 A pro-consumer group has released a new report that refutes claims from the telecommunications industry that broadband reform represents an investment killer and takeover of the Internet by the Obama Administration.
A pro-consumer group has released a new report that refutes claims from the telecommunications industry that broadband reform represents an investment killer and takeover of the Internet by the Obama Administration.
Free Press this week challenging 10 of the wildest claims in its report, “The Truth About the Third Way: Separating Fact from Fiction in the FCC Reclassification Debate.” Aparna Sridhar, Free Press’ Policy Counsel used publicly available evidence to effectively debunk the multi-million dollar lobbying campaign to stop broadband reform.
Unfortunately, more than a handful in Congress have accepted those discredited claims as fact. Free Press hopes truth will prevail over the enormous money-fueled opposition effort, especially as the FCC begins proceedings next week on its proposed “Third Way” approach to broadband oversight. The agency is expected to issue a Notice of Inquiry and to seek public comment on the issues of broadband reform and reclassification.
A sampling from the report, which we encourage you to read:
Fiction #3: Placing broadband services back under the Commission’s explicit authority will stifle investment in broadband networks.
Fact: The FCC’s proposed policy merely preserves the status quo prior to the recent uncertainty created by the federal appeals court ruling. As a result, it should have little to no effect on company investment decisions.
Many industry representatives and investment analysts have dismissed the notion that the FCC’s Third Way will deter investment. Furthermore, history contradicts the claim that applying some of the rules contained in Title II of the Communications Act to broadband service providers (as the Commission has proposed) will adversely affect investment in the networks. Telecommunications industry investments soared during the period when carriers were subject to the full panoply of rules contained in Title II. Investments only began decreasing once the FCC began dismantling many of the pro-competition rules stemming from this part of the Communications Act.
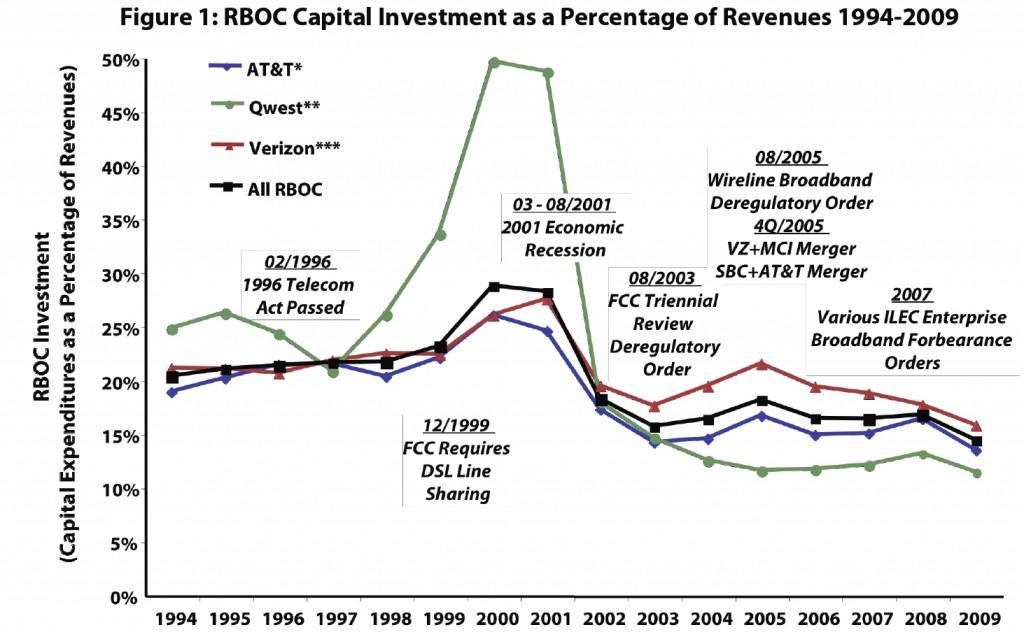
As we've said at Stop the Cap! for two years now, providers' investments in upgrading and expanding their networks are declining, even as demand (and prices) for those services are increasing.
