![]() A growing scandal over alleged diversion of British taxpayer funds intended for fiber broadband rollouts has now cost one whistleblower his job, terminated after suggesting British Telecom (BT) is artificially inflating infrastructure expenses.
A growing scandal over alleged diversion of British taxpayer funds intended for fiber broadband rollouts has now cost one whistleblower his job, terminated after suggesting British Telecom (BT) is artificially inflating infrastructure expenses.
The Conservative government’s Department for Culture, Media, and Sport (DCMS) oversees £1 billion in public subsidies to improve broadband in Britain. Much of that is earmarked to construct fiber to the neighborhood facilities in smaller towns and villages — the rural subsidy providing the only chance most of these residents have for better broadband service. But a whistleblower inside the DCMS has said the primary government-approved contractor, BT, is artificially inflating its prices — pocketing a growing amount of taxpayer funds instead of enhancing its broadband buildout.
The whistleblower, identified as Michael Kiely, a DCMS broadband project consultant, was fired after he detailed BT’s ever-growing (and highly confidential) cost estimates to several village and town councils fighting for a better deal from the phone company. The issue has been closely watched by the Br0kenTeleph0n3 blog, which reports on how Britain’s broadband stimulus funding is being spent. The blog reported the DCMS sacked Kiely, apparently for exposing BT’s secret pricing schemes.
“I am getting increasingly concerned at the way in which whistleblowers are being bullied,” Margaret Hodge, chair of the Public Accounts Committee, told the Guardian newspaper while demanding an investigation. “All too often people hide behind commercial confidentiality. This culture denies us the right to know how our money is being spent.”
Many local governments are matching broadband subsidies with local funds to increase the number of homes reached by fiber-enhanced Internet access. The demand for fast broadband is so great in the UK, the initial plan to spend £530 million has now been effectively doubled, with even more money coming from the European Commission and other sources. Britain’s broadband expansion plan envisions reaching as many rural homes as feasible with the available funds. The more funds diverted away from broadband expansion into the pockets of others, the fewer number of homes can be reached.
The enormous amount of available government funding appears to have caught BT by surprise, and Kiely suspects the company is inventing new fees, while inflating others, to ‘soak up’ the additional money without having to deliver any improvements in service.
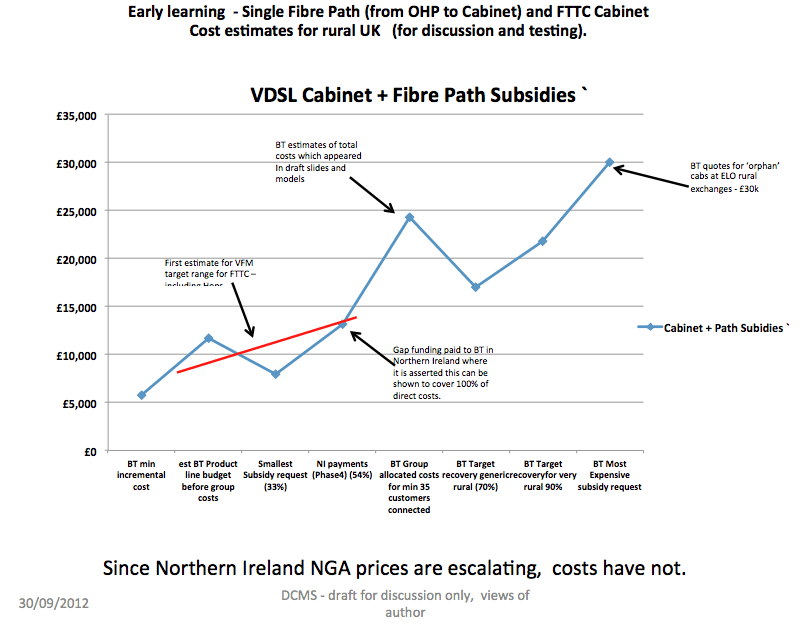
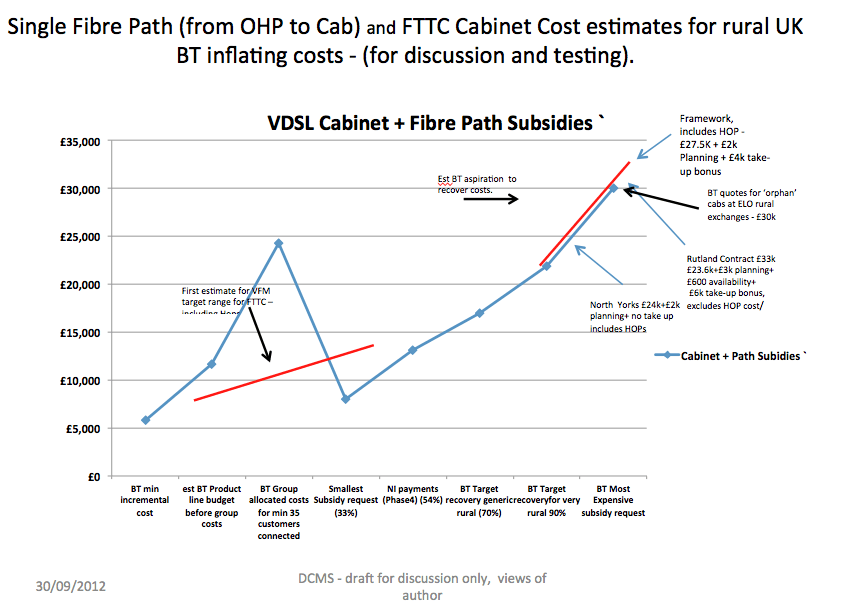
Kiely noted BT appeared to be setting new wholesale rates for fiber cabinets, despite the fact costs vary widely in different regions. Kiely notes that even as BT enjoys economies of scale, the price it charges for rural cabinets appears to be rising, even though costs are declining.
