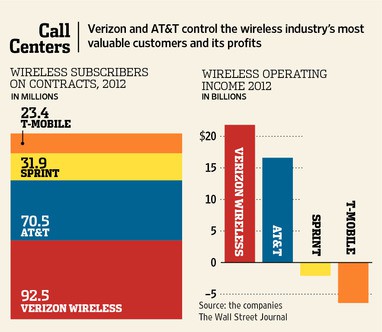
AT&T and Verizon Wireless have the largest share of wireless customers. (Wall Street Journal)
The Department of Justice has recommended the Federal Communications Commission promote competition by setting aside certain future low-frequency wireless spectrum for auctions open exclusively to smaller wireless carriers including Sprint and T-Mobile USA.
“Today, the two leading carriers have the vast majority of low-frequency spectrum whereas the two other nationwide carriers have virtually none,” the Department of Justice wrote in comments to the FCC. “This results in the two smaller nationwide carriers having a somewhat diminished ability to compete, particularly in rural areas where the cost to build out coverage is higher with high-frequency spectrum.”
The Justice Department’s antitrust division has monitored the wireless industry with increasing concern consumers are not getting benefits from a robustly competitive marketplace increasingly concentrated in the hands of two wireless giants: AT&T and Verizon Wireless.
That dominance is made possible, in part, from the control of lower frequency spectrum, particularly in the 600-800MHz range that easily penetrates buildings and delivers a more reliable signal over longer distances than frequencies counted in the gigahertz. Verizon and AT&T control large swaths of these lower frequencies that work well indoors and provide longer distance coverage in rural areas. Conversely, Sprint and T-Mobile, among other smaller carriers, rely heavily on higher frequencies that need a larger network of cell towers to support good signal levels.
It often means rural customers may find reception with AT&T or Verizon Wireless but end up with a roaming indicator or no service at all with smaller providers.
The Justice Department worries that auctioning off future prime 600MHz spectrum carved out of the UHF television band reallocated for wireless services will end up in the hands of the deepest pocketed providers — AT&T and Verizon Wireless, and further hamper the ability of Sprint, T-Mobile and other small carriers to compete.
“Due to the scarcity of spectrum, the Department is concerned that carriers may have incentives to acquire spectrum for purposes other than efficiently expanding their own capacity or services,” writes the DoJ. “Namely, the more concentrated a wireless market is, the more likely a carrier will find it profitable to acquire spectrum with the aim of raising competitors’ costs. This could take the shape, for example, of pursuing spectrum in order to prevent its use by a competitor, independent of how efficiently the carrier uses the spectrum. Indeed, a carrier may even have incentives to acquire spectrum and not use it at all.”
 The Justice Department echoes critics’ contentions that given a chance, large wireless carriers will “warehouse” acquired spectrum, unused, denying it from the competition. Carriers object to that claim, calling it baseless. But incentives remain for providers to drag their feet: spectrum warehousing forces competitors to pay even higher prices for other scarce spectrum, the necessity of constructing a larger network of costly cell towers to offer robust coverage, and fighting customers’ perceptions of inferior quality indoor phone reception.
The Justice Department echoes critics’ contentions that given a chance, large wireless carriers will “warehouse” acquired spectrum, unused, denying it from the competition. Carriers object to that claim, calling it baseless. But incentives remain for providers to drag their feet: spectrum warehousing forces competitors to pay even higher prices for other scarce spectrum, the necessity of constructing a larger network of costly cell towers to offer robust coverage, and fighting customers’ perceptions of inferior quality indoor phone reception.
In response, AT&T sent a multi-page, thinly veiled threat to sue if the Commission adopted the recommendations of the Justice Department.
“The Department is quite candid about its motive for this blatant favoritism: it hopes that reducing competition for the spectrum may enable Sprint and T-Mobile ‘to mount stronger challenges’ to AT&T and Verizon,” AT&T wrote in response. “Picking winners and losers in this fashion would be patently unlawful.”

AT&T also claimed the Justice Department’s recommendations were specifically tailored to help the two competitors, despite the fact neither company has shown much interest in acquiring low-frequency wireless spectrum, much less further expand the reach of their wireless networks:
“It is especially puzzling that the Department feels the need to help Sprint and T-Mobile in particular. Sprint already has by far the largest nationwide portfolio of spectrum, and holds vastly more spectrum than either AT&T or Verizon. It will also have ample financial resources at its disposal, as the Department has already approved Sprint’s purchase by Softbank, a financially strong Japanese company, and Dish Network has now made a competing offer for Sprint, citing the financial and strategic advantages of its own proposed combination.
Regardless of how this bidding war turns out, Sprint will receive a sizable infusion of cash, spectrum or both. T-Mobile, which is owned by Deutsche Telekom, one of the largest telecommunications companies in the world, just recently acquired substantial amounts of spectrum from both AT&T and Verizon, and is on the verge of completing a merger with MetroPCS that will add another trove of spectrum. So it is surely not for a lack of spectrum resources or financial backing that the Department needs to propose a financial giveaway to these companies.
Moreover, neither company even chose to bid at the Commission’s last auction of low-frequency spectrum, nor have they availed themselves of opportunities to acquire such spectrum in secondary markets. If low-frequency spectrum was critical to their business plans, as the Department simply assumes, someone should have informed their management, which has, instead chosen to acquire deep holdings in [higher frequency] PCS, AWS, and BRS/EBS spectrum.”
The Justice Department filing did not name Sprint or T-Mobile directly, but both companies are the only remaining national competitors to both AT&T and Verizon Wireless.
Spectrum set-asides are not unusual in telecommunications regulation. The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission set aside significant wireless spectrum exclusively for new entrants to promote competition. Ultimately, the new competitors had little impact with less than a 10 percent market share and all three are now considered up for sale. That spectrum may eventually end up in the hands of the largest Canadian wireless companies regardless of the CRTC’s original intentions when license transfer restrictions expire in 2014. All three could be acquired by one or more of the major providers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 After more than a year of aggressive promotions for new customers and those threatening to switch to a competitor, Time Warner Cable has pulled back to boost revenue and make greater profits.
After more than a year of aggressive promotions for new customers and those threatening to switch to a competitor, Time Warner Cable has pulled back to boost revenue and make greater profits.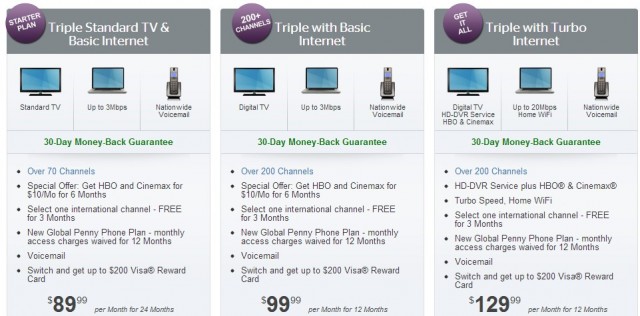


 Cable One has announced it will invest $60 million in network upgrades across 42 cable systems in its mostly rural footprint to enhance reliability and deliver faster Internet service.
Cable One has announced it will invest $60 million in network upgrades across 42 cable systems in its mostly rural footprint to enhance reliability and deliver faster Internet service.
