Early reaction and declarations of a price war notwithstanding, yesterday’s “price cuts” from Verizon Wireless and AT&T Mobility on their unlimited calling plans may bring price increases for many customers who don’t need all of the components of the wireless industry’s Cadillac plans.
Early reaction and declarations of a price war notwithstanding, yesterday’s “price cuts” from Verizon Wireless and AT&T Mobility on their unlimited calling plans may bring price increases for many customers who don’t need all of the components of the wireless industry’s Cadillac plans.
First, an explanation of what has changed.
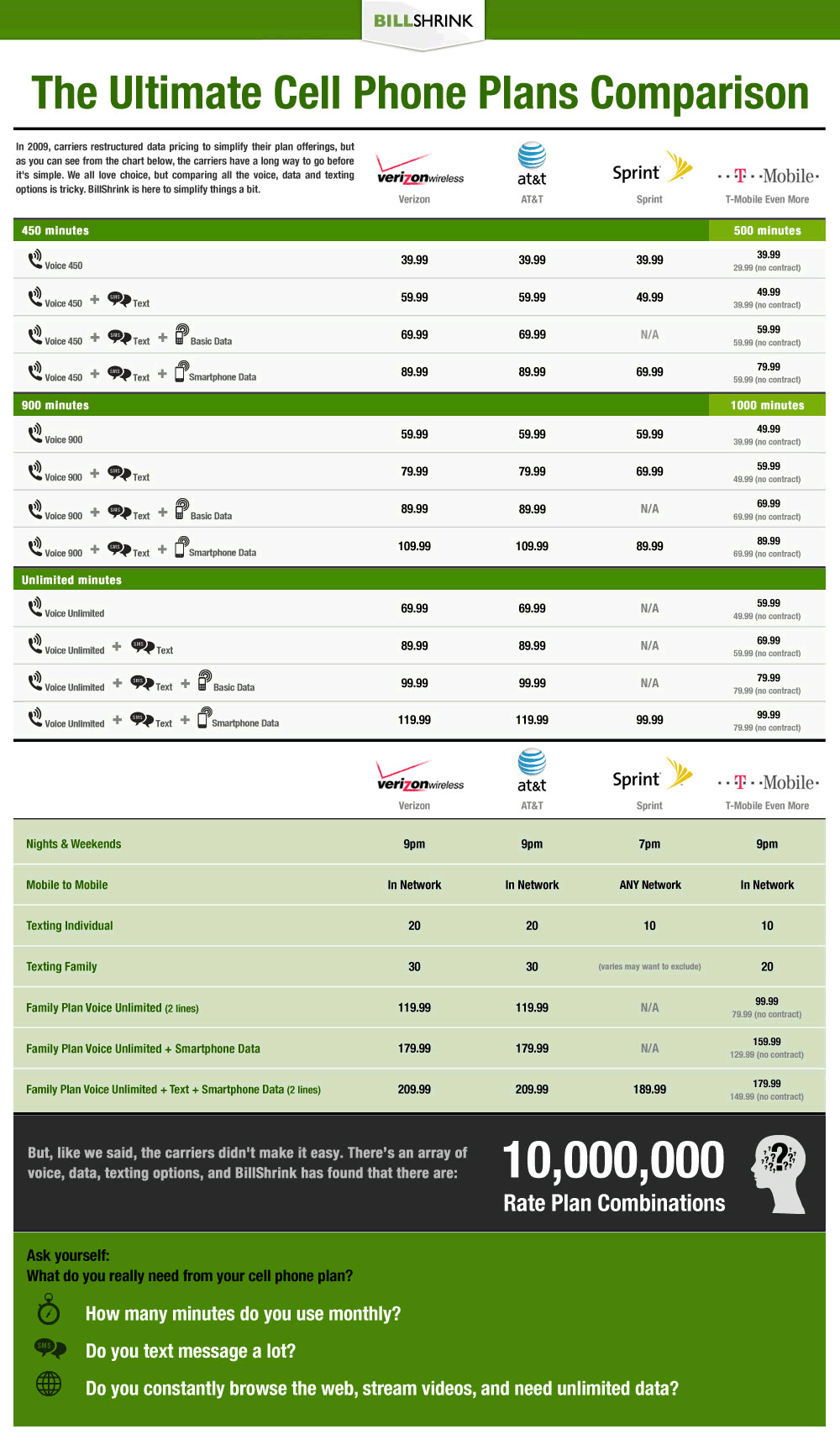
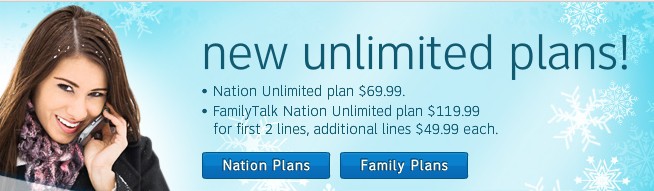
Verizon started the ball rolling announcing a $30 price cut on their Nationwide Unlimited Talk plan. Formerly $99.99, customers now pay $69.99. For those with multiple phones on a single account, Verizon’s Nationwide Unlimited Talk Family SharePlan, which includes two lines, now drops to $119.99. AT&T immediately matched Verizon’s new pricing. AT&T’s Nation Unlimited plan is now also $69.99 and their shared line plan, FamilyTalk Nation Unlimited is $119.99 and also includes two lines.
