The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding traffic growth has apparently taken its toll on network capacity at Mediacom, forcing the company to reach out to a growing number of its heavy uploaders and telling them to reduce usage or face a speed throttle or the possible closure of their account.
An East Moline, Ill. Mediacom broadband customer of 10 years was offended to receive a phone call from Mediacom’s “Fraud and Abuse Department” telling him he was overusing his gigabit internet account, which includes a 6 TB data cap. The customer was certain he never exceeded Mediacom’s data cap, and in fact recorded 2.5 TB of usage over the last month, well below his data allowance.
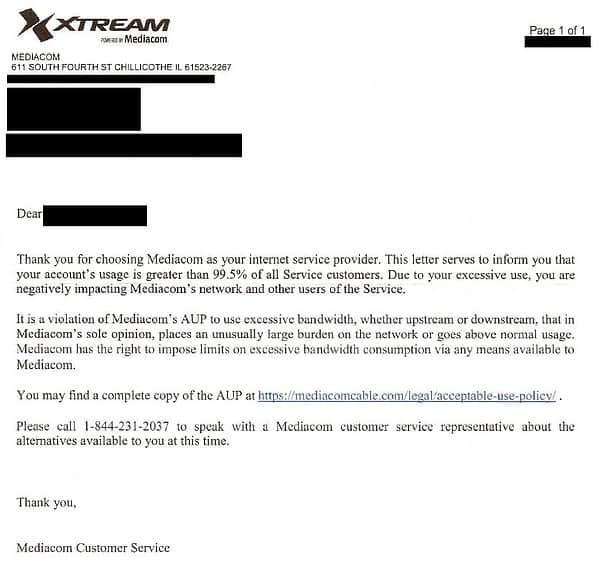
Mediacom’s representative explained the problem was not with how much he downloaded.
“He told me my upload was 450 GB over their average and if I didn’t reduce my usage they would either throttle or disconnect me,” DSL Reports‘ reader poonjahb wrote. “I argued that I used less than half of the total data allowed by my plan, but he said my 1.2 TB of upload was too much and that this was my warning.”
Other Mediacom customers across the Midwest also received similar letters in early January, and several contacted Stop the Cap! Many were already annoyed Mediacom had earlier imposed a data cap, but were incensed they were now being threatened when usage was well under that cap.
“I am paying for gigabit internet service just to never have to worry about a data cap,” said Cory, a Mediacom customer in Missouri. “It comes with a 6,000 GB monthly allowance, which is way more than I will ever use, but I still received a warning letter claiming I was uploading too much. I discovered I used about 900 GB over the last two months, setting up a cloud backup of my computer. At most I can send files at around 50 Mbps, which they claim is interfering with other customers in my neighborhood. I don’t understand.”
Several filed complaints with the FCC, which the agency forwarded on to Mediacom customer service. Most received form letter replies.

COVID-19 Pandemic Causes Traffic Surge, Mediacom Tells Stop the Cap!
“Mediacom routinely reviews both download and upload usage trends to determine if any customers are using a disproportionate share of bandwidth compared to average users,” explains Thomas J. Larsen, senior vice president of government and public relations at Mediacom. “If a customer falls into the top 0.5% of downstream or upstream capacity users in a given month, they may receive a letter or call from Mediacom regarding their usage. This would apply to both business and residential customers. The reason for contacting the customers is to explain that their usage patterns may be degrading the performance of the network and affecting other users.”
Larsen pointed to statistics from the cable industry’s largest trade group, NCTA – The Internet & Television Association, which reported a 31.8% total cumulative growth in downstream internet traffic and a 51.1% increase in upstream traffic since the spring COVID-19 lockdowns back in March 2020.
A Mediacom letter sent to customers complaining to the FCC about the practice cited network “stress” caused by excess upstream traffic. Larsen told Stop the Cap! the company regularly reviews customers’ download and upload traffic trends, looking for outliers that use a disproportionate share of bandwidth compared to average users. Larsen would not admit if heavy users were noticeably affecting other customers with congestion-related slowdowns, but said the company was “reaching out … more frequently than before” to the top 0.5% of traffic generating users anyway. He also noted this policy equally applied to both residential and business accounts.
“This is not the easiest topic to explain because internet usage is growing rapidly in this work from home/study from home environment, so it is difficult to give an exact number that puts a customer into the 0.5% category because that number changes from month to month,” Larsen noted. “Understandably, that may make the policy seem arbitrary when we are really just trying to stay in line with moving usage trends.”
 Internet Service Providers Have Wide Latitude to Cut Off Heavy Users
Internet Service Providers Have Wide Latitude to Cut Off Heavy Users
Virtually every internet service provider has a provision in their acceptable use policy allowing them to terminate or restrict service when a customer causes problems for that provider. Mediacom is no exception, telling subscribers “without limitation, customer’s usage of the service cannot restrict, inhibit, interfere with or otherwise disrupt or cause disruption, performance degradation of other users or impair or threaten to impair the operation of Mediacom’s systems or network.” This policy is in addition to whatever data usage plans are in place.
But Larsen insists Mediacom is not trying to alienate its customers.
“[We want to] work with our customers to address this issue in a productive manner,” Larsen told Stop the Cap!
At the moment, the only solution seems to be to reduce usage enough to stay off of the company’s “top 0.5%” radar.
Mediacom’s Warning Letters Uncommon Among Other Providers
Mediacom’s crackdown on heavy usage has not been copied by most other U.S. providers. Although traffic growth has been measured by virtually every provider in the country, most providers are mitigating possible service degradation by aggressively upgrading capacity or quietly node splitting neighborhoods experiencing the highest traffic growth, which immediately eases congestion issues.
The company did not indicate if its usage crackdown was temporary or if any planned network upgrades would allow it to ease restrictions sometime in the near future.
Other small providers dealing with congestion issues found a better solution sending letters to high traffic customers explaining forthcoming upgrades and temporarily requesting they limit upstream traffic during peak usage times, while not penalizing them for any off-peak traffic. That might prove to be a useful compromise between Mediacom and its customers and preserve goodwill.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.
Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.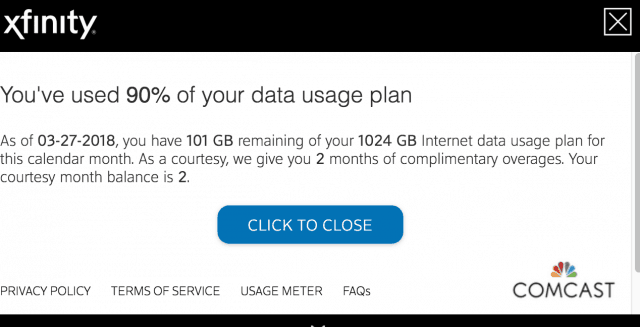 Video Games Consoles/PCs
Video Games Consoles/PCs Canadians, living under a regime of three national wireless carriers (Bell, Rogers, and Telus) pay some of the highest wireless prices in the world. A new plan announced today from Rogers Communications is unlikely to change that.
Canadians, living under a regime of three national wireless carriers (Bell, Rogers, and Telus) pay some of the highest wireless prices in the world. A new plan announced today from Rogers Communications is unlikely to change that.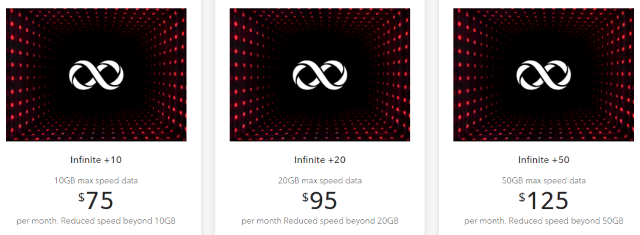


 A 2016 study suggests Comcast may have more heavy users than it is willing to admit. The research firm iGR found average broadband usage that year was already at 190 GB and rising. There is no third-party verification of providers’ usage statistics or usage measurement tools, but there are public statements from Comcast officials that suggest the company faces a predictable upgrade cycle to deal with rising usage.
A 2016 study suggests Comcast may have more heavy users than it is willing to admit. The research firm iGR found average broadband usage that year was already at 190 GB and rising. There is no third-party verification of providers’ usage statistics or usage measurement tools, but there are public statements from Comcast officials that suggest the company faces a predictable upgrade cycle to deal with rising usage.