The Netgear CM700 is the target of a class action lawsuit filed in California.
As consumers increasingly spend money out-of-pocket to acquire their own cable modems to avoid leasing fees, alleged defects in those modems are spurring class action lawsuits to force manufacturers to fix the problems or issue refunds.
Two separate class action cases have been filed this month in Calfornia courts alleging “serious defects” in the Netgear CM700 and Arris SURFboard SB6190 — both newer DOCSIS 3.0 modems. But those modems are not the only ones affected by a serious firmware bug that can dramatically degrade internet performance.
Both modems rely on a relatively new Intel Puma 6 chipset, which some media outlets have also implicated in similar defects in a variety of cable modems including the Hitron CGNV4, the Compal CH7465-LG, and Puma 6-based modems like Virgin Media’s Hub 3 and Comcast’s top-end Xfinity boxes. Other newer modems branded by Linksys and Cisco also use the same system-on-chip and may also be affected.
The law firm of Schubert, Jonckheer & Kolbe, which is handling the Netgear legal case, says these cable modems may be affected:
- Arris SB6190
- Arris TG1672G
- Arris TM1602
- Super Hub 3 (Arris TG2492LG) (commonly, Virgin Media)
- Hitron CGN3 / CDA / CGNV series modems:
- Hitron CDA-32372
- Hitron CDE-32372
- Hitron CDA3-35
- Hitron CGNV4
- Hitron CGNM-3552 (commonly, Rogers)
- Hitron CGN3 (eg CGN3-ACSMR)
- Hitron CGNM-2250 (commonly, Shaw)
- Linksys CM3024
- Linksys CM3016
- TP-Link CR7000
- Netgear AC1750 C6300 AC1900
- Netgear CM700
- Telstra Gateway Max (Netgear AC1900 / C6300) (Australia)
- Cisco DPC3848V
- Cisco DPC3941B / DPC3941T (commonly, Comcast Xfinity XB3)
- Cisco DPC3939
- Compal CH7465-LG / Arris TG2492LG (commonly, Virgin Media Hub 3)
- Samsung Home Media Server
Customers of Comcast, Charter, and Cox in the United States are impacted, as well as Rogers and Shaw customers in Canada and Virgin Media in the United Kingdom. The faster your internet connection, the more likely you will notice the defect, which causes dramatic latency spikes and degraded internet performance.
Intel admitted there was a problem back in December, but ISPs have been slow to respond.
Intel acquired the Puma family of chips from Texas Instruments in 2010, and the latest — the DOCSIS 3.0-compatible Puma 6 – uses an Atom x86 processor designed to handle up to 1.6Gbps connections. Unfortunately, the engineers who developed the firmware have tasked the Atom CPU with too much work while it also copes with processing network packets on a high-speed internet connection.
As The Register reported back in December:
Every couple of seconds or so, a high-priority maintenance task runs and it winds up momentarily hogging the processor, causing latency to increase by at least 200ms and, over time, about six per cent of packets to be dropped. It affects IPv4 and IPv6 – and it spoils internet gaming and other online real-time interaction that need fast response times.
This problem is easily seen in two graphs provided to the Register by a reader in Phoenix who plugged in two different modems to his Cox Cable internet connection. The blue lines represent latency and the red lines are packet loss. The test was performed with an ICMP ping running 33 times a second to his ISP’s DNS server over a 30 minute period.
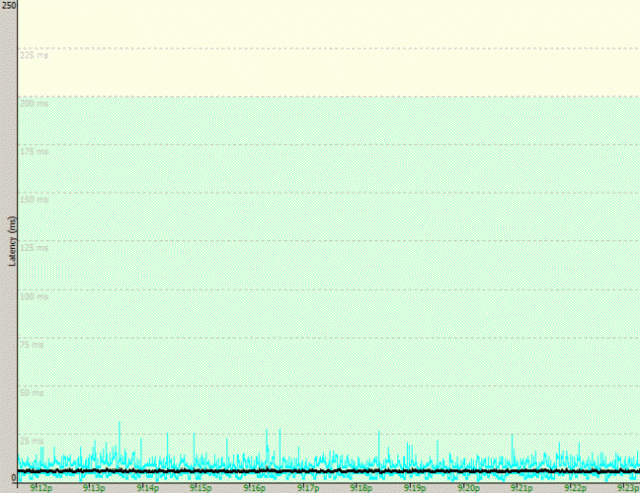
An Arris SB6183 cable modem using an older Broadcom-based chipset exhibits no problems. (Image: The Register)
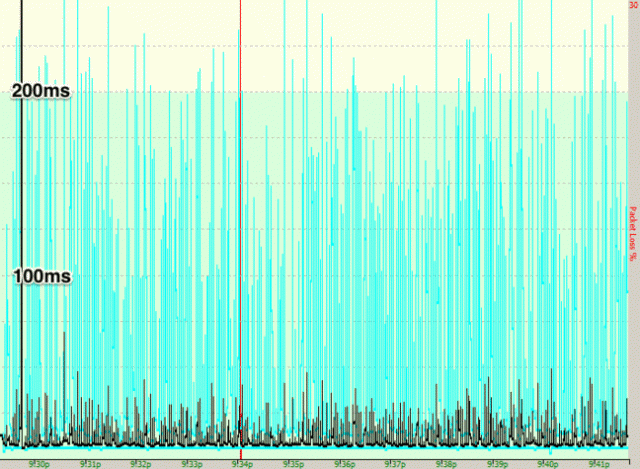
The Arris SB6190 running the new Intel Puma 6 chipset shows significant and readily identifiable problems. (Image: The Register)
Online gamers are among the most likely to be affected by latency problems.
“I excitedly swapped out my Arris SB1683 Broadcom modem for the new SB6190 Intel one expecting gigabit performance and immediately noticed slower webpage loads,” one gamer told The Register. “During first-person gaming, I was getting killed way more often for no apparent reason. I looked at an eight-year graph of latency from my home logs, and was horrified. Swapping back to my SB6183 solved all the issues.”
Arris also confirmed the problem.
“Arris has been working actively with Intel to address the issue, which resulted in some SURFboard SB6190 users reporting latency concerns,” a spokeswoman for Arris said. “We plan to quickly issue Intel’s firmware updates to resolve any latency. We remain committed to providing the best broadband experience for all users of Arris devices and regret any inconvenience this issue caused.”
Unfortunately, regardless of how fast modem manufacturers issue updated firmware to resolve the problem, end users will not notice a difference until their cable operator pushes that firmware update to customers. You cannot update cable modem firmware on your own, and any effort to do so would be futile because your provider would automatically replace it with an older “approved” version as soon as the unauthorized firmware change was identified.
The lawsuits seek a jury trial and damages forcing the manufacturers to recall the modems and either replace them or issue refunds to all affected customers. Customers who own an affected modem who want to participate in the class action case can fill out this form for more information.


 Subscribe
Subscribe




 Mediacom, perennially rated America’s dead-last cable company by Consumer Reports’ annual subscriber surveys, will invest $1 billion over the next three years to combat increasing competition from AT&T and other telephone companies by improving its broadband service.
Mediacom, perennially rated America’s dead-last cable company by Consumer Reports’ annual subscriber surveys, will invest $1 billion over the next three years to combat increasing competition from AT&T and other telephone companies by improving its broadband service.