Fiction #4: Placing broadband services back under the FCC’s explicit authority will lead to job losses in the telecom sector.
Fact: The telecommunications sector accelerated its job-shedding following industry consolidation and FCC deregulation, a trend that continues unabated even as company revenues reach historic highs.
The notion that the FCC’s move to re-establish its authority over broadband networks will harm employment is also nothing more than unsupported rhetoric. The simple reality is this sector accelerated its job-shedding following industry consolidation and FCC deregulation. And this trend continued even as overall revenues in the sector continued to expand. Unfortunately, the underlying market economics and company statements suggest this trend will continue regardless of how the FCC acts on the regulatory authority question.
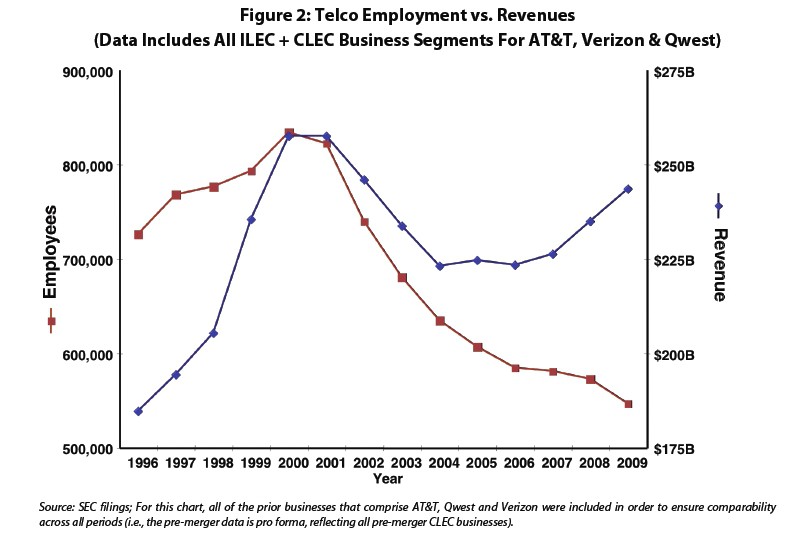
So much for the argument that regulation will cause job losses. As this plainly illustrates, even as profits fatten at AT&T, Qwest and Verizon, employment numbers are on a steep decline in today's deregulated marketplace.
Fiction # 7: The FCC’s Third Way proposal is an unprecedented power-grab which departs from Congress’s intent to leave the Internet unregulated.
Fact: The FCC’s proposal will bring the Commission’s approach to broadband networks in harmony with longstanding principles in communications policy. The law always has recognized a distinction between communications infrastructure (like broadband networks) and the content that travels over that infrastructure (such as websites on the Internet). In fact, it was the Powell FCC’s decision to abandon oversight over broadband networks that represented a radical and irresponsible shift — by treating basic connectivity services just like content, the Powell FCC undermined the Commission ability to make pro-competitive, pro-consumer policies in the broadband space. This FCC’s proposal would return to the first principles of communications policy that fostered innovation, competition and investment in the first place.
Fiction #8: The FCC’s proposal would amount to a “government takeover of the Internet.”
Fact: The FCC’s proposal would draw a line between basic two-way communications — which have always been regulated by the FCC — and Internet applications and websites, which would remain unregulated by the FCC. None of the parties in the debate before the FCC have suggested that the FCC impose any kind of content regulation on the Internet. Nor has anyone suggested that the government take over the physical infrastructure that forms the Internet. Rather, the FCC is proposing to apply some basic, light-touch rules of the road to the owners of broadband networks.
These rules will attempt to encourage private investment, promote competition, and foster innovation, economic growth, and job creation. Further, restoring its regulatory framework back in harmony with the law will insure the FCC has basic consumer protection authority.


 Subscribe
Subscribe