In rural areas, BT is seeking up to £30,000 for each fiber cabinet, despite the fact the average price in Northern Ireland’s recent broadband roll-out was just over £13,000 each.
BT’s estimate for two fiber cabinets in Great Asby, which will service hundreds of residents, was estimated at £60,000, a price Kiely also suggests is inflated.
 The phone company has made cost verification nearly impossible with strict, mandatory confidentiality agreements that prohibit local councils from learning BT’s true costs. BT’s non-disclosure agreement also prohibits local governments from comparing notes about what the company charges in nearby communities. The government has approved only two vendors for the government-funded broadband expansion — BT and Fujitsu, with BT winning the overwhelming majority of contracts.
The phone company has made cost verification nearly impossible with strict, mandatory confidentiality agreements that prohibit local councils from learning BT’s true costs. BT’s non-disclosure agreement also prohibits local governments from comparing notes about what the company charges in nearby communities. The government has approved only two vendors for the government-funded broadband expansion — BT and Fujitsu, with BT winning the overwhelming majority of contracts.
The giant, former state-owned phone company, comparable to AT&T or Bell Canada, can also hide cost reductions achieved from experience rolling out service, economies of scale like volume discounts, and other labor savings. BT’s attempt to create standardized pricing also leaves plenty of room to inflate prices by rolling in unexplained charges like “planning costs,” “availability charges,” and “take up bonuses.”
Despite this, BT says claims it is misspending public funds are completely baseless, and points to its own independent investment in British broadband.
“It is ludicrous that some people are suggesting that we are trying to pass on the full cost of deployment to our public sector partners,” BT said in a statement. “In fact, we are looking at a low double digit year payback in these areas even when the public funds are taken into account.”
Conservative party loyalist Maria Miller, recently appointed as the government’s new culture secretary during a cabinet reshuffle, has not commented on the BT controversy. Instead, she has prioritized reducing government “red tape” for providers like BT while also tamping down expectations for the broadband expansion program.
Among her deregulation priorities: scrap the right for local governments to object to the placement of often unsightly broadband street cabinets, force “reasonable” terms on private landowners where necessary infrastructure must be placed or routed across, and sweeping permission to allow virtually anyone to put overhead lines up anywhere they please. All of these objectives heavily favor BT’s interests, according to industry observers.
Miller also recently took pressure off BT to deliver game-changing speeds by redefining “superfast broadband” as “potential headline download access speeds greater than 24Mbps.” That falls far short of the 100Mbps service most expected in return for more than £1 billion in taxpayer subsidies, often directed to BT.
Even more telling, Miller considers 2Mbps broadband speeds adequate: “Our investment will help provide 90% of homes and businesses with access to superfast broadband and for everyone in the UK to have access to at least 2Mbps,” she said.
The European continent, in comparison, is targeting 30Mbps as the bare minimum speed, with at least 50% of Europeans getting 100Mbps service by 2020.
Great Britain’s broadband expansion plan is highly dependent on fiber to the neighborhood (FTTN) technology, with traditional copper phone lines carrying the service the rest of the way into a home or office. Both AT&T’s U-verse and Bell’s Fibe are examples of FTTN technology.
As elsewhere, BT considers 24Mbps a suitable maximum speed for FTTN technology, but most customers will not even achieve that. Just like traditional DSL, distance matters, as does line quality. BT has quietly told most councils the average speed most local residents will actually receive is 15Mbps on average.
[flv width=”640″ height=”372″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Jeremy Hunt Announces Superfast broadband 2010.flv[/flv]
Former Secretary of State for Olympics, Culture, Media and Sport Jeremy Hunt outlining Britain’s superfast broadband initiative in 2010. (4 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe