 The three companies that control 90 percent of Canada’s cell phone marketplace have set what they argue is ‘cut-throat’ competition aside to team up in a multi-million dollar lobbying campaign to discourage Verizon Wireless from entering the country.
The three companies that control 90 percent of Canada’s cell phone marketplace have set what they argue is ‘cut-throat’ competition aside to team up in a multi-million dollar lobbying campaign to discourage Verizon Wireless from entering the country.
Bell, Rogers, and Telus have maintained what critics charge is a “three-headed oligopoly” in the wireless business for years, leading to findings from the OECD that Canada is among the ten most expensive countries in the world for wireless service in almost every category and has among the highest roaming rates in the world.
Americans also pay high cell phone prices, and customers of both countries will find somewhat comparable pricing when comparing prices north or south of Lake Ontario. A shopper in Niagara Falls, N.Y. can find the Samsung Galaxy S4 from a Verizon reseller for $120 with a two-year contract. A shared data service plan runs as little as $80 a month for 500MB of data and unlimited domestic calling and global texting. Travel across the Rainbow Bridge to Niagara Falls, Ontario, walk into a Rogers store and the same phone runs $199 with a two-year contract (most Canadian carriers used to offer three-year  contracts until the government banned them earlier this year) and a service plan running $80 a month offering the same 500MB of data and unlimited domestic calling and texting. Rogers charges extra if customers want to text a customer outside of Canada, however.
contracts until the government banned them earlier this year) and a service plan running $80 a month offering the same 500MB of data and unlimited domestic calling and texting. Rogers charges extra if customers want to text a customer outside of Canada, however.
Verizon is no discount carrier. Verizon management has repeatedly stressed it offers premium service and coverage and can charge commensurately higher prices for access to that network. So the idea that Verizon’s interest in entering Canada is to launch a vicious price war is suspect, according to many telecommunications analysts.
Keep Verizon out of Canada at all costs!

They are coming.
In June, the Globe and Mail reported Verizon had shown serious interest in acquiring Canadian cellular upstart Wind Mobile with an early bid of $700 million. Wind Mobile, one of the three significant new “no-contract” entrants vying for a piece of the country’s cell phone market, has limped along since opening for business in 2009, unable to attract much interest from customers concerned about coverage gaps and the poor choice of mobile devices.
More recently, Wind Mobile’s new owner — the Russian mobile giant Vimpelcom — has expressed an interest in selling off the carrier because it cannot gain traction against the biggest three, which also control 85 percent of mobile wireless spectrum.
News that Verizon had taken an interest in the carrier leveled shock waves across the Canadian financial markets. Shares in the three largest telecom giants fell sharply on the news. Earlier this month, Bell CEO George Cope reported that Bell, Telus and Rogers have taken a $15-billion cumulative hit on the capital markets since Verizon hinted interest in Wind Mobile.
[flv width=”480″ height=”290″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Verizon takes aim at telecom Big 3 with possible Wind Mobile bid 8-19-13.flv[/flv]
The CBC reported earlier this summer that Verizon Wireless was interested in acquiring the 600,000 customers of independent wireless provider Wind Mobile, which has an insignificant share of the Canadian wireless market. (2 minutes)
Spending a few million, or even a billion dollars, to keep Verizon south of the Canadian-U.S. border is well worth it to the three big players who have launched an expensive campaign to block the proposed transaction and are willing to pay premium prices to keep struggling carriers from being sold to deep-pocketed American telecom companies.
 Telus had already done its part, attempting to scoop up another scrappy upstart carrier that wanted out of the wireless business. But the Canadian government rejected Telus’ proposed acquisition of Mobilicity, claiming it would harm efforts to expand Canadian wireless competition. Not to be deterred, Rogers is now attempting a cleverly structured deal to acquire Wind Mobile out from under Verizon with a proposed buyout worth more than $1 billion.
Telus had already done its part, attempting to scoop up another scrappy upstart carrier that wanted out of the wireless business. But the Canadian government rejected Telus’ proposed acquisition of Mobilicity, claiming it would harm efforts to expand Canadian wireless competition. Not to be deterred, Rogers is now attempting a cleverly structured deal to acquire Wind Mobile out from under Verizon with a proposed buyout worth more than $1 billion.
To avoid the anticipated rejection of the deal by Canadian regulators on competition grounds, Rogers has reportedly joined forces with Toronto-based private equity firm Birch Hill Partners that would make that firm the owners-in-name. Although Rogers wouldn’t get a direct equity stake in Wind, it would finance a good part of the deal and win access and control of Wind’s mobile spectrum for its own network. More importantly, it could keep Verizon out of Canada.