Customers currently paying more for a wireless plan with either carrier have to call customer service at either carrier to switch to these plans. You won’t incur a service charge or extend your existing contract.
Verizon’s plans with unlimited calling and texting features have also dropped in price. Verizon’s Talk and Text plan costs $89.99 per month, down from $119.99. The Nationwide Unlimited Talk & Text Family SharePlan is now $149.99 per month. AT&T customers can add unlimited texting to an existing plan, and the rates for doing so remain unchanged — $20 for single phone accounts, $30 for family plan accounts.
However… Here comes the tricks, traps, and gotchas.
For big families with multiple phones, these unlimited plans bring a nasty surprise — the additional charge for each third, fourth, and fifth line is $49.99 per month for each phone, not the traditional $9.99 each for those on plans with minute allowances.
Those who receive employer-related discounts from the wireless carriers may find those discounts do not apply to the Unlimited talk plans. Verizon declares all of their unlimited plans are not eligible for any monthly access discounts, period.
AT&T goes out of its way to define what they believe a “voice call” means:
Unlimited voice services are provided primarily for live dialogue between two individuals. If your use of unlimited voice services for conference calling or call forwarding exceeds 750 minutes per month, AT&T may, at its option, terminate your service or change your plan to one with no unlimited usage components. Unlimited voice services may not be used for monitoring services, data transmissions, transmission of broadcasts, transmission of recorded material, or other connections which do not consist of uninterrupted live dialogue between two individuals.
 Both AT&T and Verizon Wireless may try and up-sell you on the new data plans when you call to change your plan. Customers calling both carriers have reported customer service representatives only too willing to provide steep discounts for new handsets or try and convince you to add one of the company’s new data plans. Take advantage of their offer to upgrade your phone and you’ll likely discover yourself forced to also take a mandatory data plan with it anyway. The list of phones falling under this trap keeps expanding.
Both AT&T and Verizon Wireless may try and up-sell you on the new data plans when you call to change your plan. Customers calling both carriers have reported customer service representatives only too willing to provide steep discounts for new handsets or try and convince you to add one of the company’s new data plans. Take advantage of their offer to upgrade your phone and you’ll likely discover yourself forced to also take a mandatory data plan with it anyway. The list of phones falling under this trap keeps expanding.
Last year, Verizon started requiring customers choose data plans for the LG EnV Touch and the Samsung Rogue. With this week’s changes, customers activating LG Chocolate Touch, LG EnV, LG VX8360, Motorola Entice W766, Nokia 7705 Twist, and Samsung Alias2 are now also subject to required data plans. Don’t expect Verizon Wireless representatives to sell you on their cheapest pay-per-use option, which is priced at $1.99 per megabyte. I’ve witnessed Verizon Wireless’ store employees pushing Verizon’s new unlimited $29.99 data plan. If customers complain that’s too much, the $9.99 data plan for a piddly 25MB of access is offered next. If it looks like a balking customer might cost a sale, the representative will grudgingly sell you pay per use plans.
AT&T customers buying many midrange and “quick-messaging” phones are also going to be required to spend at least $20 a month on a combination of texting and/or data plans. Customers using phones like the LG Neon or the Samsung Propel are affected, and weren’t required to buy data plans before. Unlimited data for quick-messaging devices is priced at $15 a month.
If you already own a top of the line phone, your data plan charges remain the same. Verizon customers using Windows Mobile, BlackBerry or Android phones will still pay $29.99 a month for unlimited data. AT&T customers using the iPhone, BlackBerry, Nokia smartphone or Windows Mobile phones will also pay $29.99 a month for unlimited data.
Customers using wireless broadband with a USB dongle are also unaffected by these changes. Whether you tether or use the dongle, your usage is limited to 5GB per month.
Existing customers will not be forced to add a data plan until their contract is up for renewal or they upgrade their phones.
Do These Changes Save Customers Money?
 For most, the answers is no. In fact, these pricing changes guarantee higher bills for most customers down the road.
For most, the answers is no. In fact, these pricing changes guarantee higher bills for most customers down the road.
Only a tiny percentage of customers pay for unlimited calling plans because most calling-allowance plans provide generous usage ranges, free night/weekend calling, and often free calling for the most frequently called, or those who are also customers of your wireless carrier. AT&T even rolls-over unused minutes from month-to-month. Paying considerably more for an “unlimited” calling option makes little sense for customers not exceeding existing calling allowances.
