“Somehow in the last 100 years, every time there is a problem of getting more spectrum, there is a technology that comes along that solves that problem. Every two and a half years, every spectrum crisis has gotten solved, and that’s going to keep happening. We already know today what the solutions are for the next 50 years.” — Martin Cooper, inventor of the portable cell phone
Despite the fear-mongering by North America’s wireless phone companies that a spectrum crisis is at hand — one that threatens the viability of wireless communications across the continent, some of the most prominent industry veterans dispute the public policy agenda of phone companies like AT&T, Verizon, Bell, and Rogers.
Martin Cooper ought to know. He invented the portable cell phone, and remains involved in the wireless industry today. Cooper shrugs off cries of spectrum shortages as a problem well-managed by technological innovation. In fact, he’s credited for Cooper’s Law: The ability to transmit different radio communications at one time and in the same place has grown with the same pace since Guglielmo Marconi’s first transmissions in 1895. The number of such communications being theoretically possible has doubled every 30 months, from then, for 104 years.
National Public Radio looks back at the earliest car phones, which weighed 80 pounds and operated with vacuum tubes. Innovation, improved technology, and lower pricing turned an invention for the rich and powerful into a device more than 300,000,000 North Americans own and use today. (April 2012) (3 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
The earliest cell phones have been around since the 1940s. St. Louis was the first city in the United States to get Mobile Telephone Service (MTS). It worked on three analog radio channels and required an operator to make calls on the customer’s behalf. By 1964, direct dialing from car phones became possible with Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS), which also increased the number of radio channels available for calls.
In the 1970s, popular television shows frequently showed high-flyers and private detectives with traditional looking phones installed in their cars. But the service was obscenely expensive. The equipment set customers back $2-4,000 or was leased for around $120 a month. Local calls ran $0.70-1.20 per minute. That was when a nice home was priced at $27,000, a new car was under $4,000, gas was $0.55/gallon, and a first run movie ticket was priced at $1.75.
With many cities maintaining fewer than a dozen radio channels for the service, only a handful of customers could make or receive calls at a time. The first “spectrum crisis” arrived by the late 1970s, when car phones became the status symbol of the rich and powerful (the middle class had pagers). Customers found they couldn’t make or receive calls because the frequencies were all tied up. Some cities even rationed service by maintaining waiting lists, not allowing new customers to have the technology until an existing one dropped their account.
Instead of demanding deregulation and warning of wireless doomsday, the wireless industry innovated its way out of the era of MTS altogether, switching instead to a “cellular” approach developed in part by the Bell System.
[flv width=”412″ height=”330″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ATT Testing the First Public Cell Phone Network.flv[/flv]
In the 1970s, when the first cell phone “spectrum crisis” erupted, the Bell System innovated its way out the the dilemma without running to Congress demanding sweeping deregulation. This documentary, produced by the Bell System, explores AMPS — analog cell phone service, and how it transformed Chicago’s mobile telephone landscape back in 1979. (9 minutes)
“Arguing that the nation could run out of spectrum is like saying it was going to run out of a color.” David P. Reed, one of the original architects of the Internet
Instead of one caller tying up a single IMTS radio frequency capable of reaching across an entire city, the Bell System deployed lower-powered transmitters in a series of hexagonal “cells.” Each cell only served callers within a much smaller geographic area. As a customer traveled between cells, the system would hand the call off to the next cell in turn and so on — all transparently to the caller. Because of the reduced coverage area, cell towers in a city could operate on the same frequencies without creating interference problems, opening up the system to many more customers and more calls.
In Chicago, Bell’s IMTS system only supported around a dozen callers at the same time. In 1977, the phone company built a test cellular network it dubbed “AMPS,” for Advanced Mobile Phone System. AMPS technology was familiar to many early cell phone users. It was more popularly known as “analog” service, and while it could still only handle one conversation at a time on each frequency, the system supported better call handling and many more users than earlier wireless phone technology. By 1979, Bell had 1,300 customers using their test system in Chicago.
AMPS considerably eased the “spectrum crunch” earlier systems found challenging, and subsequent upgrades to digital technology dramatically increased the number of calls each tower could handle and allowed providers to slash pricing, which fueled the spectacular growth of the wireless marketplace.
Yesterday it was voice call congestion, today it is a “tidal wave” of wireless data. But inventors like Cooper believe the solution is the same: engineering innovation.