“The government is handing out loopholes to Verizon to beg them into Canada”
Cell phone companies in Canada are particularly angry that the government has set aside certain spectrum and guaranteed access for upstart providers to successfully establish themselves without having to outbid the cash-rich big three for wireless frequencies or have to build a nationwide network from scratch. Bell, Rogers and Telus have consistently opposed spectrum set-asides for small carriers, deeming them “unfair.” They argue Canadians’ voracious needs for more wireless service are unending, and it would be unfair not to sell the spectrum to benefit their larger customer bases. But hearing that Verizon, a company larger than Bell, Rogers, and Telus combined, could get preferential treatment and spectrum to enter the country has them boiling mad.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Telecom debate 8-19-13.flv[/flv]
Bell’s CEO George Cope appeared on “The Lang and O’Leary Exchange” to debate the fairness of Verizon’s possible entry into Canada’s wireless market. Cope argues Verizon is getting special favors. (9 minutes)

Cope
The idea of luring a company to move or begin offering service in a barely competitive marketplace is hardly new. Cities have offered preferential policies to airlines to fly in and out of particular cities, local governments have offered tax abatements to get companies to set up shop, and providing exemptions for zoning and infrastructure have been familiar to telecommunications companies for decades.
In 1880, the National Bell Telephone Company had incorporated, through an Act of Parliament, the Bell Telephone Company of Canada (today also known as BCE), which was given the right to build telephone lines over and along all public property and rights-of-way without compensation to the public or former owners. Through a series of mergers and acquisitions, Bell would later become the dominant monopoly provider of telephone service across much of eastern Canada.
When the phone companies were handed wireless spectrum to launch their wireless businesses in the 1980s, they didn’t have anything to complain about either.
None of that history impressed Bell’s current CEO George Cope, who took to the airwaves to complain Verizon was being given preferential treatment:
- Verizon could bid on two blocks of Canadian spectrum set aside for new entrants to the market in auction later this year. Because the big three Canadian firms are not permitted to bid on these blocks, they are likely to be sold at a lower price.
- Verizon would not have to build its own networks to remote or rural communities, but would be able to piggyback on existing networks.
- Verizon can bid to acquire small Canadian companies such as Mobilicity or Wind, but Bell, Telus and Rogers are forbidden from bidding on them.
“A company of this size certainly doesn’t need handouts from Canadians or special regulatory advantages over Canadian companies,” Bell said in a full-page newspaper ad. “But that is exactly what they get in the new federal wireless regulations. We’re ready to compete head to head, but it has to be a level playing field,” Cope said in a TV interview, echoing Rogers CEO who also called for a “level playing field.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Is Verizon really the bogeyman Canada’s telecom giants claim 8-19-13.flv[/flv]
Bell, Telus, and Rogers have launched a lobbying campaign designed to make life difficult for Verizon Wireless if it chooses to enter Canada. The CBC reports Verizon will be able to bid on more spectrum than Canadian carriers and will have the right to roam on Canada’s incumbent wireless networks. (2 minutes)

Industry Minister Moore
Telus went further, claiming Verizon’s entry into Canada would result in a “bloodbath” for Canadian workers, laid off by the three largest Canadian providers to cut costs to better compete with Verizon.
But Cope said at least one Canadian carrier won’t be able to compete at all, because preferential treatment for wireless spectrum will result in at least one of the big three to lose at a forthcoming spectrum auction, guaranteeing degraded wireless broadband speeds and worse service.
The three companies have found little sympathy in Ottawa, particularly from Industry Minister James Moore, now on a road tour across Canada to promote the government’s wireless competition policies. He called the big three’s loud campaign self-serving and announced a new website sponsored by the Conservative Party of Canada to prove it.
“I think that the public instinctively knows that when they have more choices that prices go down and more competition they’re well served by that,” he told CBC News in Vancouver on Monday. “The noise that we’re hearing is about you know companies trying to protect their company’s interest. Our job as a government is larger than that, our job is to serve the public interest and make sure that the public is served in this so that’s one of the reasons why I’m pushing back a little bit.”
Industry Minister James Moore appeared on CBC Radio this morning to contest the wireless industry’s claims that Verizon is getting special treatment and will bring unfair competition to the Canadian wireless market. (7 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
Oppose Verizon Wireless. Do it for Canada!
But the wireless companies show no signs of backing down and have turned towards appealing to Canadian nationalism and fairness.
 “The U.S. government is not giving Canadian wireless carriers any special access to the U.S. market,” says a website launched by the big three cell providers to drum up support for a “level playing field.” “Then why is it that our own government is giving American companies preferential treatment over our own companies?”
“The U.S. government is not giving Canadian wireless carriers any special access to the U.S. market,” says a website launched by the big three cell providers to drum up support for a “level playing field.” “Then why is it that our own government is giving American companies preferential treatment over our own companies?”
This week, a Reuters report citing unnamed sources suggests Bell, Telus, and Rogers are about to target Verizon directly with a new campaign warning Canadians the American giant has been implicated in allowing the U.S. government open access to network and customer data, which would represent a profound privacy threat to Canadian customers.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bell Rogers Telus Ad 8-13.flv[/flv]
Bell, Telus, and Rogers paid to produce this ad calling on Canadians to protest unfair competition from an American wireless company. (1 minute)
So far, Canadians’ hatred of their telecommunications providers has trumped the companies’ public relations and scare tactics. The Conservative government in Ottawa is winning support for its wireless competition war, even from unlikely places.
