Phillip "The Only One Not Being Paid" Dampier
Tim Karr from Free Press dropped me a note alerting me that the Heartland Institute had responded to the comments from both Karl Bode at Broadband Reports and myself in regards to their transparent anti-consumer Net Neutrality is Bad position the telecommunications industry and their fellow astroturfing friends have been spouting as of late.
Free Press occasionally reprints some of our content on the Save the Internet! blog, which I always appreciate. But James Lakely wanted to take issue with several points, so the cross-blog debate begins. Free Press has already responded, but now it’s my turn. The quoted sections come from Lakely’s piece:
The general theme of the responses is: Government regulation always good, wise and beneficial; the market responding to consumers’ needs always nefarious, short-sighted and harmful. It goes without saying that we here at The Heartland Institute disagree. And here are my rebuttals to the rebuttals.
My rebuttal to the rebuttals to the rebuttals begins with calling out this sweeping generalization which actually doesn’t represent my view at all. In fact, it’s wildly against what I believe personally.
Government regulation is not always good. In fact, I’d like to see as little government regulation as possible. I’d prefer robust, healthy competition on a level playing field, because as a consumer (and this site is 100% consumer, with absolutely zero industry/special interest money) I and my friends stand to benefit from that. But unlike my “free market is always right” friends who cannot say they are 100% free of industry/special interest money, I also recognize that in the absence of a healthy, free market, the abuses are sure to follow without oversight. And they have.
Let’s be honest. The broadband industry in the United States is a duopoly for most Americans. One telephone company and one cable company. Wi-Fi and wireless broadband service remains either unavailable, uncompetitive from a pricing standpoint, or heavily limited by usage caps.
Since the late 1990s, the choice for broadband has been simple – DSL from the phone company or a cable modem from the cable company. Pricing competition for most comes only for new customers in the form of promotional sign-up offers that quickly expire.
The marketplace has been stable for a decade with the business model of DSL competing mildly on price, a recognition of its often slower speed service, and cable bashing the phone company over the head for not offering “blazing fast speeds” and charges slightly more to deliver them.
Customers have made choices accordingly. When a customer doesn’t care about a speed race, gets a competitive bundle offer from the phone company throwing in something like a free netbook, and still has phone service from their local phone company, DSL can make sense for them. For those who want the fastest speeds, already dumped the phone company for a cable “digital phone” product, and got an attractively priced bundle offer from the local cable company, they’re likely using a cable modem. For a lot of Americans in rural areas it’s “take whatever you can get.”
That marketplace worked well for a decade for more populated areas with the loudest clamoring for any change coming from underserved rural areas just looking for any broadband service.
Then things began to change. In November 2005, SBC-AT&T decided it wanted to change the model. Instead of providing connectivity for customers, they decided there was more money to be made by doing away with the founding model of the Internet — providers treating all traffic equally — and pondered forcing content providers to pay for transporting that traffic across their “pipes.” Companies with no business relationship with AT&T were told they could no longer use “AT&T’s pipes for free.” Now, under AT&T’s new model, if they wanted assurances of fast speed to their customers, those independent providers would have to pony up.
That sounded like a grand idea to Wall Street who trumpeted the potential earnings enhancements a new revenue stream would provide, and several other service providers with dollar signs in their eyes yelled “me too, me too!”
Predictably, some of the loudest outrage about this came from consumers — the ISP’s own customers. They had the apparently-mistaken notion that they were paying for broadband service to build and maintain a network to serve their needs for fast, reliable, broadband service for any site they visited. Apparently not. Consumers were often unmoved by a lobbying effort that suggested other big corporations were raking in profits on the backs of service providers “forced” to deliver their traffic. Good old common sense speaks volumes. Consumers don’t want their Internet service throttled, or see the content they want to access fiddled with just to fatten industry profits. The industry didn’t listen to consumers and are back yet again fighting Net Neutrality legislation.
The reason for the fight against Net Neutrality is simple: companies answer first and foremost to their shareholders, the supporting culture of Wall Street analysts and the media that trumpets their views. Short term results matter more than long term strategies. Monetizing broadband traffic, a growth industry to be sure, was a golden opportunity, even if the companies originating the traffic already pay hosting companies to deliver it.
 From there, the story is always the same. In a healthy, competitive market, abusive practices are checked when customers flee a provider that stops listening to them. In a duopoly or limited competitive market, with reduced risk of customer defection, and in the absence of any other force to check unrestrained behavior, customer opinion becomes a low second in importance. It is the government that provides the necessary oversight and protection mechanism from market abuse running wild. Oversight does not limit competition. It can actually encourage it.
From there, the story is always the same. In a healthy, competitive market, abusive practices are checked when customers flee a provider that stops listening to them. In a duopoly or limited competitive market, with reduced risk of customer defection, and in the absence of any other force to check unrestrained behavior, customer opinion becomes a low second in importance. It is the government that provides the necessary oversight and protection mechanism from market abuse running wild. Oversight does not limit competition. It can actually encourage it.
The players have assembled:
- Consumers like myself who are fed up with the abusive practices some bad actors in the broadband industry are engaged in and have no reason to obfuscate, lie, or hide the facts;
- Providers like cable and telephone companies that actively lobby to keep regulation and oversight at bay in hopes of continuing their free-wheeling ways, even if it harms consumers;
- Lobbyists and astroturfing organizations that receive a substantial amount of funding from those providers to bolster industry opinions on issues, create fictional, biased studies to prove industry theories, and whose very existence relies on the generosity of the corporations that pay their expenses;
- Employees of astroturf organizations whose paycheck comes from “sharing” the same positions on issues as their benefactors, and whose credibility would fall seriously into question should the direct financial link between providers and their paid mouthpieces be exposed to the public.
The most absurd part of this play is that I, as a consumer, am paying for all of it, and am the only one in the group not getting anything from it. Providers are paid. Lobbyists are paid. Astroturfing groups are paid. Mr. Lakely is paid. I am not paid. In the end, that makes me the guy that can walk down any street day or night and never fear that someone driving by will roll their window down and ask “how much?”
Pretend? C’mon. By even the Federal Communications Commission’s own research, the vast majority of consumers in this country have several choices of broadband providers. I have AT&T’s DSL service, a technology that is fine for me (at the moment), but is largely considered pedestrian. Cable is better. And fiber is better still. If I’m living in a fictional world, I’d love to ask the author of my fate for a few revisions — none of which has anything to do with how fast my connection is.
Most Americans have the following choices for broadband service:
- Cable company
- Telephone company (DSL or fiber in limited areas)
- Clearwire WiMax (significant ownership interest by cable and mobile/cellular industry)
- Mobile broadband (owned by cellular industry)
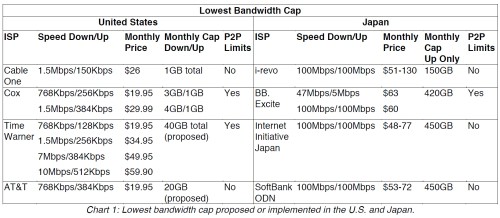
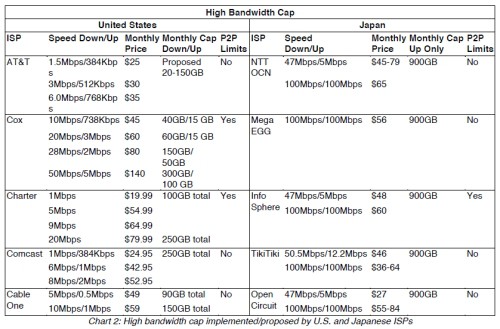
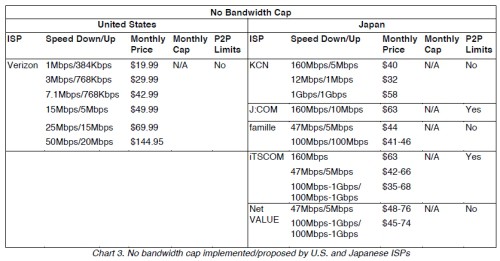
Cable and telephone companies are the two wired providers capable of providing broadband at the fastest speeds. Clearwire WiMax is being leveraged by the cable industry to offer wireless broadband to their existing customers. What are the chances Clearwire is going to bash their cable investors while competing for customers? Mobile broadband remains useful only for web browsing and e-mail because of onerous usage caps, speed issues, and pricing (which virtually every provider sets at the same level: $50/5GB per month). I didn’t even bother with satellite, because current providers offer service only slightly better than dial-up when used in real world conditions.
Your choice in broadband technology has everything to do with speed. In “broadband backwaters” where competition is exceptionally light and increasingly in areas where a fiber or advanced DSL product is not forthcoming, there is simply no competitive pressure to increase speeds no matter how loudly customers demand them.
The horror! ISPs earn “healthy profits” by providing a desirable service. It is here that Free Press and the rest of the net neutrality crowd reveal an ingrained anti-capitalist sentiment. We’re to believe that an ISP, earning healthy profits (which please both the company and its shareholders) are upset that demand for their services increases. In response, they do not see a great opportunity to expand their business and attract even more customers, but to “actively reduce investment.”
No. Instead the logical response is to be “neglectful,” and let rival ISPs in an ultra-competitive market swoop in and steal away their disaffected customers. That makes no sense to anyone who has any knowledge of how free market capitalism works. Verizon announced in 2006 that it planned to invest $18 billion in building out its fiber ViOS product by 2010. Why? Because it wants to (gasp!) pursue profits by serving more and more customers. I could care less about Verizon’s business plan — other than to note that without any government funding or “plan,” it seems to be moving quickly to bring more broadband options to more people.