“Somehow in the last 100 years, every time there is a problem of getting more spectrum, there is a technology that comes along that solves that problem,” Cooper told the New York Times. “Every two and a half years, every spectrum crisis has gotten solved, and that’s going to keep happening. We already know today what the solutions are for the next 50 years.”
Cooper believes in the cellular approach to wireless communications. Dividing up today’s geographic cells into even smaller cells could vastly expand network capacity just like AMPS did for Windy City residents in the late 1970s. Using especially directional antennas focused on different service areas, placing new cell towers, innovating further with tiny neighborhood antennas mounted on telephone poles, or building out Wi-Fi networks can all manage the data capacity “crisis” says Cooper.
New technology also allows cell signals to co-exist, even on the same or adjacent frequencies, without creating interference problems. All it takes is a willingness to invest in the technology and deploy it across signal-congested urban areas.
Unfortunately, network engineers are not often responsible for the business decisions or public policy agendas of the nation’s largest wireless companies who are using the “spectrum crisis” to argue for increased deregulation and demanding additional radio spectrum which, in some cases, could be locked up by companies to make sure nobody else can use them.
[flv width=”600″ height=”358″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/NY Times Mobile Carriers Warn of Spectrum Crisis.flv[/flv]
The New York Times offers this easy-to-follow primer on wireless spectrum and why it matters (or not) in the current climate of explosive growth in mobile data traffic. (3 minutes)
“Their primary interest is not necessarily in making spectrum available, or in making wireless performance better. They want to make money.” — David S. Isenberg, veteran researcher, AT&T Labs
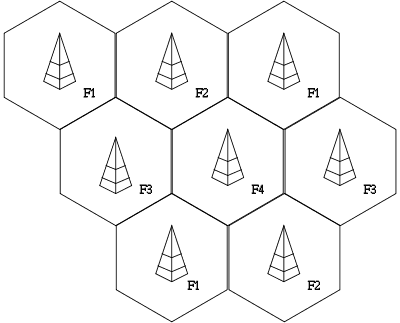
Innovation, not wholesale deregulation, allowed the Bell System to solve the spectrum crisis of the 1970s by creating today's "cell system" that can re-use radio frequencies in adjacent areas to handle more wireless traffic.
Spectrum auctions bring billions to federal coffers, but actually deliver a hidden tax to cell phone customers who ultimately pay for the winning bids priced into their monthly bills. It also makes it prohibitively expensive for a new player to enter the market. Already facing enormous network construction costs, any new entrant would then face the crushing prospect of outbidding AT&T, Verizon Wireless, Bell or Rogers for the frequencies essential for operation.
As the New York Times writes:
When a company gets the license for a band of radio waves, it has the exclusive rights to use it. Once a company owns it, competitors can’t have it.
Mr. Reed said the carriers haven’t advocated for the newer technologies because they want to retain their monopolies.
Cooper advocates a new regulatory approach at the Federal Communications Commission — one that mandates wireless phone companies start using today’s technology to amplify their networks.
Cooper points to one example: the smart antenna.
Smart antennas direct cell towers to focus their transmission energy towards the specific devices connected to it. If a customer was using their phone from the southern end of the cell tower’s coverage area, why direct signal energy to the north, where it gets wasted? New LTE networks support smart antenna technology, but carriers have generally avoided investing in upgrading towers to support the new technology, expected to be commonplace inside new wireless devices within two years.
T-Mobile calls these technology solutions “Band-Aids” that won’t address the company’s demand for more frequencies to manage its network. But that kind of thinking applied to the mobile phone world of the 1970s would have maintained the exorbitantly expensive IMTS technology discarded decades ago, since replaced by innovation that made more efficient use of the spectrum already on hand. That innovation also transformed wireless phones from a tool (or toy) for the very wealthy to an affordable success story that now threatens the traditional wired phone network in ways the Bell System could have never envisioned.
[flv width=”412″ height=”330″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Its a Whole New System.flv[/flv]
It’s A Whole New System: AT&T and other wireless phone companies might want to learn the lesson the Bell System was trying to teach their employees back in 1979: Meet Change With Change. This company-produced video implores the phone company to do more than the same old thing. No, this video is not “PM Magazine.” It is about innovation and actually listening to what customers want. With apologies to Mama Cass Elliot, there was indeed a New World Coming — the breakup of the Bell System just five years later. Don’t miss the diabetic-coma-inducing, sugary-sweet jingle at the end. Then reach for a can of Tab. (10 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe

