Stop the Cap! reader Angela sent us a print-out, by mail, of a recent guest editorial published by the online news site, the Lincoln Tribune. White, who is 89 and lives in North Carolina was irritated by the piece, written by Kinston, N.C. mayor B.J. Murphy.
“B.J., who was all of 29 when he was elected in 2009, is the first Republican mayor in Kinston since Reconstruction, and after writing pro-cable company nonsense like he did in that [online] paper, he better be the last,” White wrote. “My mother and father grew up with the same kind of monopoly these cable companies have today, only then it was the damn railroads. How we ended up electing a mayor who wants us back in that era is beyond me.”
What caught my attention early on skimming the mayor’s views was a single passage early on in his piece:
Municipal broadband, also known as Government Owned Broadband Networks (GONs) is quickly becoming our state’s new enterprise service of choice for cities and towns.
Really? GONs? Now I’ve been editing Stop the Cap! since mid-2008, and we’ve covered North Carolina’s broadband landscape extensively, and this is the first time I’ve ever seen community-owned broadband referred to as “Government Owned Broadband Networks.” A quick Google search reveals why: it’s a loaded term conjured up by corporate-funded, dollar-a-holler groups that oppose public involvement in broadband. People don’t like “government” they surmise, so let’s relabel these networks accordingly. Besides, bin Laden is dead and we can’t use him.
In this case, the acronym ‘GONs’ doesn’t even make sense — shouldn’t it be GOBN? But that wouldn’t sound as demagogic as “gones,” would it?
Your cable dollars pay for consultants who cook up these silly labels, which are not even accurate. Community-owned broadband need not be a “government-owned” enterprise it all. Some are public-private partnerships, others are co-ops or run on a not-for-profit basis independent of government. What they do have in common is the ability to offer better broadband than the “take it or leave it” service many cable and phone companies provide, if they deliver it at all.
After getting past the pretzel-twisted acronym, it’s clear Mayor Murphy is no fan of community broadband.
I believe we should refrain from the temptation to compete with private communications providers on services and infrastructure that we are not equipped to properly manage.
Who is “we” exactly? The city of Kinston? Mayor Murphy must not believe in the talents and abilities of his employees. Is Mayor Murphy confessing he is in the ironic position of attacking local government while also being an integral part of it?
Most of Murphy’s editorial is a rehash of talking points already delivered by dollar-a-holler groups like the Heartland Institute or something called the Coalition for the New Economy. The hypocrisy of both “small government” groups calling for more government regulation on certain broadband providers while exempting their corporate friends and backers is lost on them.
Murphy suggests municipal utilities are not well run, and the locals evidently complain regularly about the one serving Kinston. Are the complaints about service in other towns about companies like Duke Energy and CP&L — private providers — any fewer in number? Who exactly loves their local gas and electric company?
Murphy concedes “many cities and towns throughout the years have seen voids in service or infrastructure, not easily duplicated by the private sector. Those areas of service tend to be water, sewer, and sometimes electricity.”
Our rural grandparents lived that life, waiting for electricity and telephone service that private companies refused to provide because it was simply not profitable enough for them to do so. In fact, NC Public Power was created precisely because private companies wouldn’t deliver electric service in rural North Carolina. Just 30 years ago, the state allowed municipal construction of generating plants because there were fears private companies lacked the resources to handle the growth in electricity demand. The Three Musketeers: Mayor Murphy, the Heartland Institute, and the “Coalition” would prefer cities go dark waiting for private capital to show up? And at what rate of return would they demand from a state in desperate circumstances? Imagine the complaints rolling in over that.