The only thing Lakely avoids in this dramatic overreach is calling me a “socialist.”
Two important points here. Lakely should take his free market crash course to companies like Time Warner Cable who are doing exactly what he proclaims makes no sense: Broadband customers up. Demand for bandwidth up. Investment to upgrade networks to handle increased demand… down!
Lakely’s mistake is to assume that free market capitalism is always benevolent towards consumer interests, presuming they are first on the minds of providers when making any strategic changes in their business plans. But, for those who have lived under a throttled and capped broadband regime, like in Canada, or those in four American cities that were to be subjected to an unwarranted, unwanted pricing “experiment” on the part of Time Warner Cable to engage in all of the classic Internet Overcharging schemes – usage caps, consumption billing, overlimit penalties and fees, what the consumer wanted was completely irrelevant to the provider.
Time Warner Cable answers to investors, who howl over increased capital and upgrade costs in a normal economy. In this one, spending on virtually anything is scrutinized. Indeed, Wall Street even shudders at the thought of financing a competitor’s efforts to overbuild into another provider’s service area because it might launch a price war — a disaster for the Wall Street guy even if it’s a boon for consumers.
Lakely brings up Verizon, but leaves out the hostile reception many on Wall Street continue to have about the construction of that fiber optic network they call overspending:
FiOS has been very popular with consumers because it offers faster Internet service, more high-definition video channels and more bells and whistles than most cable systems. But Mr. Moffett’s argument is that what is good for customers is not good for investors.
“If I were an auto dealer and I wanted to give people a Maserati for the price of a Volkswagen, I’d have some seriously happy customers,” said Craig Moffett, an analyst with Sanford C. Bernstein. “My problem would be whether I could earn a decent return doing it.”

Stopping the monetizing of Internet traffic and treating content equally isn't Net Neutrality, it's Socialism in the eyes of some special interest groups.
Verizon thinks so, but has to spend an inordinate amount of time trying to convince short-term-thinking investors and skeptical darlings of the Wall Street media like Moffett that serving your customers with excellent service keeps them as loyal customers generating reliable returns.
Other companies, like Time Warner Cable, are much less interested in “seriously happy customers” when it launched its “experiment.” Of course, it limited its exposure by choosing markets where customers lacked a safety valve alternative providing equal levels of service. In Rochester, Frontier Communications retains a 5GB usage limit in their Acceptable Use Policy (currently not enforced) for broadband service and relies on traditional DSL service. In other nearby cities from Buffalo to Syracuse, and further downstate, Verizon FiOS is merrily wiring fiber optic service that does not have hostile customer policies, much faster service, and subscribers can freely switch.
When “experimenting,” it’s probably safer to choose a market that doesn’t have a powerful company like Verizon just waiting to pounce.
Where lower speed DSL prevails and the upgrade frenzy is nowhere to be found, it’s been much easier to simply maintain the same service year after year. No major upgrades. No market-changing shakeups. Just keep cashing the checks.
In some communities in the United States, such as Wilson in North Carolina, the duopoly simply refused to upgrade service no matter how often people begged and pleaded. The city finally decided to run a bond issue to finance the construction of their own municipal fiber optic network, and the incumbent providers did two things — try and stop it at all costs, and when that failed, finally made plans to upgrade their own networks to compete.
Lakely and I do agree: competition is wonderful. But I always add “when it exists.”
What happens when that competition doesn’t appear is an issue Lakely prefers to tap dance around, misstating my own position in hopes his readers won’t notice:
Super. Hurray! I wish the petitioners luck. But why, in a free-market economy, must the government force Verizon to “overbuild” in Rochester? Or why is it essential that taxpayer money be used to fulfill the wishes of some Rochester petitioners?
No reader here has ever seen me advocate the government “force” Verizon to overbuild my community. In fact, I’ve always been skeptical Verizon could be attracted to compete here legislatively or with $10 bribes would-be customers mail to Verizon corporate offices to show there is demand here. That’s because the telecommunications industry is loathe to overbuild in someone else’s territory. Phone companies and cable companies will nominally compete, but two traditional phone companies and two cable companies going head to head is something else. Nor have I advocated taxpayer money be given to Verizon to build a network in Rochester. In fact, it’s the providers themselves who want the government handouts without oversight of what they do with that money. By the way, does the Heartland Institute oppose broadband stimulus funding?
The tapdance continues when Lakely attempts to connect two different ideas to suggest they are contradictory:
There’s a lot to unpack from Dampier’s post, including the following contradictory passages:
The only thing Net Neutrality protects IS the status quo, a free and open Internet.
