The merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable includes castoffs that will be served by a completely unknown spinoff – GreatLand Connections, that nobody can speak with and does not have a website.
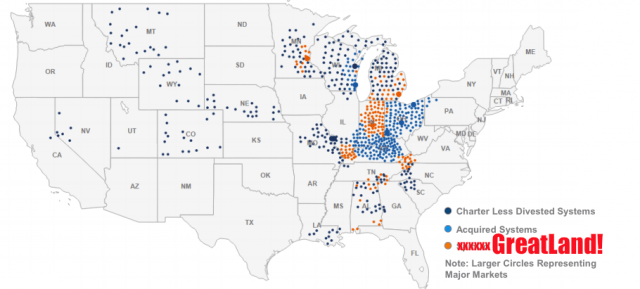
At least 2.5 million Comcast customers in cities like Detroit and Minneapolis could soon find their service switched to a new provider that doesn’t have a website, doesn’t answer questions, and won’t give detailed information to municipal officials about its plans, pricing, or service obligations.
GreatLand Connections is the dumping ground for communities Comcast no longer wants to serve, including cities in Alabama, Indiana, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Tennessee and Wisconsin.
Formerly known as “SpinCo” for the benefit of Wall Street investment banks advising Comcast, the new cable company has been created primarily to help Comcast convince regulators to approve its merger with Time Warner Cable. Comcast believes supersizing itself with Time Warner Cable will win a pass with the FCC by self-limiting its potential television market share. The deal is also structured to dump a large amount of debt on the brand new cable company, allowing Comcast to avoid a significant tax bill.
GreatLand will, for all intents and purposes, be Charter Cable under a different name. Charter will act as the “management company,” which means it will be in charge of most consumer-facing operations.
Beyond that, almost nothing is known about the new cable company, except that it will open its doors laden with $7.8 billion in debt, according to a securities filing. That is equal to five times EBITDA, or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization. In comparison, Comcast is 1.99 times EBITDA and Time Warner Cable is 3.07 times EBITDA, making the new cable company highly leveraged above industry averages. Charter Cable, which declared bankruptcy in 2009, is loaded down it debt itself, as it continues to acquire other cable operators.
Finances for the new company appear to be “less-than-middling,” according to MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett, in a note to investors.
Because cable operators face little serious competition, the chances of any significant cable company liquidating in bankruptcy is close to zero, but a heavily indebted company may be very conservative about spending money on employees and operations. It may also leverage its market position and raise prices to demonstrate it can repay those obligations.
 With many customers having only one choice for High Speed Internet access above 15-25Mbps — the cable company — the arrival of GreatLand concerns many municipalities facing deadlines to approve a transfer of franchise agreements from Comcast to the new entity.
With many customers having only one choice for High Speed Internet access above 15-25Mbps — the cable company — the arrival of GreatLand concerns many municipalities facing deadlines to approve a transfer of franchise agreements from Comcast to the new entity.
Jodie Miller, executive director of the Northern Dakota County Cable Communications Commission in suburban Minneapolis said it was impossible to find anyone to talk to at GreatLand. The commission needs to sign off on franchise transfers by mid-December, but nobody can reach GreatLand and the company has no track record of service anywhere in the country.
“We’re not even saying it’s unqualified,” she told Businessweek. “We’re saying we don’t really have information.”
Coon Rapids, Minn. has put franchise renewal negotiations on hold. Michael Bradley, a municipal cable TV attorney and the city’s longtime cable counsel said the deadline has been extended from Oct. 15 to Dec. 15.
“It’s a challenge,” he said. “No one knows who we can deal with locally. Nothing is certain yet and discussions are on hold.”
“We don’t have the answers we need,” added Ron Styka, an elected trustee with responsibility for cable-service oversight in Meridian Township, Michigan, a town served by Comcast about 80 miles west of Detroit.
“Answers have been inadequate at best and mostly not forthcoming,” echoed David Osberg, city administrator of Eagan, Minn. in a filing to the Federal Communications Commission.”It’s not clear whether GreatLand will be financially qualified.”
Eagan has had problems with Comcast in the past, and does not want new ones with GreatLand, especially with broadband service, which is vital to an effort to attract technology jobs to the community.


 Subscribe
Subscribe