential curve of data traffic has morphed into an s-curve.
In fact, with wireless pricing so high in the United States, traffic growth here is minimal in comparison to Sweden, Hong Kong, South Korea and Japan. Most shift their usage to Wi-Fi as often as possible instead of chewing up their monthly data allowance.
Analysys Mason believes the forthcoming introduction of LTE-A — the more efficient next generation of 4G — will allow carriers to expand capacity on existing cell towers as quickly as future demand mounts without the need for massive numbers of new towers or small cells.
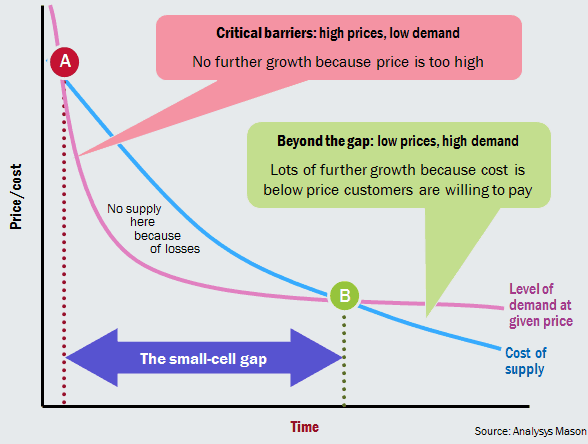
The analyst firm labels today’s cellular platform as a low-volume, high-cost network. If providers cut prices or relaxed usage caps, traffic would grow. It recommends operators should focus on increasing the supply of, and stimulating the demand for, data usage, and not simply expecting demand to come at some point in the near future. The analyst believes constructing a network of fiber-connected small cells may open the door to an exponentially higher capacity wireless network that performs better than traditional wireless data services and is robust enough to support high bandwidth applications that demand a strong level of network performance.
It would also benefit fiber to the home providers that could also market wireless backhaul service to wireless companies, helping defray the costs of constructing the fiber network and further monetizing it.


 Subscribe
Subscribe