Changes to calling plans and the features associated with them occur year to year, but many customers prefer to remain on legacy plans that may offer fewer minutes, but have far fewer revenue-enhancing tricks and traps. Verizon customers hanging on to their America’s Choice II FamilyShare plan offered four years ago maintain 700 minutes of calling time between multiple phones, get free night and weekend calling, and can access data features on their phones that deduct from their airtime allowance instead of billing for data usage charges. The price? $60 a month for two lines. The equivalent plan today is priced at $69.99 for the voice calling plan, plus a mandatory data plan for the increasing number of phone that require one. Even for phones on a pay-per-use plan, any data access will incur a minimum charge of $1.99 per month.
Where the real money will be made is from overpriced data plans forced on customers whether they want them or not, especially for midrange phones.
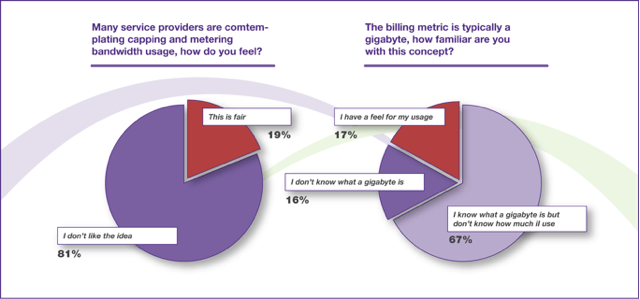
Wireless consultant Chetan Sharma estimates fewer than 10 percent of these customers buy data plans.
“There’s a significant number of consumers out there who like the idea of a cutting-edge handset but not of paying for services,” Michael Nelson, founder at Nelson Alpha Research told Business Week.
Wall Street analysts know mandatory data plans will bring exceptional new revenue to both major providers, especially at current prices.
“We could see a move upwards rather than downwards [in revenue/earnings],” says Jennifer Fritzsche, an analyst at Wells Fargo Securities in Chicago, who recommends buying shares of AT&T and Verizon Communications. “Any kind of voice pricing is very much a commodity,” Fritzsche tells Bloomberg News. “Data is the future.”
JPMorgan is celebrating the potential windfall for both companies and their stocks, estimating just two percent of customers will realize any savings from these pricing changes, while many more will see prices increase.
For Verizon Wireless, it’s party time. Even though Credit Suisse analyst Jonathan Chaplin estimates the carrier will sacrifice $540 million in voice revenue, they’re likely to gain $630 million in data plan sales. The costs of providing the service are likely to be minimal, considering most of the customers now forced to choose a plan are unlikely to use it much.
“Price War” or “War on Customers”
Still, some on Wall Street are unhappy with the prospects of any pricing changes that head downwards, especially if it sparks a price war. Some have dumped their wireless stocks as a result of industry trends this year. But what they may need to worry more about is the prospect of middle class customers switching from traditional postpaid two-year contract plans to prepaid services that offer light and medium mobile users better value with fewer tricks and traps.
As families face the prospect for $100+ monthly bills just for cell phone service, with mandatory data charges likely to add another $20-30 on top of that, will non-power-users stick with AT&T and Verizon for service? Sprint and T Mobile argue they already offer better value for the hard-hit middle class, but prepaid mobile has garnered new respect for its simpler plans and easy-to-understand billing (and taxes and fees are typically included in the prepaid plan price.)
Formerly the domain of those willing to pay a steep per minute fee and buy top-up cards at convenience stores, today’s prepaid wireless plans often offer month-to-month service with familiar “minute bucket”-allowances or unlimited calling, and operate on Verizon, AT&T, Sprint, or T-Mobile’s nationwide networks.
A real price war has broken out in the prepaid wireless sector, with competitors offering unlimited calling plans as low as $40 a month. Straight Talk, using Verizon Wireless’ network, goes even lower for a simple 1,000 minute/1,000 text/30MB web access plan for $30 a month. The only downside is a very limited selection of phones. Regional players like MetroPCS and Cricket offer comparable pricing for their unlimited plans, but their network coverage is a shadow of the larger players, roaming agreements notwithstanding.
As major carriers pile on extra fees for services many customers don’t want, many will find far better values in the prepaid phone marketplace. Without the two-year contract common on major carriers, customers can switch providers at will, taking their phone number with them in most cases, if one provider doesn’t provide good service. Best of all, they don’t have to pay for a cancellation fee or take services they don’t want or need just to satisfy AT&T and Verizon’s quest for cash.
[flv width=”480″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WIVB Buffalo Price War Between Cell Phone Providers 1-19-10.flv[/flv]
WIVB-TV in Buffalo appeared to be drinking the industry’s Kool-Aid about the benefits of new, ‘lower pricing,’ but towards the end even they admitted there are tricks and traps involved. (3 minutes)



 Subscribe
Subscribe