The German Internet is functionally broken.
Deutsche Telekom, the largest telecommunications company in Germany, has announced it will introduce a brazen Internet Overcharging scheme for customers signing up for its broadband DSL service, including a throttle that reduces speeds to just 384kbps after as little as 75GB of monthly broadband usage.
For now, only new Telekom Deutschland customers signing up after May 1 will be affected by the usage limits. Customers will be offered the option of upgrading their Call & Surf package to get a larger usage allowance, although many parts of Germany are still reliant on DSL and its variants that cannot deliver the advertised speeds that go with the larger allowances:
- Up to 16Mbps: 75GB per month
- Up to 50Mbps: 200GB per month
- Up to 100Mbps: 300GB per month
- Up to 200Mbps: 400GB per month
“We want to offer customers the best network in the future and we will continue to invest billions to make that happen,” said Michael Hagspihl, marketing director of Telekom Deutschland. “However we cannot continue to sustain higher usage demand while lowering our prices. Customers with very high data volumes will have to pay more in the future.”
Company officials argue German broadband usage demands are accelerating at an ever-increasing rate, putting strain on the company’s network resources.
But critics question if usage demands are the root of the problem, why is DT exempting itself and its “preferred partners” from the data cap, including certain services that offer very high bandwidth video?
The Net Neutrality activist group Netzpolitik.org says DT is “massively violating Net Neutrality while the federal government looks away dreaming that the free market will solve the problem somehow.”
The group points out DT has admitted the speed throttle only applies to content providers who have not partnered up with the German telecom giant.
DT is exempting all of its own in-house content providers, the private television service Entertain, and telephone services (when provided by DT). For everyone else: the speed throttle gets closer the more customers use services like Apple iTunes or Amazon’s Lovefilm service. But DT says those companies can also get special treatment for the right price.
DT’s preferred partner cooperating agreements let “high quality content producers” pay for a managed services contract that guarantees exemption from the speed throttle and prioritization of their traffic on DT’s network, even if it means slowing down non-preferred partner content.
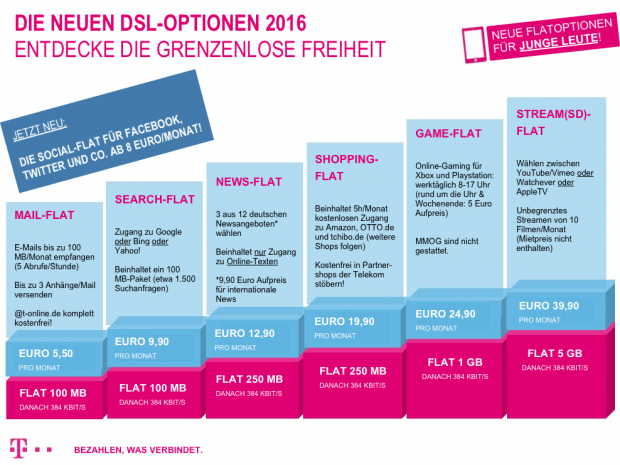
A parody future offer from DT.
“You cannot thumb your nose at Net Neutrality principles any better if you tried,” said Rene Pedersen, an Internet activist in Köln. “DT will have their emasculated two-tier Internet and all of Germany will have to suffer the consequences. Their own arguments do not even make sense. If there is a capacity crisis, how can they exempt some video providers that now consume the most network resources?”
 “Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,” said Netzpolitik’s Andre Masters. “This principle is called Net Neutrality – the equal treatment of data packets on the Internet, regardless of sender, recipient, or content. Now providers want to have a direct influence on the content sent, because they want to earn more money.”
“Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,” said Netzpolitik’s Andre Masters. “This principle is called Net Neutrality – the equal treatment of data packets on the Internet, regardless of sender, recipient, or content. Now providers want to have a direct influence on the content sent, because they want to earn more money.”
Technology publisher Heise Online says the new usage restricting tariff has “triggered a veritable sh**storm” among net users who consider a 75GB usage limit untenable, particularly for families with multiple Internet users.
Heise is also critical of claims DT has made in the press that suggests German Internet users must either accept the usage caps or understand the company will have to spend at least €80 billion ($108 billion) to build a national fiber network to manage growing traffic.
In contrast, Goldman Sachs last year estimated the cost of wiring every home in the United States with Google Fiber would cost $140 billion, a number now considered inflated. Verizon FiOS managed to get costs down for its own fiber network to a level that suggests Google would only need around $90 billion — $10 billion more than DT claims it needs.
“DT is being disingenuous when they suggest it will cost €80 billion to solve their capacity problem. For that amount every household in Germany would get their own fiber cable with 200Mbps speeds or more,” Heise writes in their editorial. “To avoid slowing users down with a speed throttle, only a small fraction of this amount is needed to extend the Internet backbone and peering agreements between providers. For years network traffic has grown exponentially and DT has kept up with demand. So why does DT suddenly need to reshuffle the cards now?”
DT has also received criticism for how it has depicted its heavy users — mostly as content thieves and software pirates using file swapping networks to steal copyrighted works. But instead of dealing with copyright violations, DT wants a sweeping usage cap system that punishes every customer that wants to use their broadband connection.
“Customers are not insatiable Gierschlünde who want everything for free,” writes Heise. “They already pay a lot of money to Telekom: 12.5 million DSL customers roughly translates into around a half billion euros in sales per month.”

