 The Federal Communications Commission today approved Verizon’s acquisition of low-cost carrier TracFone Wireless, which will bring a familiar brand for prepaid wireless service under the wireless giant’s corporate umbrella.
The Federal Communications Commission today approved Verizon’s acquisition of low-cost carrier TracFone Wireless, which will bring a familiar brand for prepaid wireless service under the wireless giant’s corporate umbrella.
Sources indicate there were enough votes in favor of the deal late last week for FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel to distribute an approval order on Friday ahead of the formal vote.
The approval means Verizon will control the country’s largest wireless carrier for low income subscribers enrolled in the federal government’s Lifeline program, which offers substantial discounts on phones and service. About 1.7 million customers currently use TracFone under the Lifeline program, and Verizon committed to the FCC that it would continue participating in the program for at least the next seven years. The company also promised to maintain TracFone’s existing rate plans for at least three years and would continue to promote and educate consumers about Lifeline service.
A separate agreement with the California Public Utilities Commission commits Verizon to provide subsidized wireless service to low-income California residents for at least 20 years, and a free phone to qualified customers starting in late 2022.
“Verizon welcomes the FCC’s approval today of our TracFone acquisition,” said Kathy Grillo, Verizon SVP & DGC, public policy and government affairs, in a statement. The deal will provide customers with the best of both worlds: more choices, better services and new features thanks to Verizon’s investment and innovation. Customers will benefit with enhancements in devices, network performance and innovative products and services — as well as a continued commitment to Lifeline.”
TracFone was one of the country’s largest independent wireless brands. The company was formerly a unit of Mexico’s America Movil, controlled by billionaire Carlos Slim.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


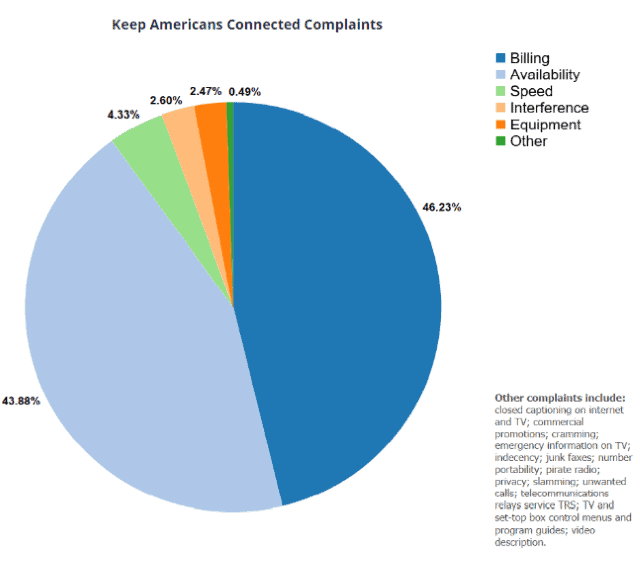
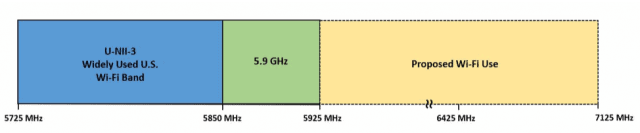
 WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The U.S. Federal Communications Commission voted 3-2 on Tuesday to maintain its 2017 repeal of Obama-era net neutrality rules, even after a federal court directed a review of some provisions of the repeal.
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The U.S. Federal Communications Commission voted 3-2 on Tuesday to maintain its 2017 repeal of Obama-era net neutrality rules, even after a federal court directed a review of some provisions of the repeal.