 Windstream Holdings filed a suit against Charter Communications (d/b/a Spectrum) on Friday, claiming the cable company is trying to poach its customers with a “despicable” false advertising campaigned designed to make people believe the phone company’s days are numbered.
Windstream Holdings filed a suit against Charter Communications (d/b/a Spectrum) on Friday, claiming the cable company is trying to poach its customers with a “despicable” false advertising campaigned designed to make people believe the phone company’s days are numbered.
“Shortly after Windstream filed for Chapter 11 protection, Charter commenced a false and misleading advertising campaign designed to cause irreparable injury and damage to Windstream’s reputation and business,” the lawsuit filed with the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York states. “Charter targeted Windstream customers in Alabama, Georgia, Kentucky, Ohio, Nebraska, and North Carolina, which are several of Windstream’s top performing states.”
“On the envelopes for the advertisement, Charter intentionally utilized Windstream’s trademark and signature color pattern to mislead Windstream customers into believing that the advertisement came directly from Windstream. Indeed, Charter’s advertisement stated that it was ‘Important Information Enclosed for Windstream Customers.’”

Inside the envelope was an ad for Charter Spectrum:
Windstream Customers,
Don’t Risk Losing Your Internet and TV Services.
Windstream has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, which means uncertainty. Will they be able to provide the Internet and TV services you rely on in the future? To ensure you are not left without vital Internet and TV services, switch to Spectrum.
With a network built for the future, Spectrum is here for the long haul.
Goodbye, Windstream.
Hello, Spectrum.Windstream’s future is unknown, but Spectrum is here to stay—delivering internet and TV services you can count on. . . .
Windstream told the Bankruptcy Court the ads were evidently effective, based on call transcripts and messages sent from customers to Windstream’s customer service department. Windstream’s attorneys attached multiple examples:
“I got a letter in the mail saying that ya’ll were going bankrupt and for me to go with Spectrum so I have gone to Spectrum and I have just called to have the services of Windstream disconnected.”
“I’ve got Spectrum over here so they go everything hooked up and so they told me not to call you until they got everything going like it’s supposed to be but I got that letter in the mail from Windstream and told me to get with you guys – to get with Spectrum so that’s what I did.”
“Oh, well I was just going there because it says hello I mean goodbye Windstream and uh..to got to Spectrum.”
“Oh lord, well I’ve been [Inaudible] on ‘em honey. I thought the letter was from you cause it said Windstream Corporation.”
The lawsuit complains Windstream had to take 160 calls regarding the Charter mailers over a 10-day period.
The phone company is demanding compensation for a number of reasons, but in part because it was forced to offer inquiring customers a better deal in order to convince them to stay with Windstream.
“As a direct result of Charter’s advertising campaign, Windstream has been forced to expend substantial time, money, and resources to combat these false claims. When distressed customers have called in, Windstream has offered upgrades, which many customers have taken,” the lawsuit states. “Windstream has also incurred costs and resources to educate its customer care associates on how to provide a comprehensive response to Charter’s false claims, which includes an explanation of the true effects of the Chapter 11 proceedings. In addition, as a direct result of Charter’s advertising campaign, Windstream has undertaken an extensive mailing and advertising campaign, at significant cost and expense, to counter Charter’s false and misleading advertising campaign. Windstream’s Legal department has also expended extensive time and effort in researching and responding to this matter.”

Windstream also complained Charter somehow disconnected service to approximately 350 Windstream customers on March 14, 2019, without notice to the phone company. The phone company also alleges Charter has told customers that Spectrum is buying out Windstream.
“When Windstream customers contacted Charter to have their services reinstated, they were told by Charter that service was not being reinstated because of Windstream’s failure to pay certain amounts due to Charter,” the lawsuit claimed. “Windstream, however, is not currently authorized to make any payments to Charter on account of prepetition debt as a result of the Chapter 11 filing.”

Keith
Windstream sent two angry letters to Charter complaining about the mailers.
“This misconduct is unacceptable and will not be tolerated,” Windstream’s deputy general counsel Carol Keith wrote. “This goes beyond a mere marketing decision made in bad taste and is clearly an illegal targeting of Windstream’s services and/or business in the marketplace using ‘false and misleading’ representations. Furthermore, when given the opportunity, Spectrum employees have been directed to double down and outright lie to Windstream customers that Spectrum has a contract to buy Windstream out.”
When Windstream took their complaints straight to Charter, their claims were rebuffed.
“On March 26, 2019, Charter responded to Windstream’s letters, contending that its advertisements were not false or misleading, and that it was proper to describe Windstream’s bankruptcy as creating an ‘uncertainty.’ According to Charter, a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing ‘creates ‘uncertainty’ regarding Windstream’s future until the bankruptcy is resolved.’”
Charter also told Windstream it believed the confusion over a “buyout” has to do with the cable company’s long-standing offer to pay up to $500 in contract termination fees for new customers switching to Spectrum.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Windstream Holdings, Inc.
Windstream Holdings, Inc. 
 Windstream is relying on the Federal Communications Commission’s Connect America Fund to double the areas where it will offer 100 Mbps broadband service, expected to reach 30% of the company’s 18-state local service area by the end of the first quarter of 2019.
Windstream is relying on the Federal Communications Commission’s Connect America Fund to double the areas where it will offer 100 Mbps broadband service, expected to reach 30% of the company’s 18-state local service area by the end of the first quarter of 2019.
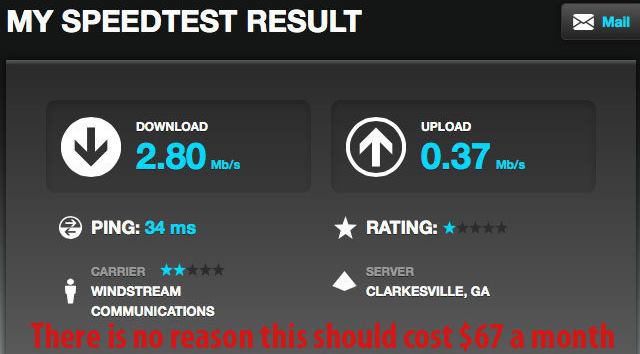
 “We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.”
“We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.” Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.
Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before. Despite claims from some industry-backed researchers and former members of Congress that Net Neutrality
Despite claims from some industry-backed researchers and former members of Congress that Net Neutrality 