Back to the future.
The German news magazine Spiegel writes DT’s usage limits strangle the Internet for millions of Germans, especially for competing video providers:
When throttled, customers will need more than 23 hours to watch a DVD-quality movie. At Blu-ray resolution, it will take about two weeks to watch just one film.
[…] The implications of the end of Net Neutrality in Germany represents a form of economic censorship, and German politicians are standing by to watch it happen.
The federal government sees the Internet as a political bargaining chip and not as the social, cultural and economic tool it represents. The government acts in the interests of certain lobbyists, not Germany’s digital future. This allows German telecommunications companies to focus on their economic self-interests without government policies that demand investment in digital infrastructure.
A number of German Internet users are expected to switch to a cable provider, where available, to escape DT’s impending speed caps.
According to the Frankfurter Rundschau, many German cable companies also reserve the right to limit speeds for customers. But in practice, most don’t impose limits until traffic exceeds 60GB daily, and the speed cap is lifted the next day. A cable industry official says its cap currently impacts about 0.1 percent of customers, almost all who use peer-to-peer file swapping networks. Exempt from measurements that bring customers closer to a speed cap: web browsing, video streaming, and video-on-demand.
For now, Germany’s cable operators facing the same traffic growth DT speaks about find no need to impose further limits, stating their networks are handling the traffic with network upgrades as a normal course of business.
“It calls out DT’s claims as fraudulent, because cable Internet users visit the same websites and do the same things DT’s customers do and there only seems to be an ‘urgent’ problem in need of a speed throttle solution on BT’s network,” says Pedersen. “What needs to be throttled are the financial expectations of DT management and shareholders. The Internet is not their personal vault waiting to be plundered.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/What if Net Neutrality.mp4[/flv]
What if Net Neutrality did not exist? [Subtitled] (1 minute)



 Subscribe
Subscribe Time Warner, Inc. (not the cable operator) and CBS Corp. are being encouraged by Wall Street to hurry up and just get married.
Time Warner, Inc. (not the cable operator) and CBS Corp. are being encouraged by Wall Street to hurry up and just get married. A merger deal involving CBS would run at least $35 billion, and Bloomberg says it would be the biggest U.S. media deal in more than a decade. Time Warner is definitely the larger player among the two companies with nearly twice the market capitalization of CBS.
A merger deal involving CBS would run at least $35 billion, and Bloomberg says it would be the biggest U.S. media deal in more than a decade. Time Warner is definitely the larger player among the two companies with nearly twice the market capitalization of CBS. Sprint will focus its postpaid wireless business on profitability in 2013, with reductions in customer discounts and a tighter upgrade policy that will raise prices for some and slow down others seeking new subsidized smartphones.
Sprint will focus its postpaid wireless business on profitability in 2013, with reductions in customer discounts and a tighter upgrade policy that will raise prices for some and slow down others seeking new subsidized smartphones.



 “Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,”
“Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,”