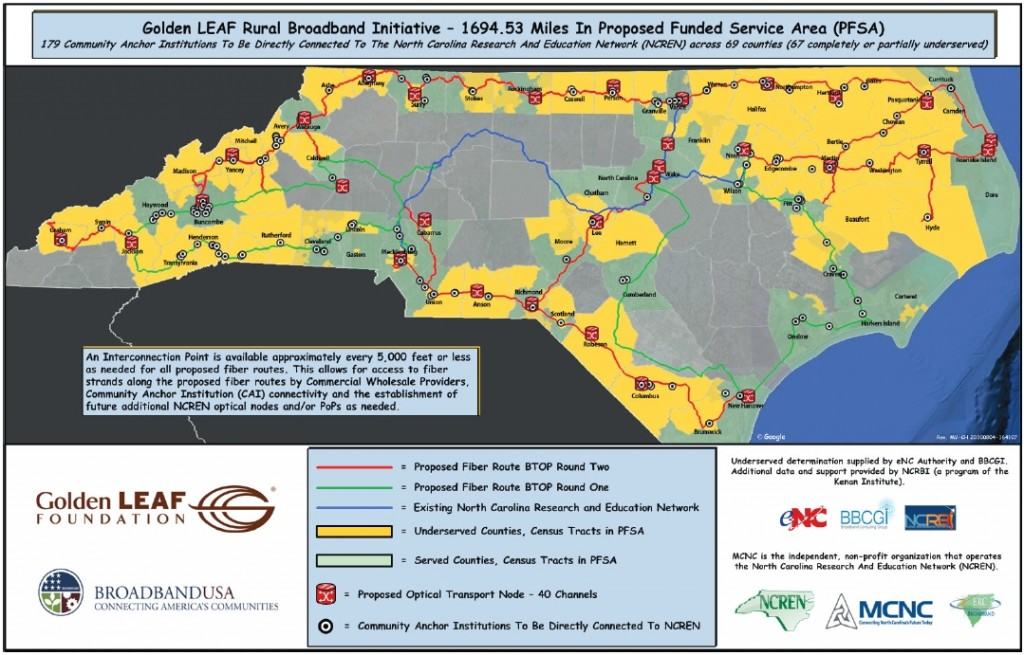
And so it goes with rural broadband — a service still not reliably available throughout rural communities in Murphy’s state and 49 others. The problem of rural North Carolina’s pervasive lack of consistent service is so bad, the Golden LEAF Foundation targeted rural broadband development in 69 North Carolina counties, most lacking more than the slowest speed DSL. Lenoir County, which includes Kinston is not among them. Perhaps Murphy’s myopic views apply in his local community, but they certainly don’t in large parts of the rest of the state. Nobody is forcing the mayor to build Kinston a broadband network. It would be nice if he didn’t advocate away that right for other less fortunate areas.
Golden LEAF’s initiative, which is just one of several projects in the state, has garnered more than 130 letters of support including approximately 70 from state, county and municipal officials and 12 from middle-mile and last-mile service providers interested in using the fiber network to reach consumers and small businesses. Part of the project is being funded by federal tax dollars. Many of the providers eager to connect to that network are private companies, who seem to have no problem hopping on board a fiber backbone paid for, in part, by taxpayer dollars.
Other projects are community fiber to the home networks, designed to support high bandwidth requirements of the digital, knowledge-based economy. These community providers didn’t appear out of nowhere. Communities built these networks after incumbent providers refused upgrade requests, repeatedly. Some communities even open up their existing municipal fiber networks to residential use.
The hue and cry among those opposing community broadband usually begins when these new providers start selling service to the public. Private providers don’t complain when public networks provide service only to schools, health care facilities, and public buildings. But when anyone can sign up, the complaints rage from corporate-funded dollar-a-holler groups, the companies themselves, and certain politicians, some who take campaign contributions from the other two. The talking points are remarkably similar. Too similar.
Mayor Murphy makes an unfortunate comparison in his editorial — to those railroads which made Angela’s hair stand on end.
“His only experience with that monopoly and the barons who ran it came from his American History class and he wasn’t paying attention,” she says.
Government better serves the people by creating the framework for private business to thrive, not by actually owning or competing with private, tax-paying businesses. Rarely, if ever, will one see two railroad tracks side by side owned by different companies. Yet, that is what would happen with broadband service in many communities. In many cases, GONs would essentially use taxpayer dollars to build Internet infrastructure on top of that which has already been put in place by private providers.
Uh…
Is the mayor actually promoting a monopoly for broadband? I suggest the mayor read our earlier piece about the historical plight of Danville, Virginia — a community on the border with North Carolina. He will learn that those one-railroad-towns desperately wanted a second or third railway serving their community, if only to escape the horrible and expensive service monopolies and duopolies provided in places without sufficient competition. It took decades to break the railway monopolies up, and consumers and businesses overpaid millions of dollars to robber barons who fixed prices and the type of service communities would receive. That kind of control could make or break the economy of a town or city. So it will be with broadband.
Of course, the mayor could suggest we liberalize access to existing broadband infrastructure and allow competitors to sell services on every available network, or allow a community to build one giant fiber optic pipeline on which every provider can deliver service, but we know what his free market friends would say about that.
Boiled down, Murphy’s arguments come from a position of already having access to the broadband resources he needs, wants, and can afford. That’s a classic example of “I have mine, too bad you don’t have yours”-politics.
That seals the fate of rural North Carolina to an indefinite future of never getting broadband service.


 Subscribe
Subscribe