Followed shortly by …
… in a world without codified Net Neutrality protections — the free market at work under today’s reality — we’re seeing continued evidence of price increases and a decline in investment in networks, and some providers continue to drag their feet on upgrades.
So which is it? Is “today’s reality” worth preserving? (My view.) Or are government controls needed to protect the “status quo.” Can’t really have it both ways — unless your not really being clear about what it is you advocate.
Nice try. A law codifying Net Neutrality protects the free flow of traffic on the Internet tomorrow from the “monetize and control everything” mentality customers are already fighting providers about on pricing and usage limits today.
A foreshadowing of broadband service in America without Net Neutrality principles protected by law can be found in Canada. Do as Lakely suggests and it’s only a matter of time before broadband providers begin throttling speeds of undesirable online applications, favor traffic from paid content partners over those who didn’t pay for that privilege, and use traffic management to delay necessary infrastructure upgrades to meet the needs of paying customers. Customers will discover “blazing fast speeds” only from those websites that ponied up the money to guarantee that. In short, an online protection racket.
Provider mentality under “the free market at work under today’s reality” tells the story of what broadband customers are facing today in this country — Internet Overcharging schemes, astroturfing propaganda efforts to bolster claims that “controls” are necessary to balance traffic, and financial reports illustrating a pervasive lack of willingness by some providers to upgrade their networks. All this makes selling those “controls” to a frustrated public waiting for a web page to display much easier.
Be it trying to fiddle with the traffic passing through a network, or overcharging for access to it, the only reason consumers are increasingly calling for government oversight and protection is because providers have engaged in practices which demand such a response.
And those who want to impose their vision of how the Internet should work under the guise of “net neutrality” want to change it. I don’t think they make a very good argument for messing with a market that has brought the world the online wonders we take for granted.
Lakely has it entirely backwards. The Internet’s vision has, since inception, been one where legal content traveled freely without foe or favor. It was the providers that sought to change the “vision” (or as they would see it, their “business model”). Lakely and I agree that the Internet has brought online wonders we take for granted. But I know that is threatened when providers decide to control and monetize it. That’s about as acceptable as charging your aunt in San Francisco for a long distance call you made at your own expense, all because it traveled across the phone company’s wires.
Although Lakely did some pretty serious taffy pulling to stretch my arguments to fit his premise, his most recent hit piece on Free Press was a site to behold:
McChesney is an avowed socialist/Marxist. Through Free Press, he is promoting an agenda that would replace the free market system that has led to once-unimaginable advances in information technology — including freedom of communication — with a state-controlled system directed by government on behalf of “the people.” In short: McChesney and Free Press see the Internet as the last, best realm to finally usher in the long-dreamed socialist utopia.
Establish net neutrality principles by force of law, and the socialist/Marxist revolution (at least online) is underway.
Part two will follow shortly. Stay tuned.
Oooh, can’t wait for that. (Make sure you throw in some Hugo Chavez references. No self respecting “socialism under every rock” rant is worth reading without some Chavez sprinkles on top.) I just hope Lakely gets it written before he and his industry friends get their way. Otherwise, he’ll discover providers at his door demanding some ‘scratch’ to protect the Heartland Institute’s position as a “preferred content partner.”
What I am sure really upsets Lakely and his astroturf friends is that the Internet has allowed individuals to determine the merit and value of content based on its quality and integrity, not based on how much money is blasted into the amplification process. The proof of this in action exists right here, right now. Stop the Cap!, funded by me out of my own pocket and run in my spare time, with the help of other consumers volunteering to contribute their own content here, can stand toe to toe with an industry-funded Heartland Institute trying to create a right-left divide on an issue that is neither.
That leaves groups like theirs forced to respond to ordinary consumers like myself capable of blowing astroturf fluff out of the water with the most basic research and application of common sense. To think, a consumer website without the six or possibly even seven figure annual budget astroturf groups blow through can get as much attention and exposure as even the most well-financed industry propaganda festivals, all because of a free and open Internet.
That burns up the special interests to no end. That’s not a people-powered “socialist utopia.” That’s consumers fighting for their rights, organizing consumer-powered activism, and taking on, and hopefully eventually taking out, the special interest lobbyists that work against our best interests, and are well paid for doing so. No wonder Net Neutrality represents a threat so serious, it can provoke rhetoric invoking the Red Scare.
 An electrical fire at Time Warner Cable’s headquarters in El Paso, Texas knocked out cable television, Internet, and telephone services for customers across El Paso Tuesday.
An electrical fire at Time Warner Cable’s headquarters in El Paso, Texas knocked out cable television, Internet, and telephone services for customers across El Paso Tuesday.

 Subscribe
Subscribe