 “Someone mark the date,” Tweeted one Halifax woman not inclined to vote Conservative. “Stephen Harper has done something I mostly support.”
“Someone mark the date,” Tweeted one Halifax woman not inclined to vote Conservative. “Stephen Harper has done something I mostly support.”
“Eat it Telus/Bell/Rogers,” wrote a Calgary man fed up with the lack of competition in Canadian wireless.
John Lawford, executive director of the Public Interest Advocacy Centre in Ottawa, says opposition from the big three telecom companies is obvious because they don’t want to face a fourth, powerful competitor.
“They should be scared because chances are they’re going to have more competition in the Canadian market if Verizon comes in and they are going to have to lower their prices and compete harder,” Lawford told CBC News. “It’s pretty rich of them to be talking about unfairness” when they already control 90 per cent of Canadian spectrum, he added.
Iain Grant of the SeaBoard Group, a telecommunications consultancy, said government policies to open up more competition are designed to shake things up.
“[The new rules weren’t] meant to be a level playing field,” said Grant. “[They were] meant to give a leg up [to new competitors].”
“To talk of loopholes, as some do, is to not understand that the same companies who complain most loudly about loopholes in 2013 were the recipients of even greater public largesse in 1985 when the government gifted their initial spectrum as an incentive to build a wireless business in Canada,” said Grant.
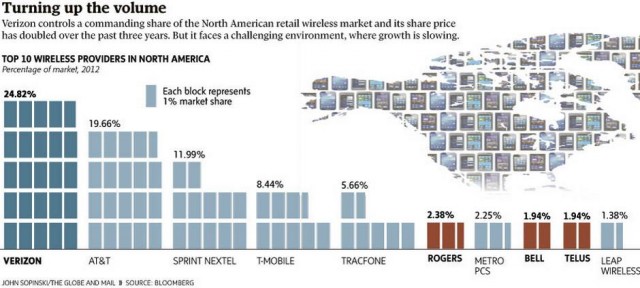
Few companies have taken on the Canadian big three telecom providers because of their enormous market share, at least inside Canada.
Nine out of ten Canadian wireless users are subscribed to Bell, Telus or Rogers. Trying to convince a banker to extend capital loans to effectively confront a wireless oligopoly in a country with an enormous expanse of land but not people and find enough airwaves among the 15% not controlled by the big three is an uphill battle.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Wireless war heats up 8-19-13.flv[/flv]
CBC reports Industry Minister Moore believes increasing competition is the best way to cut Canadian cell phone bills. Regardless of whether Verizon enters Canada, the current government will continue to push for more competition. Even the threat of Verizon coming to Canada has already reduced prices. (2 minutes)
Why does Verizon want to enter Canada?
 Analysts suspect Verizon’s interest in Canada has little to do with wooing Canadians to Big Red. Many suspect Verizon’s true interest is to make life easier for its traveling American customers who head north for business or pleasure.
Analysts suspect Verizon’s interest in Canada has little to do with wooing Canadians to Big Red. Many suspect Verizon’s true interest is to make life easier for its traveling American customers who head north for business or pleasure.
Chief among the possible benefits is the elimination of roaming charges for Verizon customers.
“Verizon’s customers come into the country every day through all the bridges and ports of entries and they want to roam where they want to roam, whether that’s fishing in Saskatchewan or hunting in northern Ontario or wherever,” said Grant.
There are other apparent impediments that could limit the usefulness of Wind’s mobile network to Verizon. In addition to only operating in the largest Canadian cities, Wind’s infrastructure is built by Chinese firm Huawei and is not compatible with Verizon’s technology.
Huawei has been the subject of significant controversy because of its reported ties to the Chinese military. Fears that data could be intercepted by the Chinese government have kept many North American firms from doing business with the company.
Verizon also lacks bundling options for Canadian customers. The biggest three Canadian providers can offer telephone, television, and wired broadband service to their customers. Verizon can only offer wireless service.
Verizon has second thoughts
Perhaps most remarkable are late reports that Verizon may be having second thoughts about jumping into Canada’s wireless market.
Desjardins analyst Maher Yaghi said Verizon may have delayed its plans until after Ottawa’s auction of 700MHz spectrum planned for January to better understand the potential spectrum costs it will incur entering Canada.
Others speculate incumbent providers may be attempting to end the rationale for Verizon to enter Canada in the first place. One major development includes a much more favorable roaming deal for Verizon that could dramatically cut the costs for Verizon customers to roam on Canadian networks.
Regardless of what Verizon does, Industry Minister Moore says Canada’s goal of getting increased competition will continue.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Verizon doubts 8-15-13.flv[/flv]
CBC reports Verizon may be having second thoughts about entering Canada. Verizon may not be interested in entering a political battle to win licenses to provide service and may want to acquire its own spectrum before considering buying either Wind Mobile or another competitor like Mobilicity. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
The big three companies will just relent and offer up a decade or longer contract to Verizon with roaming fees at near cost in order for get Verizon to agree to back off from entering the Canadian market.
It’s their best play, they have no public or government support, and Verizon is too cheap to make a huge investment in the market if they have a cheap way to get what they really want.